This problem is an important border area between childhood diseases and urology: recognition of the characteristic signs of the disease and its successful treatment requires cooperation between a pediatrician and a urologist.
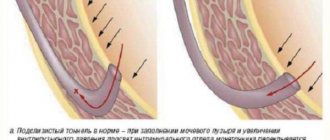
The outflow of urine from the renal pelvis to the urethra can be impaired at any site. Recognizing and treating these disorders is critical, as the resulting complications associated with urinary stasis can lead to irreversible kidney damage. Obstacles to the outflow of urine 1. Obstacles located above the bladder or in the bladder: 1) valves, narrowings, impacting stones on any segment of the ureter; 2) disorders of the innervation (the relationship of the organ with the brain and spinal cord, carried out through the nerves) of the bladder. 2. Obstacles located under the bladder: 1) narrowing, valves of the urethra; 2) narrowing of the bladder neck. 3. reflex or compression of the ureters by vessels or tumor. 4. Vesicoureteral reflux - reverse flow of urine from the bladder into the ureter. Narrowing of the urethra may be due to inflammation or congenital defects. It occurs on any part of the urethra; when urinating, congenital membranes are straightened by a stream of urine and, like valves, interfere with its outflow. Narrowing of the bladder neck can be caused by hypertrophy (increase in volume) of the muscles. Disorders of the innervation of the bladder occur with lesions of the spinal cord and with the congenital absence of nerve cells in the walls of the bladder. Narrowing of the ureters can occur at any distance from the renal pelvis to the point where the ureter enters the bladder; in some cases they are congenital. Valves can be found throughout the ureters. If the opening of the bladder is narrow, a urethrocele develops (protrusion of the wall of the urethra). Kinking of the ureter or compression of it by blood vessels and tumors is common. The clinical problem is vesicoureteral reflux. In healthy individuals, when urinating, there should be no reflux of urine (reflux) into the ureter, since the ureters enter the wall of the bladder and its cavity in an oblique direction. When urinating, the walls of the bladder, contracting, compress part of the ureters, which open obliquely in the wall of the bladder. due to this, increased intravesical pressure during urination directs the stream of urine only downward, preventing its reverse flow into the ureters. Reflux can occur with subvesical constrictions, but more often it occurs with abnormalities of the ureter at the entry into the bladder. In such cases, urine flows back into the ureteral cavity. Hydronephrosis The consequence of abnormalities of the urinary tract is hydronephrosis, associated with an obstruction of the outflow of urine, as well as stretching of the renal elements - the pelvis and calyces. If the disorders persist for a long time, the renal tissue undergoes atrophy (the supply of nutrients to the tissue is disrupted, as a result of which its constituent cells die) from compression, huge cavities arise, and the functioning tissue makes up the thin wall of these cavities. Stagnation of urine, hydronephrosis and reflux lead to the development of chronic inflammation of the urinary tract and pyelonephritis - an inflammatory disease of the kidneys affecting the pelvis and calyces. Signs of the disease. Signs of blockage in the lower urinary tract and bladder are usually much more severe. Urination is difficult: the stream of urine is thin, intermittent, or urine is released in drops. The bladder is dilated and can often be palpated; After the end of voluntary urination, a catheter (a special rubber tube for collecting urine) can be used to remove the remaining urine. With paralysis (lack of muscle tone) of the bladder associated with damage to the spinal cord, the bladder is maximally expanded and urine gradually leaks. If there is an obstruction above the bladder, there are almost no complaints indicating urinary tract disease. Sometimes children complain of dull pain in the abdomen or lower back, sometimes - with a temporary decrease in blockage - a significant amount of urine may be released; an enlarged kidney is palpable. Advanced cases of hydronephrosis can result in complete impairment of kidney function (renal failure). When making a diagnosis, in addition to the usual urine and blood tests, monitoring the act of urination is of great importance. If difficulty passing urine is suspected, a thorough urological examination is required. The first stage is intravenous urography - an x-ray method for examining the kidneys and urinary tract. Treatment consists of surgical removal of the obstruction and treatment of possible concomitant infections. The prognosis depends on the possibilities of surgical treatment and complete elimination of urinary outflow disorders. The condition of the kidney tissue, which depends on the duration of the blockage and infection, has a decisive influence on the prognosis. medportal.com
Symptoms of deviation
An additional symptom of pathology can be a jump in temperature.
- frequent desire to go to the toilet;
- unstable and poor urine flow;
- exerting excessive effort during urination;
- presence of blood in urine;
- pain syndrome during physical activity;
- temperature surges.
Residual urine is just one of the various symptoms found when the genitourinary tract becomes blocked and becomes inflamed.
But if its appearance is associated with neurological disorders, then such a problem is much more difficult to detect, in particular, if the problem is in a small child. If before this you felt like a healthy person, then the first sign of urinary retention will be the presence of a sluggish urge to urinate. This symptom develops gradually, like organ atony. This can be felt by several signs.
- Pressure in the bubble. Since a small child will not be able to tell about this, you can feel this by an increase in volume and a painful reaction of the child to his examination.
- A feeling of incomplete emptiness.
- Intermittent, sluggish or thin stream when urinating.
- Men may also experience impaired sexual function, swelling of the head of the penis, as well as pain in the pubic or lower back area.
- Pain in the urethra.
- Frequent urge to defecate can also be an indicator that there is residual urine due to prostatitis or other diseases.
Symptoms of childhood PMR
Children's PMR manifests itself in a pronounced symptom complex, which manifests itself in:
- slow physical development;
- underweight in newborns;
- high temperature, which is difficult to bring down;
- attacks of pain, colic, cutting;
- presence of bloody discharge during urination.
During the period of inflammation, the child’s temperature remains at 39C for a long time; clinical analysis shows the presence of a high level of leukocytes in the urine; the child, as a rule, has a painful appearance and pain in the lumbar region and side.
For information! In children of the first year of life, reflux is detected by ultrasound of the genitourinary system.
Mechanism of urination
Depending on the amount of urine accumulated, the bladder expands or contracts. The accumulation process itself occurs sequentially. The first urge to urinate appears when 150 ml has accumulated. In adults, the volume of the bladder is 250–500 ml. For some people, the norm reaches 750 ml.
Structure of the bladder
The basis of the muscular membrane of the bladder is the detrusor muscle, a muscle that expels urine. The shell consists of 3 layers, and the detrusor is a combination of longitudinal and spirally twisted fibers. There are 2 ureters that empty into the bladder and carry urine through them. The lower part of the bladder narrows, gradually moving into the urethra, and is called the neck.
Externally, the excretory canal differs in women and men. The male duct is long and narrow (30/8 mm). For representatives of the weaker half, it is short and wide (4/15 mm). In a child during intrauterine development, the formation of the bladder occurs at 7 weeks.
The mechanism of action of an organ is determined by the functions it is designed to perform. There are only two of them:
- cumulative;
- excretory
When the physiological norm of capacity is reached, the bladder should empty. In this case, neuro-reflex mechanisms are activated, sending an impulse to the detrusor to contract it. Our usual process occurs in two stages under the control of the spinal cord and brain. When the bladder is filled to a certain level, urine output does not immediately occur.
Impulse the detrusor to contract it
The act of urination (innervation) is a combination of the work of the muscular layer (detrusor) of the bladder, which, by contracting, ensures the removal of fluid, and the sphincters of the urethra, which regulate the retention of urine in the process of its accumulation until the desire to perform the act of urination arises.
Depending on the development of pathological changes in any of the structural elements of the urinary tract responsible for the removal of urine, various disorders occur, leading to damage to the detrusor of the bladder with the subsequent development of atrophy and, accordingly, the inability to contract sufficiently.
Important! Although urine amounts greater than 50 mL are clinically significant, the maximum residual amount may exceed 1 liter.
Table: Permissible volume of residual urine by age
| Age | The volume of residual urine is normal |
| Children under 1 month | {amp}lt; 3 ml |
| Up to 1 year | {amp}lt; 5 ml |
| Up to 4 years | {amp}lt; 7 ml |
| Up to 10 years | {amp}lt; 10 ml |
| Up to 15 years | {amp}lt; 20 ml |
| Adults of both sexes | {amp}lt; 50 ml |
Why should we drink water?
Water is necessary for all cells and organs of the human body so that these organs can function properly. Water is also used to lubricate joints, protect the spinal cord and other sensitive tissues, regulate body temperature and help the passage of food through the intestines.
Although some of this essential fluid comes from consuming foods high in water content, such as soups, tomatoes, and oranges, the body still gets most of its water from drinking water and other beverages.
A normally functioning body loses water daily, and the lost amount must be replenished. It should be noted that we lose the most amount of water due to body activities such as sweating and urination, but water is lost even through breathing.
Drinking water, whether from a tap or a bottle, is the best source of fluid for the body. Drinks such as milk and juices are also good sources of water. But drinks containing alcohol, such as beer, as well as soft drinks and drinks containing caffeine, are less than ideal because they have diuretic properties, meaning they help remove moisture from the body.
The recommended amount of water to drink during the day varies from person to person depending on factors such as how active the person is and how much they sweat. That is, there is no universal water consumption threshold that must be achieved.
According to the Institute of Medicine, adequate water intake for men is approximately 13 cups (three liters) per day. For women, adequate intake is about nine cups (2.2 liters) per day.
Many people may have heard the phrase, “Drink eight glasses of water a day.” This amount is about 1.9 liters, which is close to the recommendations that experts give to women. Drinking eight glasses of water a day is an easy-to-remember amount that, in terms of water intake, can get a person on the right path.
Water also helps dissolve minerals and nutrients so that they become more available to the body. Water also helps remove processed food waste from the body. It is these two functions that make water vital for the kidneys.
Diagnostics
When symptoms of incomplete bladder emptying occur in men, treatment consists of identifying the underlying disease. Diagnosis is carried out by laboratory testing of urine, ultrasound, urethroscopy. If necessary, a hormonal examination of the prostate gland is prescribed. When the symptoms of difficulty urinating disappear, they talk about properly selected complex therapy, including:
- relieving inflammation with antibacterial agents;
- surgical treatment.
Urethroscopy
Surgical removal is prescribed for adenoma and prostate cancer. Therapeutic treatment is carried out when prostatitis is detected. If the condition of incomplete emptying occurs as a result of an infectious lesion in a man, the woman is prescribed antibiotics.
If a child has difficulty urinating, it is necessary to wait for the results of blood and urine tests, which often confirm inflammatory processes. If a woman has a feeling of incomplete emptying in the presence of a gynecological disease, efforts are aimed at eliminating the root cause with the help of specific therapy.
This process consists of several neurological, urological, laboratory tests and interviews. When you first visit a urologist, you will be prescribed the following procedures.
- Ultrasound of the bladder and pelvic organs. This study is carried out in two phases. The first is when the bladder is full to measure its volume and size. The second ultrasound is 5-10 minutes after emptying. To ensure accurate results, calculations are carried out at least three times. There are special formulas for calculating the amount of liquid, which require the following parameters:
- height;
- width;
- length of the ultrasound shadow of the bladder.
If the patient is currently taking diuretics, or before the examination, drank drinks or ate foods that could irritate the organ for examination, then the doctor must be warned about this, since the diagnosis may be erroneous due to these influencing factors.
Ultrasound is considered a non-invasive method, since the rate of residual urine in men and women is not determined accurately. But it is used more often due to its general availability.
- Clinical analysis of blood and urine, urine culture to determine bacterial infection.
- Cystoscopy and contrast urography – if necessary. The first type of examination is prescribed as a last resort, as it is quite traumatic. But it quite accurately indicates the volume of residual urine, if any was detected.
Do not forget that the calculation of volume and urine analysis for prostatitis and other diseases in which this symptom appears may turn out to be erroneous during ultrasound and other examinations due to nervous strain.
Determining the presence and quantity of residual urine is the main purpose of the examination, which includes asking the patient for the presence of clinically significant symptoms. Next, instrumental research methods are carried out, the list of which includes:
- studying the dynamics of changes in stream pressure during urination (urofluometry);
- orthostatic urine test;
- measuring pressure in the bladder at different moments of urination (cystometry);
- assessment of the contractility of the muscular layer of the bladder walls (electromyography);
- study of the functional state of the sphincters and urethra (urethroprofilometry);
- Ultrasound of the bladder before and after urination;
- Ultrasound of the prostate gland.
Laboratory research methods:
- clinical urine analysis (determining the presence of bacteria, proteins and nitrogen in the urine);
- clinical blood test;
- determination of prostate specific antigen (PSA).
A reliable method for determining the amount of residual urine is the direct catheterization method. But due to the difficulties associated with its implementation (invasiveness, risk of damage to the urethra, provocation of inflammatory processes), assessment of the amount of residual urine is mainly carried out using ultrasound.
The diagnostic technique consists of two stages:
- Ultrasound of a full bladder.
- Ultrasound performed 10 minutes after urination.
In this case, the dimensions of the three-dimensional image of the bladder and the length of its ultrasound shadow are estimated using mathematical formulas.
Important! In cases of suspected prostatic hyperplasia in men, the most informative diagnostic method is transrectal ultrasound.
Technique for performing transrectal ultrasound
Since residual urine is just a symptom, restoring bladder detrusor function involves treating the underlying disease and regularly removing urine using stimulating methods (washing with warm water, massage of the sacral spine, use of antispasmodics).
A positive effect can be achieved by using methods that improve blood circulation in the pelvic organs (aerobic exercise, walking, breathing exercises), relieving inflammation, and reducing the amount of fluid consumed before bed. In the vast majority, with timely consultation with a doctor, the tone of the muscle wall can be restored without the use of surgical treatment methods.
About the doctor
Make an appointment with a urologist-andrologist of the highest category - Andrey Nikolaevich Klokov today. We will do everything to accommodate you as quickly as possible. The Rainbow Clinic is located in the Vyborg district of St. Petersburg, just a few minutes walk from the Ozerki, Prospekt Prosveshcheniya and Parnas metro stations. See the directions map.
Welcome, friends, to the site about the treatment of urolithiasis. What is harmful to the kidneys, you wonder when the kidneys start to bother you. What foods are harmful to the kidneys, is beer harmful to the kidneys - read this article. We recently looked into what's good for your kidneys and discussed the top 5 tips that are vital for your kidneys. Following these tips will significantly increase your kidneys' chances of living a healthy life.
The kidneys bear a huge responsibility for the stability of all human life systems, from the urinary system to the cardiovascular system. The fact that our kidneys begin to fail us is entirely our fault. We begin to think about the need to protect our kidneys when illnesses occur. We do not take care of our kidneys, enjoying poor nutrition, we often put our kidneys in extreme conditions. So, let's discuss what is harmful to the kidneys.
Causes of bladder dysfunction
Neurological disorders are always associated with disruption of the part of the nervous system that is responsible for three functions of the bladder:
- reservoir (function that ensures the accumulation of urine in the bladder cavity);
- evacuation (a function that facilitates the removal of urine);
- valve (a function that allows you to hold a certain volume of urine in the bladder).
Damage to any level of the nervous system - from the nerve endings located on the inner surface of the bladder to disturbances in the functioning of the brain - can lead to a number of abnormalities, including hyperfunction of the urethral sphincter. As a rule, the cause of the development of this pathology is damage to the spinal cord due to:
- tumor formations;
- intervertebral hernia;
- spinal injuries;
- congenital pathology of the central nervous system (observed, as a rule, in a child).
Due to difficulties that arise during urination even with a full bladder, atony of the muscle layer develops, which, under constant pressure, loses the ability to contract and push out liquid, accumulating a large volume of residual urine.
Treatment of neurogenic bladder consists of psychological, physical and medicinal methods of influence:
- correction of behavioral lifestyle (streamlining drinking and urination patterns);
- stimulation of urination by massaging the back area;
- physiotherapy;
- drug effects on weakening sphincter tone;
- drugs that regulate the functioning of the central nervous system;
- physiotherapy.
The plexus of nerve endings in the lumbosacral region stimulates the process of urination
The health of the bladder depends on the processes occurring inside its mucous membrane, and dysfunction of the organ in an adult significantly changes the quality of life. The causes of impaired urination differ depending on gender and due to the specifics of the disease.
A common female problem is cystitis. The disease has an infectious status and is associated with the female anatomical structure. When the mucous membrane becomes inflamed, a symptom appears such as incomplete emptying of the bladder in women. Difficulty urinating in men is associated with inflammatory processes and changes in the prostate or kidneys.
The products of inflammation, in addition to the mucous membrane, affect the muscle layer and nerve elements. As a result, the urge to urinate occurs in a smaller capacity, therefore, the bladder is not completely emptied, and the person visits the toilet more often. If the symptoms of a disease are accompanied by severe pain and a person does not seek medical help for a long time, neuroses develop.
If there is severe pain during urination, consult a doctor.
A decrease in muscle tone of the urinary organ and incomplete removal of fluid indicate not only pathologies of the pelvis, but also diseases of other organs. Diseases of the spinal cord impair the excretory function of the bladder. These include:
- mechanical injuries of the spine;
- multiple sclerosis;
- radiculitis.
Overactive bladder
Increased pulsation of the brain against the background of appendicitis and pyelonephritis also causes a residual phenomenon in the bladder. This means that during the act of full urination, the brain receives an impulse that there is a residue in the bladder that needs to be eliminated. Then there is an erroneous urge to urinate.
Diseases of the central nervous system that cause residual urine in the bladder in men and women include myelitis, dysfunction of the spinal cord and brain.
The feeling that urine remains in the bladder may have psychological causes - prolonged stress, shock.
Upper urinary system
Kidneys
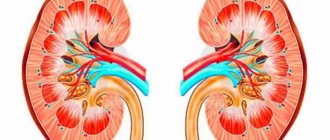
The kidneys are a paired organ, they are located on both sides of the spine in the retroperitoneal space just above the lumbar region and have the appearance of a large bean and are approximately the size of a fist. The right kidney is located slightly lower than the left due to the position of the liver. In an adult, the average kidney is 10 cm long, 6 cm wide and 3 cm thick, and weighs about 120-200 g. The left one is usually slightly larger than the right kidney.
Each kidney is covered by a fibrous capsule that protects the kidney from injury. All pain sensations are associated with this capsule: the organ itself has no pain receptors. When the capsule is damaged or stretched, pain of varying nature and intensity appears.
Kidney tissue or parenchyma consists of outer (cortical) and inner (medullary) layers.
Blood enters the kidney through the renal artery (a branch of the aorta) and is filtered through the microscopic structural working units of the kidney, the nephrons. Each kidney contains about a million nephrons. Their job is to filter blood and produce urine. Each nephron consists of a ball formed by small blood capillaries (the glomerulus), surrounded by a dome-shaped structure, the glomerular capsule (or Bowman's capsule), and a small tube called the renal tubule. Here, the blood plasma is filtered, which leads to the formation of urine.
The urine storage system consists of small renal calyces, which, merging with each other in 2-3 groups, form a large renal calyx, and these in turn form the renal pelvis. The renal pelvis passes directly into the ureter.
All functions normally performed by two kidneys can be adequately performed by one healthy kidney. Some people are born with only one kidney, while others choose to donate one kidney for transplantation into a person with kidney failure.
Basic kidney function
is to maintain the correct balance of water and minerals (including electrolytes) in the body.
An important function of the kidneys is to regulate fluid balance by excreting excess water in the form of urine while maintaining the required amount of water in the body, which is necessary for life. When the kidneys lose their ability to remove excess water, edema appears.
The kidneys regulate the balance of minerals and substances such as sodium, potassium, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium and bicarbonate and maintain normal blood composition. Changes in sodium levels can affect a person's mental state, while changes in potassium levels can have serious adverse effects and cause problems with the heart and muscle function. Maintaining normal levels of calcium and phosphorus is essential for healthy bones and teeth.
Additional functions of the kidneys include:
- Filtration and removal from the body of food processing waste, medications and harmful substances (toxins).
- Creatinine and urea are two important byproducts of kidney function that can be easily measured in the blood. Their values in blood tests reflect kidney function. When kidney problems occur, creatinine and urea levels increase.
- Regulate Blood Pressure – The kidneys produce various hormones (renin, angiotensin, aldosterone, prostaglandins, etc.) that help regulate the amount of water and salt, the levels of which play a vital role in maintaining blood pressure. Impaired hormone production and salt and water regulation in a patient with, for example, kidney failure can lead to high blood pressure.
- Blood volume regulation
- Regulating blood pH
- Converts vitamin D into its active form, which is necessary for the absorption of calcium from food, growth of bones and teeth, and maintenance of their health. Decreased levels of active vitamin D lead to decreased bone growth rates. Slow growth may be a sign of kidney disease in children.
Erythropoietin
is a hormone produced in the kidneys and plays an important role in the production of red blood cells. With kidney failure, the production of erythropoietin decreases, which in turn leads to a decrease in hemoglobin levels (anemia). This is the reason why the hemoglobin count does not improve in patients with kidney failure despite taking iron supplements and vitamins.
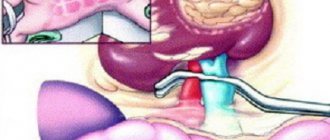
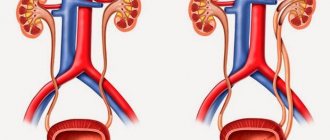
Ureters
These are fibromuscular tubes that drain urine from the renal pelvis to the bladder and are about 25-30 cm long and 6-8 mm wide. They enter the bladder from behind and at an angle, ending in the lumen of the bladder in the form of holes - the mouth of the ureters. The lower ureter is compressed by the bladder wall passively during urine storage and dynamically during voiding. Essentially, it is a valve that prevents vesicoureteral reflux (i.e., stops urine from flowing back into the kidneys). The wall of the ureter is made up of three layers, including a layer of muscle that helps it contract and move urine from the kidney to the bladder. Small portions of urine enter the bladder from the ureters approximately every 10-15 seconds.
Along the length of the ureter there are three physiological narrowings: at the level of the transition of the pelvis to the ureter, the place of intersection with the common iliac vessels and in the thickness of the bladder wall. With urolithiasis, stones can get stuck in places where the ureters are narrowed, causing renal colic.
Emergency organ emptying
If a lot of fluid has accumulated in this organ, and the patient does not have the opportunity to remove it naturally, then catheterization is required.
This procedure may be contraindicated in some patients, for example if there is urethral sphincter spasm, in which case botulinum toxin is injected into the area to relax the muscle tissue.
In some situations, a urethral stent can be installed with a short-term period of operation - from 3 to 6 months. It looks like a cylinder made of a thin wire spiral, 1.1 mm in diameter. The material used in the manufacture is absorbable organic material, which soon disappears.
How to quickly fill your bladder?
It seems to me that speed is needed only in one case: CATCHING FEAKS
As I understand it, you must undergo a medical examination of the bladder when it requires filling
Before the ultrasound, you need to drink about five glasses of water an hour before the ultrasound. And you really don’t want this. Then there is another way when saline solution is injected using a catheter, but this is done only when the study needs to be CARRIED OUT URGENTLY, and IT IS VITAL NECESSARY
And if you REALLY WANT it, take a FUROSEMIDE tablet, but don’t forget to add liquid while drinking. Otherwise, you will not pass the examination.
My bladder filled up the fastest when I was given a drip in the hospital, as far as I remember, about 1 liter of saline is poured into your vein within about 15 minutes. solution, and even if the bladder had been emptied before, I could barely wait for the procedure to end) I can’t imagine anything faster than 15 minutes)))
Also, when you swim in the pool for 1 hour, at the end of the swim you are “already ready”, since the skin, being in the water, absorbs it very actively)))
I believe that in order to quickly fill the bladder, you need to drink a lot of fluid first, and then a diuretic. Or you can do the opposite, first a diuretic, and then a lot of liquid. And you are guaranteed frequent trips to the toilet! ))
The bladder must be filled before an ultrasound of the pelvic organs, and filled by a certain time. I did the following: I started drinking mineral water two hours before the appointed time.
One and a half to two liters. Within an hour and a half.
Twenty minutes before the study, I took a furosemide tablet. And by the appointed time I was completely ready.
There is one drawback to this method: if there is a delay in the study (for example, the doctor is delayed for 10-20 minutes), then it will be very difficult to resist going to the toilet.
I think that the easiest way is to start drinking beer 40-60 minutes before the start of the study. By that time, your bladder will definitely be full, and it’s better not to sit too long in line, otherwise you’ll be asking for beer. I'll have to run to the toilet. Although if you drink three liters, you can run there, anyway, in 15-20 minutes it will be full again.
At least that's how it is for me personally.
When you need to undergo an ultrasound examination, doctors often ask you to fill your bladder. I don’t know about others, but personally I don’t immediately feel like drinking. I pour water into myself almost forcefully. But it’s impossible to quickly fill your bladder any other way.
The best solution is to take a large glass, pour water into it and drink
You can drink a couple of cups of green tea - your bladder will quickly fill up.
I don’t take the option with soda - it will harm the body.
And of course, a cup of coffee without sugar will help fill your bladder quickly
You just need to start drinking plenty of water a couple of hours before you need it - if you don’t want to, then force it. Everyone's bladder capacity is different, but you need to drink at least two liters of water. The task is not easy, but if it is necessary, then it is necessary. Good luck!
Inflammatory and infectious processes
As a rule, the role of inflammatory diseases in the formation of residual urine is the formation of urethral edema or sphincter spasm due to soreness and tissue irritation. A similar reaction can be observed with cystitis, balanitis and urethritis. Prostate inflammation in men occupies a special place among inflammatory diseases that cause persistent urination problems.
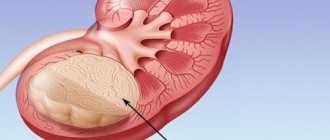
Enlargement of the prostate gland, due to an inflammatory process or the formation of a benign (prostatic hyperplasia) or malignant (prostate cancer) neoplasm, causes, in the initial stages of the disease, minor urination disorders, which subsequently lead to more pronounced:
- increased urge to go to the toilet;
- intermittency of the stream when urinating;
- the need for abdominal tension and straining to completely empty the bladder cavity;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Important! With timely consultation with a doctor, prostate adenoma can be successfully treated with the complex effects of medications and physiotherapeutic procedures, and allows you to return to normal life.
Enlargement of the prostate gland towards the bladder, creating an obstruction to the outflow of urine
Drug treatment
If there are problems with the outflow of urine, incomplete excretion of urine is usually divided into two types - partial and complete. In the first case, there is a small outflow of fluid, it is not completely removed. The urge occurs every few minutes - there is no way to move away from the toilet. In the second case, urine is not released at all, although there is a constant urge. This is accompanied by severe cutting pain in the lower abdomen.
To cope with these disorders, as well as restore functions, it is important to know the cause of the deviations. Self-medication in such cases does not help, so you need to see a doctor. In the hospital, diagnostics will be carried out and the provocateur of the illness will be identified. After which an experienced urologist will prescribe individual therapy to solve the problem. Depending on what caused the failure to urinate, antibiotics, drugs that neutralize infections, or drugs that remove stones are prescribed. It all depends on the root cause of the deviations. Sometimes hormonal and sedative drugs are used if the disruptions are caused by psychological disorders or changes in hormonal levels. Fighting methods are different. The main attention should be paid to why such deviations developed.
In particularly complex and advanced cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. Basically, such methods are applicable for oncological tumors or for the formation of stones.
Return to contents
How to relieve the feeling of incomplete emptying on your own?
You can listen to the sounds of flowing water to make emptying more complete.
In order to reduce unpleasant feelings during the course of treatment, you can use some techniques yourself:
- During the period of emptying, it is necessary to relax the muscles of the pelvis and abdomen as much as possible. When the body is in good shape, stagnant fluid is more difficult to remove from the genitourinary system.
- You can help yourself by stimulating bladder contractions. To do this, you need to press your hand on your stomach in the area below the navel. This will help increase the volume of fluid coming out.
- To make emptying more complete, you can listen to the sounds of flowing water (for example, turn on a water tap).
Return to contents
Reasons for increasing the volume of residual urine in men
Due to the fact that the structure and size of organs is different for each person and depends on physique and heredity, the indicators will be individual and may vary. The rate of residual urine in men and women varies between 40-45 ml. In children, this volume changes and grows with age. In a child, immediately after birth, residual urine is found to be less than 3 ml.
In one-year-old children, the volume of urine after release from urine is up to 5 ml. In children aged 4 years, the bladder contains up to 7 ml of urine after visiting the toilet. In 10-year-old children, the amount of residual urine is up to 10 ml. With age, the bladder grows, and the volume of urine after urination increases and reaches a volume of 20 ml at the age of 15 years.
The volume of residual urine in men increases due to difficulty in its flow through the urethra.
This is caused by the influence of several pathological causes that cause narrowing of the lumen of the urethra:
- Prostate adenoma is an increase in tissue volume (hypertrophy) of the prostate gland. As a result, the initial part of the urethra is compressed in the area of its exit from the bladder.
- Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate tissue. In which possible development of their edema (local increase in the volume of intercellular fluid) with compression of the urethra.
- Prostate cancer is a malignant neoplasm that does not always lead to an increase in residual urine in men, but only if the tumor grows into the lumen of the urethra with a decrease in its diameter.
- Suffered mechanical injuries, extensive surgical interventions, chemical burns of the urethra, as a result of which the lumen of the urethra in the area of damage is partially replaced by fibrous connective tissue, which reduces the lumen.
- Disruption of the innervation of the sphincter of the bladder outlet, leading to its spasm (narrowing).
The most common cause of increased residual urine in the bladder in men is benign prostatic hyperplasia, the incidence of which increases with age.
Symptoms and diagnosis of increased residual urine volume
Health care
When urine reflux is characterized by an initial degree, doctors take a wait-and-see approach.
Constant monitoring is established for the baby; systematic consultations and diagnostics are also recommended in order to timely consider the progression of the pathology, in which there is a reflux of urine from the bladder into the ureter and kidneys.
Parents are also advised to provide their baby with a special diet, which involves completely eliminating the use of salt in cooking.
Medications
At the same time, doctors prescribe medications that help lower blood pressure.
Conservative treatment considers forced diversion of urine as a mandatory procedure. Doctors insist that the urination process be carried out every two hours.
If the treatment helps to normalize the urinary process and does not provoke complications, this tactic continues.
In cases where conservative treatment is not able to prevent complications, all symptoms indicate a deterioration in the child’s condition, doctors perform surgery.
During surgery, surgeons eliminate reflux in children by creating an artificial valve that prevents urine from flowing from the bladder back into the ureter.
Urinary tract obstruction
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=
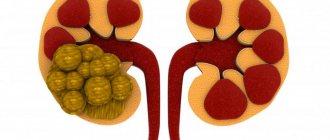
The presence of stones in the bladder is one of the most common causes of residual urine. Cystoliasis occurs with equal frequency in both men and women. Only the mechanism of stone formation differs - the male body is characterized by the formation of stones directly in the cavity of the bladder, and the female body is characterized by the migration of stones from the kidneys.
Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder
The reasons for the formation of stones can be internal or external factors:
- chronic infectious diseases of the urinary tract;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- improper diet;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- work in hazardous industries;
- improper drinking regime.
In addition to the main signs of the formation of residual urine, with cystoliasis pain in the lower abdomen with irradiation to the groin, scrotum or perineum is noted. Also a characteristic sign is a sudden interruption of a full stream during urination. Treatment consists of removing stones using medications or lithotripsy, followed by their removal naturally.
Important! Therapy with stone-breaking drugs helps dissolve stones in the kidneys and bladder within 2–6 months, but has many side effects.
The drug Canephron prevents the formation of stones and has a minimum of contraindications
Treatment for bladder stones
Depending on the characteristics of the stone, management tactics are selected.
Conservative drug therapy
Medicines to get rid of bladder stones
Antispasmodics:
- No-shpa;
- Baralgin;
- Papaverine;
- Spazgan.
Uroseptics:
- Palin;
- Furomag;
- 5 – NOC;
Alpha1-blockers:
- Omnic (Tamsulosin);
- Urorek (Silodosin);
- Doxazosin.
Herbal preparations:
- Cyston;
- Spilled;
- Phytolysin;
- Rowatinex;
- Hydrangea;
- Canephron;
- Urolesan.
Decoctions of diuretic herbs that can dissolve stones:
- Pol-pol (Erva woolly);
- Rosehip root;
- Madder;
- Golden rod;
- Lingonberry leaf.
General principles of nutrition for bladder stones
Additionally, some dietary restrictions are recommended. Of course, it is better to know the composition of the stone, but if this is impossible for some reason, then the following should be excluded:
- rich meat, chicken, fish broths;
- all offal: liver, liver, heart, tongue, stomachs, lung, etc.;
- sausages and salami;
- hot spices;
- shashlik;
- chocolate;
- coffee;
- aspic;
- mayonnaise;
- smoked meats and marinades;
- sweet carbonated drinks;
- juices with irritating effects: tomato, orange, grapefruit;
- salty fish.
You can eat second-cooking broths, lean meat, fish and chicken if you have a bladder stone.
An increased drinking regime is considered a prerequisite. If you do not have hypertension, you need to drink at least 2 liters per day.
It is not recommended to subject food to aggressive processing methods. To reduce the load on the kidneys, a diet for urolithiasis involves limiting table salt.
Surgical treatment
If conservative therapy is ineffective, severe pain, or recurrent inflammation, surgical treatment is possible.
Crushing bladder stones with ultrasound or laser (transurethral cystolithotripsy) is currently considered the most effective and safe surgical intervention for urolithiasis.
Stones with a crystalline structure and high density are suitable for crushing.
The size of the stone should not exceed 3 cm.
Transurethral lithotripsia can also be performed in combination with TUR (transurethral resection), if there are indications for it, for example, prostate hyperplasia.
Contraindications:
- pregnancy;
- acute inflammatory process accompanied by fever;
- small bladder capacity;
- fixation of the stone on a ligature;
- stone in the diverticulum;
- stone volume is more than 4 cm;
- concomitant bladder cancer;
- difficult access.
If endoscopic methods have contraindications, open surgery is performed in the amount of cystolithotomy . An incision is made on the front wall of the abdomen, and the stone is removed from the bladder cavity.
Complications after surgery for bladder stones can include bleeding, acute inflammation, trauma to the walls, and acute urinary retention.
After discharge, the patient should be observed by a urologist.
A control ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder is performed once a year.
If all recommendations are followed, the prognosis after removal of a bladder stone is favorable. If the cause of cystolithiasis has not been identified and eliminated, recurrent stone formation cannot be ruled out.
The patient is recommended to follow a diet taking into account the chemical composition of the stone and take herbal diuretics for preventive purposes.
Victoria Mishina, urologist, medical columnist
just today
- okeydoc.ru
Norms of residual urine in the bladder in men, women and children
| Causes | Description |
| Neurological | Disruption of the functions of the nervous system responsible for the accumulation, retention and excretion of urine |
| Inflammatory and infectious | Swelling of the urethra, sphincter spasm or inflammation of the prostate gland |
| Obstruction | Formation of kidney or bladder stones |
| Selected pathologies | Diverticulum, urethral stricture |
Problems with the bladder of a neurological nature can be due to vertebral hernias.
Neurological disorders occur due to spinal injuries, tumors, and spinal hernia. In adolescents, neurological disorders include congenital abnormalities in the functioning of the central nervous system. Inflammatory processes of an infectious nature push the body to pathological changes in the genitourinary system if a person has cystitis, balanitis or urethritis.
In men, inflammatory processes in the prostate lead to the fact that the remaining urine is not excreted from the bladder. With inflammation, patients complain of a frequent urge to empty the bladder, a weak stream of urine, and the inability to urinate without effort. In this case, patients are haunted by the feeling that the bladder has not emptied completely. Urolithiasis is one of the obstructive causes of urinary stagnation. In the male half, stones form in the bladder, and in women they descend from the kidneys.
Neurological disorders occur due to spinal injuries, tumors, and spinal hernia. In adolescents, neurological disorders include congenital abnormalities in the functioning of the central nervous system. Inflammatory processes of an infectious nature push the body to pathological changes in the genitourinary system if a person has cystitis, balanitis or urethritis.
In men, inflammatory processes in the prostate lead to the fact that the remaining urine is not excreted from the bladder. With inflammation, patients complain of a frequent urge to empty the bladder, a weak stream of urine, and the inability to urinate without effort. In this case, patients are haunted by the feeling that the bladder has not emptied completely.
Additional symptoms
- Disorders in the spine can cause problems with urination.
After visiting the toilet, you still have the feeling that you were unable to empty your bladder completely. - After a short period, new urges to evacuate arise again (for several minutes). There is a dependence on the toilet, which creates discomfort.
- Painful and frequent urination, possible burning and other unpleasant feelings.
Basically, these signs are not a disease as such. Rather, it is a syndrome of the development of other types of disorders, in particular, problems with the genitourinary organs. There is a whole range of such diseases: urethritis, cystitis, urolithiasis, benign and malignant neoplasms, the formation of stones in the ureters, neurogenicity and hyperactivity of the empty bladder, etc. In addition, this symptom refers to possible disorders in the spine (trauma, mechanical disorders, radiculitis, etc.). Thus, it is necessary to pay attention to additionally present signs. With the help of a specialist, you can make a correct diagnosis and take timely measures to eliminate deviations.
Return to contents
Diverticulum
A diverticulum is a sac-like cavity formed from the wall of the bladder. There are two types of diverticula – true and false. A true diverticulum consists of the mucous and muscular layers of the bladder tissue and, as a rule, is a congenital anomaly.
False diverticulum (acquired) develops as a result of increased intravesical pressure that occurs against the background of pathological conditions accompanied by difficulty urinating and systematic incomplete emptying of the bladder. Due to high fluid pressure, atrophy of the muscle layer develops, the destroyed fibers diverge, and the mucous membrane protrudes into the abdominal cavity under pressure.
The main difference between a false diverticulum and a true one is the absence of muscle fibers in the structure of its wall. The main clinical sign of diverticulum is urination twice with the appearance of cloudy urine.
Treatment consists, first of all, in eliminating the causes causing increased intravesical pressure (if the diverticulum is acquired) and subsequent surgical removal of the deformity.
Urethral stricture
Pathological narrowing of the urethra is called urethral stricture. Metaplasia of the tissues of the urethral mucosa can be caused by various reasons, causing damage of varying severity:
- thermal or chemical burns of the urethra;
- inflammatory processes (cystitis, urethritis);
- injuries or bruises of the perineum;
- injury to the mucous membrane during catheter installation;
- congenital pathologies of the urinary tract.
Due to the replacement of damaged cells with mucous connective tissue, scar formation occurs, which significantly complicates the process of urination, resulting in urine remaining in the bladder.
Stricture of the urethral canal on x-ray
How dangerous is the pathology?
If the first symptom occurs, you should seek help from a doctor and undergo a diagnosis. If you do not pay attention and the disease progresses, urine will stagnate in the bladder and pathogenic flora will begin to multiply in it. This will lead to the onset of an infectious-inflammatory process. Additionally, stagnation of urine increases the chance of stone formation. Due to the increase in pressure, residual urine will rise to the kidneys and provoke:
- hydronephrosis;
- pyelonephritis;
- renal failure.
Does water quality affect stone formation?
Of course, water affects kidney function and promotes the formation of stones. This is evidenced by the fact that kidney stones are common in regions where the water is too “hard” and rich in mineral salts.
The risk of getting stones increases when drinking unboiled, unfiltered water, so residents of regions with “bad” conditions are advised to periodically undergo an ultrasound of the kidneys in order to determine the presence of stones in time.
The question arises: is it possible to remove kidney stones by simply stopping drinking tap water and replacing it with bottled water? Unfortunately, no, it will only be possible to prevent the formation of new stones, but the old deposits will not go away.
The amount of liquid you drink is also very important. If it does not exceed one and a half liters per day, including first courses, urolithiasis will become quite real. A decrease in the amount of fluid entering the body increases the concentration of salts (urates, oxalates), from which stones are formed.
Signs and complications
Urine, which remains in the bladder cavity after urination, not only causes a large amount of discomfort, but is itself an alarming symptom, the severity of which directly depends on its quantity.
Residual urine is an important clinical sign, as it leads to dysfunction of the upper urinary tract and is a consequence of pathological processes leading to functional disorders of the bladder.
The main symptoms accompanying excess residual urine are:
- increased urge to urinate;
- weak or intermittent stream;
- the need to strain the abdominal muscles in order to begin the process of urination or prevent its interruption;
- inflammatory processes in the urinary tract.
In the absence of timely treatment, the risk of developing inflammatory processes increases, since stagnation creates a favorable environment for the development of pathogenic microflora and the formation of stones. Impaired urine flow can also lead to the development of hydronephrosis, pyelonephritis and renal failure.
When treating acute urinary retention, it is removed using a rubber catheter.
Complications and consequences
- Hydronephrosis is an expansion of the collecting structures (that part of the kidney where ready urine flows (the renal collecting system)).
- Acute or chronic pyelonephritis (bacterial inflammation of the renal pyelocaliceal system).
- Formation of kidney stones (urolithiasis).
- Bleeding from the urinary tract.
- Kidney atrophy is the replacement of kidney tissue with scar tissue that does not produce urine.
- Vasorenal arterial hypertension (persistent increase in blood pressure above 140/90 mm Hg (millimeters of mercury), which is difficult to treat).
- Chronic renal failure (impairment of all kidney functions, leading to disruption of water, salt, nitrogen and other types of metabolism).
How to determine the presence of pathology?
The disease can be diagnosed using cystometry.
- uroflowmetry;
- orthostatic urine test;
- cystometry;
- electromyography;
- urethroprofilometry;
- Ultrasound of the bladder;
- Ultrasound of the prostate.
To determine the residual urine volume (RVV), an ultrasound examination is performed in 2 stages. To begin with, a diagnosis is made with a full bladder. Then they ask the patient to empty the bladder and sit for 15 minutes, and then again examine the changed organ on the monitor of the device. The difference in size and volume visible on ultrasound is calculated using standard tables.
Treatment of the disease
The choice of treatment method determines the disease due to which urine remains in the bladder. If the treatment is carried out correctly and the patient manages to achieve positive results, the residual urine in the bladder in men and women will cease to reach critical volumes and return to normal. It is possible to eliminate the root cause that caused the deviation using the following methods:
- conservative or surgical intervention to restore the patency of the urinary canals;
- relief of inflammation;
- restoration of the contractile muscles of the urinary system.
Don't people drink enough water?
A 2013 study by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention analyzed data from the National Cancer Institute's 2007 Food Attitudes and Behaviors Study. Attitudes and Behaviors Survey). This was done to evaluate the characteristics of people who drink too little drinking water.
In a sample of 3,397 adults, researchers found the following:
- 7% of adults reported that they do not drink drinking water;
- 36% of adults reported drinking only one to three cups of drinking water per day;
- 35% of adults reported drinking four to seven cups of drinking water per day;
- 22% of adults reported drinking eight or more cups of drinking water per day.
People who ate a serving or less of fruits or vegetables per day often drank fewer than four cups of drinking water per day. The study found that in this sample, too many people did not drink enough fluids throughout the day.
Although the study only measured drinking water consumption and fluid can be obtained from other drinks, water alone, due to its easy availability, lack of calories, lack of caffeine and alcohol, can be considered an ideal source of fluid.
It's worth noting that 7% of people surveyed reported drinking almost no water at all, and respondents who drank too little water tended to eat few fruits and vegetables. This allows scientists to assume that there is a certain number of people who do not get enough fluids, thereby risking their health.
Even if respondents who reported low water intake were still getting enough fluid from other sources, it is likely that they may have been getting that fluid from potentially hazardous sources, compromising their health in other ways as well.
The study authors write that the biological need for water can be satisfied with plain water and with the help of other foods and drinks. Previous epidemiological studies suggest that water intake may be inversely related to the amount of calorie-sweetened beverages and other liquids consumed.
Urine does not completely exit the bladder
This is how patients describe their condition when they see a specialist. There can be many reasons for the presence of residual urine. The main ones among them are:
- Inability of the bladder walls to contract due to some disorder.
- An obstruction in the bladder or urethra that prevents the normal flow of urine.
- Disorder of interconnectedness in movements between muscles due to damage to innervating nerve endings. It concerns the detrusor (responsible for the excretion of urine) and the sphincter (designed to retain urine in the bladder).
- Neurogenicity of the bladder, with diseases of the brain or spinal cord and with damage to the nerve ganglia.
- The use of drugs from the group of anticholinergics and other drugs that help suppress propagating nerve impulses.
- Severe constipation, during which the overcrowded rectum begins to put pressure on the bladder, causing it to move slightly and thereby narrow the internal opening of the urethral canal.
- Diabetes mellitus, Parkinson's disease and multiple sclerosis contribute to urine retention in the bladder.
- Performing surgical operations performed on any of the organs in the pelvis and allowing damage to the nerves in this area threatens the development of residual urine.
- Urinary retention in women can be a sign of genital herpes, which causes severe pain and swelling of the lower part of the urinary system.
Factors contributing to stone formation
Predisposing factors to the development of this pathology are the following aspects::
- All diseases associated with impaired urine flow. With severe prostatic hyperplasia, bladder atony, tumor processes, bladder diverticula, impaired innervation, urine stagnation occurs. Gradually, salts precipitate, from which single or multiple stones are formed.
- Impact of pathogenic microflora. Cystolithiasis is aggravated by the addition of a secondary bacterial infection, which changes the physicochemical properties of urine, accelerating the process of stone formation.
- Congenital or acquired metabolic disorder. Dysmetabolic nephropathy is the body’s tendency to increased crystalluria. Even a small child is diagnosed with the periodic appearance of salts in the urine.
- Foreign body of the bladder. An example would be a stone on a ligature after a history of surgery. Prolonged standing of a functioning epicystostomy, as a way to resolve bladder outlet obstruction, often leads to cystolithiasis. Here, in addition to the constant presence of a foreign body, aggressive microflora and the natural process of phagocytosis, in which lymphocytes are not able to digest the silicone material, are important.
- Diverticulum. A diverticulum is a protrusion of the bladder wall (a defect in the muscle layer), in which, like in a bag, urine stagnates. Often a calculus forms in a diverticulum, which subsequently leads to chronic inflammation.
- Violation of the anatomical position of the bladder. Pathology is more often detected in women with weakened pelvic floor muscles and prolapse of the vaginal walls.
As a rule, they have a history of several independent births and work related to heavy lifting.
In addition to the listed conditions, we must not forget that the stone could migrate into the bladder from the upper urinary tract, and gradually become overgrown with salts and linger for a long time.
Stagnation of urine
With chronic urine retention in the bladder, regular stagnation occurs, which in itself is unnatural and therefore unsafe. First of all, the pressure begins to build. First in the ureters, then in the renal pelvis, after which, under its influence, the renal tubules expand, and after this the most key organ in the urinary system, the kidneys, is affected.
If residual urine is a constant phenomenon, then:
- the possibility of the formation of stones, both in the bladder and in the structures located above, cannot be ruled out;
- favorable conditions for the habitat and activity of infections in the urinary tract;
- the worst consequence is kidney failure, which develops with prolonged stagnation of urine.
For older people, this disorder is no less dangerous due to the high risk of infection with urogenic sepsis, during which the infection spreads through the bloodstream throughout the body, affecting every element of it.
How to quench your thirst?
Experts from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have developed a number of suggestions that can help people increase the amount of water they typically drink:
- Carry a bottle of water with you so that fluid is available when needed, such as at work or on a walk.
- Water can be frozen in the freezer so that ice water is available throughout the day, as it can be more enjoyable than drinking other drinks in certain situations.
- Adding a slice of lime or lemon to your water can improve the taste without affecting the nutritional value of the water.
Drinking enough water to maintain your health should be an easily achievable goal. Under normal conditions, most people can drink enough fluid to meet their water needs. Although this is a relatively simple step that can be taken without much time or effort to maintain kidney health, in the busyness of life many people still forget to take this step.