Author of the article
Pastushok Vladimir Georgievich
Practicing nephrologist, experience over 11 years
Articles written
52
Contact the author
When conducting a urine test, an indicator such as specific gravity (or density of urine) is necessarily studied. This indicator gives an idea of both the functioning of the kidneys and the activity of the brain, central nervous system, and pancreas. Its decoding (decrease or increase) may indicate various processes occurring in the body.
What is meant by specific gravity?
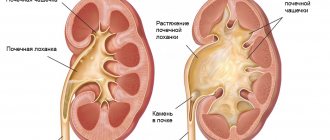
The specific gravity of urine refers to how densely the dissolved substances are present in it. Various salts, acids and other breakdown products are excreted in the urine. The more of them there are in urine, the denser it is.
What does density mean? Thanks to this indicator, the filtering function of the kidneys and their ability to dilute urine are assessed. A decrease in density may indicate renal failure, and an increase may indicate insufficient urine excretion.
If strong deviations are detected, additional diagnostics of the body should be carried out and the cause of this condition should be analyzed. Impaired kidney function affects the entire body and causes serious complications.
Functional tests
To determine the functional state of the kidneys, it is not enough just to do a urine test. Specific gravity can change throughout the day, and in order to accurately determine how much the kidneys are able to secrete or concentrate substances, functional tests are performed. Some of them are aimed at determining the state of the concentration function, others - the excretory function. It often happens that disturbances affect both of these processes.
Urinalysis, urine density, as one of its parameters
Characteristics of the composition and appearance of urine can provide a lot of information about a person's health status. The most basic test is a general urine test. During urine analysis, parameters are studied - color, smell, content of salts, acids and other substances.
One of the parameters is the specific gravity or density of urine. This indicator is measured using a special device called a urometer. The unit of measurement for urine density is g/liter.
A general urine test is the main type of research. To clarify its results, other, narrower analyzes can be used:
- Zemnitsky's method. With its help, the ability of the kidneys to filter, excrete and dilute urine is determined. For analysis, collect a sample during the day at regular intervals in separate jars;
- The concentration method involves severe fluid restriction and collection of samples throughout the day. There are contraindications;
- The dilution method is to study the dilution function of the kidneys with increased fluid intake. The dosage of liquid is selected depending on body weight. There are also contraindications.
Rules for preparing for urine analysis in adults (men, women, pregnant women)
It is very important to properly prepare and collect a sample for a general urine test. This will allow you to obtain the most reliable analysis results.
The preparation is as follows:
- the day before collection, avoid coloring foods, salty, fatty and spicy foods;
- avoid physical activity;
- give up alcohol;
- stop taking medications. If it is impossible to cancel, notify your doctor.
Urine collection:
- before collection, it is necessary to carry out hygiene procedures and wash the genitals;
- women use a tampon in case of heavy discharge or menstruation;
- prepare a sterile container for collecting the sample;
- start urinating into the toilet, stop after an interval of 2-3 seconds and collect the middle portion in a container, then you can urinate into the toilet again;
- Urine collected in the morning on an empty stomach is best suited for analysis. As a last resort, it is necessary to collect a sample no earlier than 5-6 hours after the last urination;
- A urine sample must be submitted for testing no later than 1-2 hours after collection. Long-term storage is unacceptable and leads to unusability of urine.
Tips for preparing your child for urine testing
The rules for preparing and submitting a urine sample for testing in adults and children are almost the same. The slight differences are in the collection. In young children who do not yet know how to go potty on their own, urine is collected using a special urinal. It can be purchased at any pharmacy.
Collecting from a child's potty, diapers and diapers is strictly prohibited. With this collection, bacteria, dirt particles and fibers enter the urine, which ultimately leads to distorted results.
Indicator norms
The norms for the specific gravity of substances in urine are not constant. What do they depend on? The standards are influenced not only by age and gender factors, but also by many others:
- ambient temperature level;
- amount of liquid drunk;
- Times of Day;
- excess salt or spices in food;
- the volume of water that is released through sweat and breathing.
Despite this, there are certain ranges of values for different ages by which kidney function is assessed.
In men
The norms for various urine indicators differ between men and women. As a rule, men drink less fluid during the day. For this reason, the density of their urine is slightly higher. The norm for men is 1.020 – 1.040 g/liter.
Among women
For women, this indicator is practically no different from that for men. By nature, women monitor their slimness and health, so they drink more liquid. Therefore, the norm is considered to be a value in the range from 1.003 to 1.025 g/liter.
In pregnant women
During pregnancy, toxicosis, nausea and frequent vomiting, which lead to fluid loss, become common. Or, on the contrary, swelling. As a result, the specific gravity of urine can vary significantly in different directions during certain periods of pregnancy.
The range of normal density in pregnant women is slightly wider than in women in general. It varies from 1.001 to 1.035 g/liter.
Children's indicators
In children, there are large differences in density depending on age:
- after birth - 1.007 - 1.017 g/liter;
- up to six months – 1.003 – 1.005 g/liter;
- up to 1 year – 1.005 – 1.015 g/liter;
- up to 3 years – 1.010 – 1.018 g/liter;
- up to 5 years – 1.013 – 1.020 g/liter;
- up to 12 years – 1.009 – 1.025 g/liter
Indicators for the elderly
With age, changes occur in the body. The functions of almost all organs decrease and metabolic processes slow down. This also applies to kidney function. The ability of the kidneys to filter is reduced, which leads to an increase in urine density. The normal value for older people is considered to be from 1.01 to 1.04 g/liter.
Zimnitsky test
The Zimnitsky test allows you to simultaneously evaluate both the ability of the kidneys to concentrate and the ability to excrete urine and do this against the background of a normal drinking regimen. To carry it out, urine is collected in portions every 3 hours during the day. In total, 8 portions of urine are obtained per day, in each of which the quantity and specific gravity are recorded. Based on the results, the ratio of nighttime and daytime diuresis is determined (normally it should be 1:3) and the total amount of fluid excreted, which, along with monitoring the specific gravity in each portion, makes it possible to assess kidney function.
Hypersthenuria
When density increases above the maximum permissible values, a certain condition of the body occurs, which is called hypersthenuria. It is noted when the specific gravity of urine increases above normal already at a value of 1.04 g/liter.
Symptoms of hypersthenuria include the following:
- reducing the number and size of urine portions;
- darkening;
- the appearance of clots or sediment;
- the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen;
- weakness and increased fatigue;
- swelling of the whole body.
Causes in adults
All reasons contributing to the development of hypersthenuria can be divided into physiological and pathological. The first type includes:
- small amount of fluid consumed;
- taking medications (laxatives, antibiotics);
- excessive sweating in hot weather or during physical activity;
- dehydration as a result of poisoning, diarrhea, vomiting;
- severe body burns.
In these cases, it is necessary to replenish the fluid supply in the body, which will help reduce the relative density of substances in the urine.
Hypersthenuria can occur as a result of the development of certain pathologies. The second group of factors includes the following diseases:
- heart failure, which is accompanied by edema;
- diabetes mellitus, which is accompanied by a high concentration of glucose in the blood;
- the presence of inflammatory diseases in the urinary system and kidneys;
- acute or chronic form of glomerulonephritis;
- development of oliguria;
- pathologies that cause excess protein concentration in urine;
- disorders of the thyroid gland (for example, hypothyroidism).
In children
Many parents, having seen in the test results that the density of urine in children is increased, do not know what this means and what needs to be done. The phenomenon of hypersthenuria can be diagnosed even in children. Its symptoms are similar to those in adults. Among the reasons are:
- pathologies of congenital or acquired nature of the urinary tract;
- frequent cases of poisoning, diarrhea and vomiting;
- In very young infants, an increased level of density may occur due to an excess of fatty and protein foods in the mother's diet.
In the elderly
Hypersthenuria often occurs in older people due to decreased kidney function. As a result, the filtration capacity of glomerular filtration decreases and resistance in the vessels of the kidneys increases. All this leads to the fact that the saturation of urine in older people decreases.
Concentration test
To conduct this examination, drink and liquid food are excluded from the patient’s diet for a day and food high in protein is included. If the patient suffers from severe thirst, drinking in small portions is allowed, but not more than 400 ml per day. Every four hours, urine is collected, assessing its quantity and specific gravity. Normally, after 18 hours without fluid intake, the relative density should be 1.028-1.030. If the concentration does not exceed 1.017, then we can talk about a decrease in the concentration function of the kidneys. If the indicators are 1.010-1.012, then isosthenuria is diagnosed, that is, the complete loss of the kidney’s ability to concentrate urine.
Hyposthenuria
With a strong decrease in the level of urine density, a state of hyposthenuria occurs. In this case, frequent urination, severe discoloration of urine, and possible swelling are noted. Too low specific gravity of urine is observed when the indicator is below normal at a value of 1 g/liter.
Causes of decreased density in adults
There are certain reasons for the occurrence of low urine density:
- drinking large amounts of liquid;
- taking diuretics;
- severe food restrictions, strict diets, fasting.
Reducing water consumption and normalizing nutrition help ensure that the specific gravity returns to normal without additional treatment.
The danger should be caused by hyposthenuria, which occurs against the background of pathologies:
- psychological diseases accompanied by a great feeling of thirst;
- diabetes insipidus;
- pathologies of the central nervous system (encephalitis, meningitis);
- renal failure;
- amyloidosis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- kidney tumors;
- infectious diseases.
In this case, hyposthenuria is a symptom of the underlying disease, and treatment should be aimed specifically at the main cause.
Why does a child’s density decrease?
After birth, children experience a decreased level of urine density. This is a normal occurrence during the first month of life. Subsequently, this indicator returns to normal.
If a low level of density is diagnosed in older children, then first the dynamics of the indicator are monitored over a certain period of time. In the case of persistently low density levels in a child, a thorough examination and identification of the cause is required. The most common cause of the condition is renal failure.
Factors reducing urine density in the elderly
It is not uncommon to see a decrease in the permissible specific gravity of urine in older people. Age-related changes affect all organs, including the urinary system. As a person ages, the immune system and the body's resistance to various diseases decrease.
Factors in the development of hyposthenuria can be:
- urinary tract infections;
- prostatitis;
- gout;
- diabetes;
- urolithiasis, etc.
Additional Research
It should be noted that based on a single change in the indicator, one can only conditionally suspect something is wrong in the renal concentration ability. To make the assessment more reliable, the patient is asked to retake the sg urine test for normal, or to conduct a diagnostic urine test according to Zimnitsky, when daily fluctuations in density are assessed. During the day, a person collects approximately 8 portions of urine at regular intervals (~every 3 hours). Then, using the device, the difference between daytime and nighttime diuresis is determined. There should be a discrepancy of approximately 30% at different times of the day.
If blue is considering food coloring, some medications, pseudomonas infection. If orange can be concentrated urine from dehydration, fever, heat stroke, laxatives, bile, drugs, carrots, carotene, riboflavin, food coloring.
If dairy considers a bacterial or urinary tract infection, vaginitis, some products. If browns are considered acute hepatitis or cirrhosis, blood, bilirubin, urobilinogen, miloma, melanoma, Addison's disease, sulfonamides. If red, consider consumption of beets and berries, blood from infection, menstruation or lesions. Porphyria, cascara, senna, aniline dyes, Dorban.
Also, to confirm fluctuations when the specific gravity of urine is increased/decreased, several other types of functional tests can be used. For example, a dry food test (or it is called a concentration test). The essence of the study is to change the patient's diet. All foods with a large amount of liquid (soups, compotes, teas, etc.) are excluded from the menu for the day, and the consumption of the liquid itself should be reduced to a few sips per day.
Functional diuresis tests
If blacks consider liver kidney disease, tyrosine metabolism, kidney damage from infection.
The color of the urine should be clear when the light particles are fine. If completely clear, without particles, consider an anabolic state, and if high turbidity consider a catabolic state, urinary tract infection, vaginitis, fat or sugar problems. Sweet implies the presence of sugars. The ammonia smell may be bacterial growth or potassium deficiency alkalosis or cyclic, which is the worst stage of metabolic alkalosis. The offending odor could be toxicity or a possible inflammatory response. The medicinal odor may be medicine that changes the chemistry of the urine.
This routine is quite difficult for many patients, but with this method it will be easier for doctors to assess the physiological parameters and relative density of urine. If, after a day, the indicator remains low (within 1.015-1.017 g/l), it means that the kidneys are still not coping with their ability to properly concentrate urine before excreting it. If the result shows that after such a “dry” test method, the density of urine is increased or close to normal, then the kidneys are functioning as they should.
Urine specific gravity is a laboratory test that shows the concentration of all chemical species in the urine. Once you provide a urine sample, it will be tested immediately. The health care provider uses a dipstick made with a color-sensitive pad. The color the dipstick changes will show the supplier the specific gravity of your urine. The dipstick test only gives an approximate result. For a more accurate result, your provider may send your urine sample to a laboratory.
Sometimes I use a water load test, which also allows us to evaluate the concentration ability of the kidneys.
Therapist advice
Significant deviations from the norms of the specific gravity of urine should alert a person. Hypersthenuria and hyposthenuria can cause serious complications and therefore require consultation with a nephrologist or urologist. You should initially consult a therapist.
It is imperative to establish the exact cause of deviations in urine density. Therapy is selected depending on the identified disease.
A prerequisite is adherence to the dietary diet:
- refusal of fatty, salty, smoked and spicy foods;
- getting rid of bad habits;
- compliance with the drinking regime.
The diet helps speed up the treatment process and improve the patient’s condition. In addition, the doctor’s advice includes:
- Regular visits to the doctor to assess your health;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- analysis at least 2 times a year;
- Seeing a doctor immediately after the appearance of unpleasant symptoms or problems with urination.