Types and forms of injury
Classification of types of bladder rupture according to urological science:
- extraperitoneal;
- intraperitoneal;
- combined.
Extraperitoneal trauma can be complete or partial and manifest itself in mechanical damage to the wall of the bladder, its rupture or separation from the urethra.
Most often, the damage occurs due to a strong blow, dislocation or fracture of the hip bones when the tank is full.
.An extraperitoneal rupture is also divided into:
- complete break;
- partial rupture.
In the second case, only the mucous and muscular membranes are injured, but the serous covering remains intact. It also happens that the serous cover and mucous membrane are torn, but the muscular layer remains unharmed.
With a complete rupture, hemorrhage almost always occurs into the pelvic tissue, which provokes necrotic tissue changes.
If urine is not drained in time, this can lead to stagnation in the thighs, scrotum, and buttocks, and this in turn can provoke the formation of fistulas and pelvic urinary phlegmon.
Intra-abdominal rupture usually occurs due to gunshot, stab and cut wounds to the groin area. In this case, an outpouring of urine occurs into the abdominal cavity, which inevitably provokes peritonitis at best and purulent inflammation of the pelvic tissue at worst.
With a combined rupture, a fracture of the pelvic bones most likely occurred at a time when the reservoir itself was overfilled.
Characteristic symptoms
With closed injuries, a person feels pathological symptoms only after a few hours, or even days. This is due to the fact that the patient is in a state of shock, in which painful feelings are dulled. If the bladder ruptures, a person will experience the following symptoms:
A rapid pulse may be a symptom of organ injury.
- improper excretion of urine, in which it will be problematic for a person to go to the toilet on his own;
- blood in urine;
- frequent trips to the toilet if the urethra is damaged along with the bladder;
- decreased blood pressure due to heavy bleeding;
- rapid pulse;
- paleness of the skin.
If the patient's bladder ruptures inside the peritoneum, then symptoms resembling peritonitis are noted:
- painful sensations of a sharp nature, which intensify when taking a lying position;
- temperature increase;
- bloating and nausea;
- tension of the abdominal muscles.
Extraperitoneal trauma is not characterized by signs of peritonitis; it is manifested by other symptoms:
- swelling in the groin and pubic area;
- hematoma in the lower part of the peritoneum.
Causes of damage
The main causes of bladder rupture include:
- falling from a high point, accompanied by a strong blow to a hard surface;
- strong shaking of the human body when the tank is overfilled;
- a strong blow to the pelvic area (mostly this occurs as a result of an accident);
- stabbing, cutting and gunshot wounds in the groin area;
- a state of drug or alcohol intoxication, when the urge is greatly dulled.
Surgical and medical surgical procedures can also lead to bladder rupture:
- insertion of catheters into the cavity of the urinary reservoir;
- bougienage of the urinary canal (its enlargement with metal devices for the purpose of removing urine);
- any other operations in the groin area.
Diseases associated with disruption of the normal flow of urine can also lead to injury:
- prostate cancer or adenoma (malignant and benign forms of tumor, respectively);
- cystitis in advanced forms;
- pathological narrowing of the urinary channel.
What will happen and what are the consequences if a person’s bladder bursts?
Sometimes the symptoms of bladder rupture are not too intense. However, even mild symptoms should alert a person and prompt them to seek medical help. Injury to the lower abdomen of a person and rupture of the bladder can provoke a deterioration in health, as well as a number of irreversible changes in the urinary, reproductive and other systems.
Injury to the lower abdomen of a person and rupture of the bladder can provoke a deterioration in health
Bleeding
If bleeding is severe, the patient may go into shock. He falls into an unconscious state, his pulse is rapid, his blood pressure is below normal. If emergency assistance is not provided to the patient in the near future, death is possible.
Bleeding may cause shock in the patient
Purulent formations
Due to inflammatory processes, purulent formations form along the perimeter of damaged tissues. If treatment is not started in time, this condition will lead to blood poisoning and serious consequences. Without treatment and medical intervention, death is possible.
Due to inflammatory processes, purulent formations are formed
Peritonitis
The disease is one of the most severe complications of urinary rupture. It can be recognized by a number of characteristic signs, among which the most common are pain in the abdomen, constant muscle tension of the anterior abdominal wall, nausea and vomiting, absence of stool for a long time and hyperthermia.
Characterized by painful sensations in the abdomen, constant muscle tension of the anterior abdominal wall, nausea and vomiting
The patient's condition will continue to deteriorate until, due to inflammation, poisoning of the body begins, as well as a malfunction of various organs and systems.
Osteomyelitis
The impetus for the development of the disease can be an injury received by a person. With osteomyelitis, a purulent-necrotic process develops, which affects the bones, bone marrow, and nearby soft tissues. Surgery and antibiotic treatment are required.
Osteomyelitis requires surgery
To avoid these complications, the patient is carefully examined to detect hidden damage and begin therapy in a timely manner. In this case, it can be ensured that the patient will recover quickly and be able to return to his normal daily routine.
Symptoms of injury
Symptoms of a ruptured urinary reservoir are as follows:
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen;
- discharge of blood at the time of urination;
- difficult and painful urination;
- increased desire to emit urine, which remains largely unsuccessful;
- some signs of internal bleeding (white skin, dizziness, increased pulse and low blood pressure).
With extraperitoneal injury to the reserve, the following signs of such injury may also be observed:
- bloating in the lower abdomen, swelling above the pubis (this symptom appears when a rupture of the walls has already occurred);
- blue color of the skin (this comes from the accumulation of blood above the pubis).
Possible consequences of bladder injury
The consequences of complete or partial rupture of the bladder, no matter what the cause, largely depend on timely diagnosis and the nature of treatment.
- Heavy bleeding accompanying the patient's shock and symptoms such as shallow, rare breathing, rapid pulse, low blood pressure and lack of consciousness). This condition of the patient can lead to death, and the patient can die at any time.
- In the event of a rupture, when the patient is not provided with prompt first aid, pathogenic bacteria can enter the bloodstream and provoke inflammation throughout the body - urosepsis.
- Neglect of the injury also often leads to suppuration of urine and blood around the bladder itself.
- Bladder rupture often provokes the formation of painful fistulas, which are very difficult and slow to treat.
- Peritonitis and osteomelitis - inflammation of the walls and bones of the abdominal cavity are one of the most severe consequences of a rupture.
Disease Prevention
There are no effective preventive methods to help avoid injury to the urinary system organ, due to reasons beyond the control of the person that lead to injury. But each person is able to independently take care of preventing dangerous situations and worry about personal safety equipment:
- Health monitoring and timely consultation with a doctor. Men - control of the prostate; for women - constant examination by a gynecologist and monitoring after childbirth.
- Avoiding traumatic situations.
- Exclusion of alcoholic beverages.
- Regular follow-up with a specialist after injury for 3 years.
It is important to monitor prostate-specific substance. The special antigen is a protein that monitors the functioning of the prostate gland. Deviations from the norm found in the tests indicate problems with work or the possible development of a neoplasm. Timely diagnosis and treatment provides favorable health outcomes.
Diagnosis of injury
A patient with a suspected bladder rupture is first referred to a urologist, who performs a visual examination and then prescribes an ultrasound of the genitourinary system. But it can only partially reflect the real picture of injury in the pelvis.
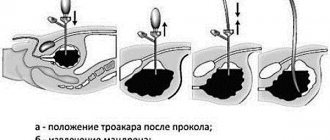
Based on the results of the ultrasound, the patient is prescribed urography or cystography (injection of a special labeled liquid into the urine using a catheter, which will show how urine leaves its reservoir.
Using these diagnostic methods, you can determine the nature of the injury and its location, how large the tears are, how the reservoir ruptures, and much more.
If, based on the results of the examination, a small intra-abdominal rupture was detected in the patient, then it is possible to do without surgery. Otherwise, to restore the integrity of the organ, the patient will be prescribed laparoscopy, laparotomy, or another operation.
What can cause a bladder to burst?
Bladder #8211; This is a fairly elastic organ, but under certain circumstances it can rupture. If your bladder has burst, you cannot postpone visiting the hospital, as otherwise irreparable harm will be caused to your body. Next, we will consider the main reasons that can lead to rupture of the bladder, symptoms and methods of treating this phenomenon.
What can cause a bladder rupture?
In most cases, bladder rupture is a consequence of mechanical trauma. In an empty state, this organ can be damaged by a strong blow or a penetrating wound, while in a full state it will be enough to use relatively little force.
Often, bladder damage occurs as a result of a sharp and unexpected physical impact on the lower abdomen. In this case, intra-abdominal injury is observed. With fractures of the pelvic bones, there is a high probability of direct damage to the bladder by bone fragments.
- falling from a great height;
- a traffic accident, especially if the victim is a pedestrian with a full bladder;
- sports or street injury to the abdominal cavity;
- injury at work.
There is an opinion that the bladder can burst due to holding the process of urination for a long time. However, this theory is largely a myth. This is due to the fact that if the bladder is overly full, urine will begin to rise through the urinary tract back to the kidneys. After some time, this will lead to poisoning of the body and loss of consciousness, which will result in involuntary urination and, accordingly, a weakening of the pressure on the walls of the bladder.
Symptoms of a bladder rupture
Only timely hospitalization can minimize the consequences of bladder injury, since in most cases, when the walls of this organ are damaged, surgical intervention is necessary. The burst membrane needs to be sutured, because it itself can heal only in the case of microdamage, but this is only possible with proper drug treatment in combination with physiotherapeutic procedures.
In order to promptly detect damage to the hollow muscular organ of the urinary system, it is necessary to know the symptoms that are observed. If you have the following symptoms, you should immediately contact a medical facility:
- Serious disturbances in the urination process. The patient cannot relieve himself; the urge to urinate is too frequent or absent.
- Pain in the lower abdomen. They can be cutting or dull, weak or strong, constant or periodic. It all depends on the size of the damage and its location. In some cases, the pain radiates to the lower back and other organs.
- Increased body temperature.
- Presence of blood in the urine.
- The appearance of swelling in the lower abdomen or perineum. This may indicate extraperitoneal injury.
What happens if your bladder bursts?
This phenomenon can bring a lot of complications, among which it is worth noting:
- Severe bleeding with the possibility of shock (lack of consciousness, rapid pulse, low blood pressure). This condition is very dangerous and can be fatal.
- Formation of ulcers around the damaged area with subsequent blood poisoning.
- Peritonitis #8211; inflammation of the abdominal cavity, accompanied by poisoning of the body and malfunctions of many organs and systems.
- Osteomyelitis #8211; a purulent-necrotic process occurring in the pelvic bones.
Diagnosis and treatment of bladder rupture
When diagnosing a ruptured bladder, the doctor relies not only on the symptoms present in the patient, but also on the results of cystoscopy, catheterization, urography and cystography. During catheterization, urine either does not come out of the bladder at all, or is released very weakly and contains blood.
Cystoscopy is not always used. It is prescribed only when examination by other means has not given an accurate result. The most effective method for diagnosing bladder rupture is cystography, which is based on the introduction of a radiopaque substance followed by monitoring its movement throughout the urinary system. If this substance leaks outside the bubble, we can talk about its injury.
Treatment for a bladder rupture depends on the nature and complexity of the injury. In case of extra-abdominal injury, the rupture is sutured through a suprapubic incision without capturing the mucous membrane. For minor damage, traditional therapy is carried out using hemostatic, detoxification and antibacterial drugs.
In case of intra-abdominal injury or if there is a suspicion of rupture of not only the bladder, but also the intestines, emergency surgical intervention is performed and a catheter is installed.
A few weeks after the operation and the process of urination has normalized, the catheter is removed. In some cases, patients in the postoperative period experience hyperactive bladder syndrome, which is characterized by involuntary urination. Usually this phenomenon goes away on its own after a few months.
Treatment of injury
Treatment of bladder injuries and bladder rupture in particular is divided into 2 types: surgical and non-surgical (conservative).
A conservative type of treatment for a rupture is only possible if the urine reservoir has only been slightly injured, for example, a slight bruise, a small tear in one of the walls of the bladder, etc.).
This type of injury is almost always diagnosed in the same way in both women and men, but their treatment can differ significantly even with a similar nature of injury.
For minor injuries to the groin area, treatment will proceed according to the following plan:
- Insert a urethral catheter into the patient's bladder through the urination channel for 1-5 days. And then, its extraction.
- Bed rest. Throughout treatment with a catheter, the patient must remain in bed so as not to aggravate the injury.
- Taking medications prescribed by the urologist depending on the characteristics of the damage to the pelvis and bladder in particular (these can be painkillers, antibiotics, pills that stop bleeding or inflammation in the groin).
Moderate to severe bladder injuries are treated with surgery.
This occurs either by making an incision in the skin of the abdomen, or by the labascopic method, when special instruments with a small camera are inserted into the patient's abdominal cavity.
Surgical treatment is carried out in the following way:
- the patient is sutured at the site of the bladder rupture;
- the patient is drained of the pelvis and/or abdominal cavity;
- For men, a special tube is installed in the bladder to drain urine.
After undergoing both types of treatment, the patient is prescribed a strict diet that excludes fatty, fried and other junk foods, as well as several days of rest and several months of systematic examination by a doctor.
Bladder rupture is a very serious injury, which can still be treated, and it will be more effective the earlier you can determine the presence of injury based on symptoms.
First aid
The main task in case of a urinary injury is to deliver the victim as quickly as possible to a hospital where there is a surgical facility. First aid for bladder injury is to carry out anti-shock measures to stop bleeding. They appear according to the following procedure:
- Treat the area with antiseptic agents and apply a bandage.
- Place the victim on his back, legs in the “frog” position with a bolster placed under the knees, head raised. If the victim is in a severe state of shock, the body must be placed at an angle of 45 degrees, raising the legs and pelvis above the head.
- Apply cold to your stomach.
- Cover the patient's body with a blanket.
- If possible, administer a blood clotting medication.
If the injury is closed, painkillers should not be given.
Can a person's bladder burst?
IMPORTANT! Sergei Bubnovsky: An effective remedy for sexually transmitted diseases exists. Read more
Urologists are often asked the question of whether the bladder can burst. There is a strong belief among people that this can actually happen if you do not empty your bladder for a long time, and many scary stories are told on this topic, but most of them are far from reality. Let's figure out whether such a danger really exists and how justified these fears and concerns really are.
Let's look at what the bladder is from an anatomical point of view. This is an organ of the human excretory system that serves as a storage reservoir for urine (urine), from where it is discharged from time to time. Its walls consist of muscle tissue, they are very elastic and allow them to increase in size when filled by 2.5 times. The average capacity of the bladder is 500-700 ml, but this value can vary significantly depending on the individual characteristics of the body. This is an unpaired organ, anatomically located in the pelvis, in the lower abdomen behind the pubic bone, from possible injuries it is reliably protected by the pelvic bones and dense muscles of the peritoneum, however, if it is overfilled, its upper part can bulge into the abdominal cavity and increase the level of its vulnerability during external influences.
When does bladder rupture occur?
Let's immediately abandon the formulation “the bladder burst” as being far from correct; this is not a balloon, this is an organ for which nature has provided a very high resistance to stress and a large margin of safety. Therefore, in the future we will use the term “bladder rupture”, since it is more correct from a medical point of view.
Fortunately, violation of the integrity of the membrane (rupture) of the bladder is a rare occurrence in medical practice. This can only happen in the case of strong mechanical impact from the outside or in clinical cases when the outflow of fluid from the bladder is completely blocked (consequences of adenoma or prostate cancer in men, narrowing of the urethra). For a healthy body, ignoring even a strong urge to urinate when the bladder is full cannot lead to rupture. In this case, at critical pressure in the bladder, the sphincter simply relaxes and spontaneous emptying occurs. Nature provides, first of all, for the survival of the organism, and no fear of embarrassment in the social sense can outweigh this main task.
The vast majority of such cases occur from aggressive external mechanical influence, and in this case, the fullness of the organ is the reason that increases the risk of rupture. Among the most common reasons are the following:
- a strong sharp blow to the abdominal area (during a traffic accident, a fall from a height, etc.);
- fracture of the pelvic bones with displacement of fragments that can pierce the bladder;
- penetrating wound of the abdominal cavity (gunshot, knife, etc.);
- unqualified performance of medical procedures (surgery, catheterization or bougienage of the urethra).
The upper and posterior walls of the bladder are most often subject to rupture, since their muscles are less developed and there is no counterpressure from the peritoneum. It must be remembered that those who often practice prolonged urinary retention are at particular risk, since with frequent strong stretching, the walls of the bladder become thinner and become less tensile.
Sometimes spontaneous rupture may be diagnosed as a consequence of a serious illness, for example, adenoma, prostate cancer or urethral stricture (narrowing of the urethra).
Clinical manifestations of pathology
Along with a distinct pain syndrome (pain in the pubic area and under the navel of varying severity, worsening in a lying position), the following symptoms are also characteristic of a ruptured bladder:
- hematuria (presence of blood in the urine);
- swelling or swelling and discoloration of the skin in the groin area and above the pubic bone;
- problems with urination (pain, delay, frequent urge).
In the absence of medical care, the victim develops symptoms of peritonitis (inflammation of the abdominal cavity): fever, bloating and tension in the abdominal muscles, nausea, vomiting.
When diagnosing, studies such as a general urine test for the presence of red blood cells, ultrasound, urography and tomography are used. Laparoscopy is sometimes used.
Tactics and methods of treatment
It must be remembered that conservative treatment (without surgical intervention) is possible only in the case of a bruise of the bladder without compromising the integrity of its walls, or if the doctor has diagnosed a micro-rupture of an extraperitoneal type of injury. In this case, the patient is indicated for catheterization of the urethral canal for a period of several days to a week, strict bed rest and taking medications prescribed by the doctor (antibiotics, analgesics, anti-inflammatory and blood-restoring drugs).
In other cases, immediate surgery is indicated, during which the rupture is sutured and drainage systems are installed during the healing period.
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Sergei Mikhailovich Bubnovsky tells how to save yourself and forget about venereal diseases. Read the interview
In any case, if you suspect the described signs, you should contact a medical facility.
Only timely consultation with a doctor can prevent the dangerous consequences of this injury!
Preventive actions
The main prevention of bladder rupture is to empty it in a timely manner. This prevents its walls from stretching and thinning and makes it more resistant to damage. It is also useful to exclude from the diet excessively salty, fried, smoked and other unhealthy foods.
Take care of yourself, take care of yourself and be healthy.
Who said that curing sexually transmitted diseases is difficult?
- Incredibly You can cure syphilis, gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis and other sexually transmitted diseases forever!
- This time.
- Without taking antibiotics!
- That's two.
- During the week!
- That's three.
An effective remedy exists. Follow the link and find out what venereologist Sergei Bubnovsky recommends!
Bladder burst - can this happen?
The bladder is a hollow muscular organ that performs the functions of storing and excreting urine through special urethra. This organ is located behind the pubic symphysis in the small pelvis. Bladder burst - can this happen?
Bladder: structure and functions of the organ
The shape of the bladder can be varied, it all depends on the degree of its fullness and the location of neighboring organs. The bladder consists of a body, neck, fundus and apex. The neck of the bladder passes into the urethra, the peritoneal bladder is covered on top, and its mucous membrane most often gathers in folds. The urge to urinate occurs according to the degree of fullness of the bladder, so during normal operation you will always feel a kind of discomfort, which will signal that it is time to empty your bladder. In the above case, the consequences can be very serious, even fatal.
The most important function of the bladder is the accumulation and subsequent removal of urine, that is, we can say that the bladder performs a reserve and evacuation function. The capacity of the bladder in an ordinary person ranges from 200 to 400 milliliters, but, nevertheless, under certain conditions, under heavy load or stress, the bladder may have increased elasticity.
Bladder burst - can this happen?
Most often, pain in the bladder occurs due to various pathologies of this organ; patients note the frequency of urination along with pain. Diseases such as bladder stones and cervical cystitis are characterized by painful urination during the day, and for prostate adenoma - at night. When studying diseases of this organ, instrumental and clinical methods are used.
Discussions on the topic “the bladder burst” are very unusual, but you should also know that the bladder is a very elastic organ, therefore, in order for it to burst, a strong mechanical force must be applied to it, which can be produced as a result of all kinds of accidents and injuries . If you ignore all signals about the filling of the bladder, then it will not burst, but most likely spontaneous urination will occur.
© Olga Vasilyeva for astromeridian.ru
Diagnostic measures
A urologist can diagnose ruptures after conducting the necessary examinations:
- Cystography. It is performed by injecting a contrast agent into the bladder. On the images obtained during the examination, the doctor can see the location of the rupture and assess its size.
- Cystoscopy. An examination through which the doctor obtains information about the condition of the bladder and the integrity of its walls. It is carried out by inserting a cystoscope device into the bladder.
- MRI and CT. These examinations help to obtain a complete picture of the damage and determine where and in what quantities urine and blood accumulate. It is also possible to determine the degree of damage to nearby organs.
Laboratory tests may also be needed to diagnose urinary rupture:
- General blood analysis. From this, the doctor will be able to determine the presence of bleeding.
- General urine analysis. If possible, this will allow the degree of bleeding to be determined.