Just a few decades ago, diagnosing diseases was seriously difficult. This could be explained by the lack of high-quality research methods. But modern medicine has stepped far forward. There are now many different options for conducting research. The most popular types of examinations today are ultrasound, CT and MRI. MRI of the kidneys is increasingly being performed. This can be explained very simply. The fact is that it is the kidneys that are often exposed to negative processes that contribute to the development of various diseases in this organ.
To clarify the diagnosis, an MRI of the kidneys is often performed.
Introduction
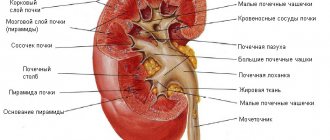
The kidneys are a paired, bean-shaped organ that is the main organ of urine formation. The weight of one kidney varies from 120 to 200 g. The kidneys are located in the abdominal cavity, on both sides of the spine, at the level of the XII thoracic and two upper lumbar vertebrae. They lie on the posterior abdominal wall, with the right kidney lying slightly lower than the left, and are fixed in their position by the renal fascia, blood vessels and fat capsule. Layer-by-layer scanning allows you to recreate the structure of an organ in detail, examine it from the outside and inside, and create images in three projections. This greatly simplifies the work of surgeons.
| Kidney structure diagram | MRI of the kidneys |
Causes of angiolipoma development
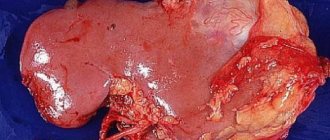
Angiomyolipoma is a benign mesenchymal tumor of the kidney containing varying amounts of mature fatty and smooth muscle tissue and blood vessels.
- Angiomyolipoma is more common in women.
- A relatively common tumor (0.3-3%).
- Small hamartoma (several centimeters)
- Usually unilateral
- Rarely, renal vein invasion may occur.
- Bilateral angiomyolipomas are common in patients with tuberous sclerosis.
Classification of tomographs
Medical magnetic resonance imaging scanners are classified according to the design features of the magnet location and the magnetic field voltage.
Based on their design features, devices are divided into closed and open tomographs.
Closed type device (tunnel)
It is a cylindrical tunnel with magnets installed along the entire perimeter of the capsule, a retractable table and a control system.
Such equipment is a priority in the field of diagnostics due to a number of advantages:
- High resolution projections.
- The ability to detect diseases at an early stage.
- Minimum duration of the procedure.
The weaknesses of closed tomographs include:
Restrictions on patient weight and dimensions. Discomfort and panic attacks in patients with claustrophobia.
Open tomograph
– a device with a lower and upper location of magnets, relative to a retractable table for placing patients.
The advantages of open type equipment include:
- No strict weight restrictions.
- Comfortable examination of children, patients with fear of closed spaces, overweight, non-standard fixation of fractures.
Disadvantages of open tomographs:
Lower image resolution. Long research time. Inability to identify pathologies in the early stages of formation.
| Open MR tomograph | Closed-type MR tomograph |
Based on the operating magnetic field voltage, equipment is divided into 4 categories:
Up to 0.5 Tesla – low-field MRI device. Up to 1 Tesla – a mid-field tomograph is most often an open type. The duration of the study is 40 minutes or more and the low quality of projections reduces the demand for equipment. 1.5 Tesla – high-field MRI machine. The high quality of the images allows you to identify even minor pathologies and disorders. 3 Tesla – ultra-high-field tomograph allows you to reduce the duration of the study by 2 times. The cost of the procedure using such a device is much higher.
The optimal apparatus for examining the kidneys is a tomograph with a magnetic field voltage of 1.5 Tesla.
| Image quality depending on equipment power |
What can you see on MRI images?
The results of the study will be ready a few hours after the scan is completed. The resulting images or CD, along with a description of the image, are given to the patient or sent to the attending physician.
This MRI image shows healthy kidneys: a - front view, b - side view
An MRI of the kidneys can reveal any abnormalities in their functioning, as well as assess the condition of the urinary tract. Even minor anomalies are clearly visible in the images obtained during the diagnosis. The images visualize the condition of the renal vessels, the size and contours of the kidneys, and any changes in the structure of their parenchyma.
The pathologies “visible” with a magnetic resonance imaging scanner include:
- adenoma or cyst of the kidney, even in the earliest stage;
- hydronephrotic dilatation of the pyelocaliceal system;
- pathology of the renal vessels;
- the smallest anomalies in the structure of the urinary organs;
- nephrosclerosis (wrinkled kidney) and many others. etc.
Indications
The following specialists can refer a patient for an MRI of the kidneys: therapist, nephrologist, urologist, surgeon, oncologist. Each doctor has his own task and the need to obtain comprehensive information.
The list of indications for the procedure is quite extensive:
- pain in the lumbar region
- swelling of the face, legs, lumbar region
- abnormalities in urine tests
- high blood pressure
- enlargement of the renal pelvis
- blood flow disturbance
- arterial hypertension
- incorrect position of the organ
- increase in kidney volume and violation of the contour boundaries
- obstruction of the urinary tract
- suspicion of a cyst
- probability of tumor formation
- suspicion of penetration of metastases from another affected system
- kidney infarction
- congenital anomalies and malformations of the organ, feeding vessels, ureters
- injuries with suspected violation of the integrity of the organ, the occurrence of hematomas, damage to the circulatory network of the kidney
- preparation for surgery, determination of the method of surgical intervention
- monitoring the results of kidney surgery
- checking the effectiveness of treatment
- checking the condition of the organ and confirming the possibility of kidney transplantation to another patient.
Indications for MRI of the kidneys
- low back pain of unknown origin, changes in laboratory tests;
- impairments of function and function;
- suspicion of the presence of neoplasms, kidney cysts;
- kidney injury, suspected abscess, other lesions;
- severe course of urolithiasis with an attack of renal colic;
- congenital and acquired malformations of the kidneys, adrenal glands, urinary tract;
- pronounced edema syndrome;
- in case of concomitant pathology, in a comprehensive examination of the liver and kidneys;
- monitoring the treatment performed to remove a tumor or kidney stones.
When a patient presents with the above complaints, the attending physician conducts a thorough examination, thoroughly studying the entire history of the disease, complaints, data from laboratory, instrumental and additional examinations, and only after that, if necessary, refers the patient for an MRI scan of the kidneys.
Contraindications
The presence of pacemakers, metal implants in the human body, as well as pregnancy and lactation.
Contraindications
There are not many contraindications to MRI of the kidneys and they are generalized into two groups: absolute and relative.
Absolute contraindications
– these are conditions of the body in which exposure to a magnetic field causes harm that exceeds the benefits of the study.
These conditions include:
- The presence of an artificial pacemaker or pacemaker, defibrillator.
- Vascular hemostatic clips.
- Cochlear hearing implant for the inner ear.
- Insulin or hormone pump.
- Ilizarov apparatus for healing fractures.
- Relative contraindications are factors that allow you to safely perform MRI when changing conditions for the procedure.
Time restrictions include:
- Claustrophobia.
- Anxiety disorder at a relapsing stage.
- The patient's weight is more than 120 kg.
- Severe pain syndrome.
- Permanent makeup, as metal particles are added to the coloring pigment. The same applies to color tattoos.
Contraindications to contrast for MR scanning of the kidneys are discussed separately:
- Chronic renal failure in acute form or at the terminal stage.
- Recovery period after liver or kidney transplantation.
- Pregnancy.
- Breast-feeding.
- Infant age up to one month.
- Generalized allergic reaction to the contrast solution drug.
Before undergoing an MRI by self-referral, you should consult with your doctor and determine possible contraindications to magnetic resonance scanning and the use of a contrast solution.
Possible harm and side effects
MRI is a safe procedure. Adverse reactions in a patient can only be observed after a contrast study. They develop against the background of the introduction of a contrast agent into the bloodstream. Possible side effects include:
- dizziness;
- feeling of warmth in the body;
- sneezing;
- hyperemia (redness of the skin);
- skin manifestations of allergies (rash, itching);
- dyspnea.
My husband's grandmother suffered a stroke and was sent for an MRI of her brain. But she was very scared of this procedure, since she had fixed bridges containing metal, which she certainly informed the specialist about. However, the doctor said that there was nothing to worry about. It turns out that magnetic resonance imaging cannot be performed only in the presence of ferromagnetic structures that tend to be attracted to magnets. But in modern dentistry such materials are not used for prosthetics. Even implants are made of titanium, which is not particularly sensitive to magnetic fields. The doctor also said that rumors about metal crowns and other structures burning hot and bursting out of the mouth during an MRI are nothing more than a myth.
Preparation
MRI of the kidneys requires special training to obtain the most effective diagnosis.
To prevent gas formation in the intestines from interfering with scanning, three days before the procedure you should avoid eating the following foods:
- Raw vegetables, especially cabbage
- Fresh fruits
- Legumes (peas, beans, lentils)
- Yeast-containing flour products
- Carbonated drinks and mineral water.
- Create a menu of lean meat, baked and steamed vegetables.
- One hour before the examination, you can drink espumizan.
How is tomography of the adrenal glands and kidneys performed?
In order for the study to be effective and identify existing abnormalities, it is important to know how to prepare for an MRI of the kidneys. First of all, you need to refrain from consuming food and liquid 3-4 hours before the scan. Immediately before the procedure, you must change into disposable clothing or remain in your underwear. The medical worker will ask you to remove metal objects, removable dentures, hearing aids, etc., and also leave personal belongings in the office. In addition to the fact that you need to properly prepare for the examination with a tomograph, it is recommended to provide the results of previously conducted studies - ultrasound, CT , and also show a tomography of the kidney done earlier, which will allow you to determine the information content of the scan with maximum accuracy.
How does the procedure work?
Kidney MRI is performed by appointment. Conventionally, the procedure is divided into three stages: organizing the examination, scanning itself and issuing results.
At the organization stage, the patient will have to perform the following actions:
- Provide documents for verification and register, draw up an agreement for the provision of paid medical services.
- Fill out the questionnaire to determine contraindications and restrictions.
- An MRI with contrast may require the results of blood tests to determine the degree of kidney function. This question should be clarified with the administrator when registering for the procedure.
- To accurately calculate the dosage of the contrast agent, you must be weighed.
- For a comfortable scanning, it is better for the patient to arrive in loose-fitting clothes without fasteners or decorative metal fittings. Some MRI centers provide a disposable changing kit.
- Listen to the nurse's instructions about the rules for performing an MRI, ask the necessary questions to clarify any unclear points.
Kidney MRI scan procedure:
- Once the patient is comfortable on the sliding platform, the nurse will secure the patient's body with soft straps to prevent unwanted movement during the examination.
- The table slides into the tomograph, and the diagnosis begins.
- The study with contrast takes place in two stages: a basic scan and a repeat tomography after the solution is administered.
Output of results:
- If the radiologist at the MRI center is not overloaded with work on transcripts, the results will be ready within 60 minutes.
The patient can receive images printed on film and/or recorded on electronic media, as well as a specialist’s report for the attending physician.
- If there is a large flow of clients, the delivery of results may be scheduled for the next day. Some clinics upload materials to the patient’s personal account on the website or send them by email to save the patient from having to return to the medical facility.
Price
Some patients believe that MRI is quite an expensive examination. In essence, this is true compared to other methods, but the information content of MRI of the kidneys is much higher than that of other methods, which means that the patient will receive the most detailed answer about his urinary system, as well as the most correct therapy in the presence of established diagnoses. The price of an MRI examination is influenced by many factors, mainly the duration of the procedure and the use of a dye. An MRI with contrast of the kidney will cost more because the doctor needs to make sure that there are no possible contraindications for this method, which means conducting a test. A lengthy procedure will also cost more, since the longer the examination lasts, the more accurate data can be obtained, which means the correct diagnosis can be made.
Duration of the procedure
The duration of magnetic resonance imaging of the kidneys on a high-field tomograph capable of generating a field voltage of 1.5 Tesla is 20-30 minutes.
A similar study on an open-type mid-field tomograph takes 40-60 minutes.
Innovative equipment capable of producing a magnetic field with a voltage of 3 Tesla will complete the task in 5-7 minutes.
Contrast MRI of the kidneys doubles the procedure time.
When an MRI won't help?
The magnetic resonance imaging method is simple and universal; it has virtually no restrictions in application. Still, you need to take into account some nuances:
- MRI should not be performed on people who have shrapnel from bullet wounds, metal implants such as neurostimulators, heart valves, vascular clamps, intrauterine devices, or any dental prostheses.
- Women who use permanent dye for eyebrows and eyelids are strictly not allowed to undergo the procedure.
- Patients suffering from severe dehydration, bronchial asthma, or cardiovascular diseases may be denied an MRI.
- If the study is carried out with intravenous contrast enhancement, then before the procedure you should make sure that the patient is not allergic to the drug used.
- The influence of the magnetic field on the fetus in the womb of the expectant mother has not been fully studied. Therefore, during pregnancy, a woman is recommended to replace MRI with traditional ultrasound.
- In obese patients, the test may not provide a complete picture of kidney health.
- In people with certain psychological characteristics, in particular, a fear of closed spaces (claustrophobia), a procedure performed in a closed tomograph can cause a severe attack. They can perform MRI in an open machine. But the images obtained with its help will not be as detailed as when using a closed-type tomograph.
- Alcohol or drug intoxication is a valid reason for refusal to participate in the study.
In all of the above situations, the question of diagnosing renal diseases is decided by the doctor together with the patient on an individual basis.
What does it show
MRI results are highly informative and allow you to establish a diagnosis with an accuracy of up to 95%. To determine the signs of pathology, the specialist must have the proper qualifications and extensive experience in kidney research.
Even in normal condition, the left kidney will be slightly larger than the right and located slightly higher. Organ dimensions: length 11-12 cm, width 5-6 cm, thickness 3-4 cm. An MRI image shows the boundaries of the cortex and medulla. There should be no inclusions in the lumen of the pelvis; their standard size is about 1 cm. Veins and arteries, in the absence of structural abnormalities, should have dense, smooth walls of appropriate diameter.
Thanks to MR scanning, the radiologist can establish the following parameters and conditions of the paired organ:
- Are the kidneys positioned correctly relative to other organs?
- The actual size of the organ, clarity of contours, conductivity of blood vessels and urinary tract, structure of renal tissue and possible changes in its structure.
- The condition of blood vessels, the presence of areas of varicose veins, violations of the lumens of veins and arteries.
- The degree of kidney function, the presence of renal failure, inflammatory processes, accumulation of bloody substances.
- Presence of a neoplasm, severity, size, location, prerequisites for development and growth.
- Direction of metastasis.
- Hematomas with external and internal damage to the organ, violation of the integrity of the membrane, vascular tissue.
- The presence of stones in the pelvis or ureter.
A correct diagnosis and timely treatment and/or surgical intervention guarantee the successful elimination of the pathology and the return of normal functioning of the organ.
Indicators and results of examination in adults and children
Indicators checked during MRI of the kidneys:
- shape (normally bean-shaped);
- location (normally, the kidneys are adjacent to the posterior part of the peritoneum at the level of the 11th (12th) thoracic and 1st (2nd) lumbar vertebrae, with the right organ located slightly lower due to its proximity to the liver);
- contours (must be smooth and well visualized);
- cortico-medullary differentiation (a clear boundary between the cortical and medulla layers of organs);
- the size of the renal pelvis (normally they should not be dilated);
- development and thickness of the renal pedicles (should be well developed, but not expanded);
- features of the structure of the space around the kidneys (normally they should not exist);
- presence/absence of fluid in the retroperitoneal space (normally it should not be present);
- the condition of the lymph nodes located behind the peritoneum (they should not be enlarged);
- kidney size (the norm of this indicator depends on the height and age of the patient).
Kidney sizes in children and adults depending on age and height (L - left kidney, R - right)
Survey results may also include additional information. So, during an MRI of the kidneys the following can be detected:
- cysts;
- stones (without specifying their composition);
- neoplasms (benign or malignant);
- vascular pathology (aneurysm, narrowing or expansion).
The results of the examination are usually prepared within 2-3 hours after its completion. They can either be placed in the hands of the patient or sent to the attending physician.
What's the difference with and without contrast?
MRI of the kidneys with contrast significantly expands the investigative range of the procedure. Allows you to identify neoplasms at an early stage, the vector of spread of metastases.
Contrasting is performed using a special solution based on gadolinium derivatives. The drug is administered intravenously.
Salts of the metal gadolinium, when exposed to a magnetic field, show pathological areas with more contrast compared to other tissues. New growths seem to be illuminated, which allows the radiologist to most accurately determine the location, shape, size, nature of the course and stage of tumor development.
The difference between an MRI image with and without contrast is obvious:
| On the left is an MRI performed with contrast; on the right without contrast solution |
Preparing for an MRI of the kidneys with contrast
To feel comfortable, do not overeat before the MRI procedure; small amounts of light food 40 minutes before the MRI of the kidneys are helpful.
No special measures are required, but for the procedure to be more comfortable, clothing should be loose and made from natural fabrics. If you come to the MRI of the kidneys in a formal suit, you have the opportunity to use a disposable spacious robe. Anything containing metal should be stored or left at home. Magnetic cards, watches, hairpins, jewelry lead to the appearance of defects on films, which calls into question the quality of the examination.
You should not show up for a kidney MRI with contrast hungry, as this may cause increased autonomic symptoms, which are often a response to gadolinium administration. A skinny stomach causes nausea, a metallic taste in the mouth, hot flashes, and drooling. To avoid this, have a light snack 40 minutes before the diagnosis. The other extreme of overeating is that with a full stomach, lying on your back motionless for 40 minutes is not very comfortable. For 2-3 days, give up gas-forming foods: cabbage, greens, legumes, milk, baked goods, alcohol. Take with you your passport, a referral from a doctor, an insurance policy (if the examination is carried out as part of compulsory medical insurance or voluntary health insurance), all available extracts from the medical history, the results of previous ultrasounds, urography, scintigraphy, etc. There are no contraindications to taking everyday medications.
CT or MRI, which is better?
MRI and CT of the kidneys are fundamentally different methods for examining the paired organ. Each of them has its own number of advantages and disadvantages. For an objective comparison, the following indicators must be taken into account:
Technology of influence on the body
. To visualize the internal structures of an organ, MRI uses the magnetic resonance effect. The device processes signals coming from hydrogen atoms and produces images. CT imaging uses the ability of x-rays to pass through organic tissue of varying densities. The denser the fabric, the lower the speed of the rays, which means that a clearer trace of the structure will remain on the image.
Device capabilities.
MRI diagnoses the condition of soft tissues with maximum information. This method accurately determines pathologies of the vascular bed that feeds the kidneys, neoplasms, inflammatory processes, and deviations from developmental norms. Nephrolithiasis is a weakness of MR scanning. The device cannot detect all types of stones. In this regard, CT can provide the most complete information. The device is able to determine the density of the stone, which allows the doctor to choose an effective method of removal - lithotripsy (crushing by ultrasound) or surgery.
Duration of the procedure.
MRI performs step-by-step scanning of sections of an organ in an average of 30 minutes. If the patient has injuries with suspected internal bleeding, then priority is CT. Radiation examination spends 1-2 minutes on diagnosis.
Security and restrictions
. MRI can be performed an unlimited number of times. However, the procedure is contraindicated in patients with ferromagnetic implants. They are sent for a CT scan. The disadvantage of computed tomography is the high radiation exposure to the body. Because of this, doctors set a limit on conducting the study no more than twice a year.
In some cases, determining the complete clinical picture of the pathology can be carried out using a combination of both diagnostic methods.
| CT | Kidney MRI |
CT allows you to build 3D models:
| 3D model |
MRI of the adrenal glands
If a patient needs an MRI of the kidneys and adrenal glands, then diseases of the adrenal glands requiring MRI are performed in the same way as the kidneys themselves. When examining them, the doctor can identify diseases of the adrenal glands using this procedure. Therefore, if an MRI of the adrenal glands is recommended, then it must be done. MRI of the urinary tract The kidneys in the human body are located in the urinary tract system and any problems with this system should be identified as early as possible; for this purpose MRI of the kidneys and urinary tract is often used. Using MRI of the urinary system, the doctor can establish an accurate diagnosis of the urinary tract in the early stages of the disease and apply the correct therapy much earlier, which will have a positive impact on the patient’s condition. And given that the MRI method of the kidneys is practically harmless to the patient, it is prescribed quite often.
X-ray or MRI, which is better?
MRI and X-ray of the kidneys rely on different technological processes and have different diagnostic capabilities. Their comparison will be correct if the following indicators are taken into account:
Imaging technology.
MRI is a magnetic resonance imaging study that relies on the ability of hydrogen atoms to vibrate at different frequencies, depending on the tissue structure. X-ray is a radiation diagnostics based on the ability of ionizing radiation to penetrate organic tissues of different densities, leaving a mark on the film.
Device capabilities.
MRI visualizes soft tissues best, so for examining the kidneys, the procedure is more informative than x-rays, which display dense bone structures. In some clinics, the material and technical base allows only plain radiography of the kidneys. This method involves the use of x-ray contrast solutions.
Image quality.
X-ray images have poor resolution and allow the recognition of progressive kidney pathologies. The high resolution of magnetic resonance imaging projections makes it possible to examine the early stages of the formation of pathologies, including oncological ones.
| X-ray | Kidney MRI |
Availability and cost of research.
A plain radiography of the kidneys can be performed in a city clinic. The compulsory medical insurance policy provides patients with the opportunity to undergo examinations free of charge. You can get a kidney MRI for free only in large inpatient departments. On an outpatient basis, the procedure is carried out for a fee in specialized commercial MRI centers or regional medical institutions. And the prices for it exceed the cost of an x-ray on average up to 3 times.
Safety.
MRI can be performed as many times as necessary for high-quality monitoring of pathology. Radiography was limited to 1-2 procedures per year due to the danger of ionizing radiation.
Alternatives
As an alternative, other methods of examining a person can be considered, which have their own pros and cons. Such methods could be:
A CT scan of the kidneys is, in general, very similar to an MRI procedure, but cannot be used for patients who suffer from diabetes and have high blood sugar levels at the time of examination. Ultrasound – used if the patient cannot undergo an MRI for some reason. It is worth noting that the device is available in many clinics, but this method has lower information content than MRI of the kidneys. Therefore, sometimes it is better not to be lazy and find a clinic offering MRI services. Doppler is based on the method of receiving data from the radiation of an ultrasound pulse into the body and receiving a response in the form of an echo frequency, which is called Doppler. The method is also not reliable due to receiving data from a certain frequency.
Basically, alternative examination options are resorted to when there are serious reasons not to use MRI.
Ultrasound or MRI, which is better?
Ultrasound examination is the first-line diagnostic method. It does not always detect kidney disease at an early stage, unlike more sensitive MRI scanners. These studies are based on various technological processes that endow them with personal characteristics, positive properties and disadvantages:
Method of obtaining information.
Ultrasound visualizes internal structures by analyzing reflected ultrasound waves. The tomograph forms a projection based on processing signals from the vibrational movements of hydrogen atoms.
Device capabilities.
A magnetic resonance imaging scanner visualizes the structure of the kidney not only from the outside, but also from the inside, revealing a wide variety of disorders at the stage of formation. An ultrasound machine can detect the presence of nephrolithiasis, but is not able to identify the process of formation of a neoplasm.
Duration of the procedure.
An ultrasound takes no more than 5 minutes, while an MRI scans an organ in about 30 minutes. It is better to examine mobile children using the ultrasound method. It is safe and does not require anesthesia.
Security and restrictions
. The absence of contraindications allows ultrasound examinations to be performed to monitor pathological conditions an unlimited number of times and for any category of patients. MRI is not safe for people with metal devices and life support devices (pacemaker, insulin pump).
Availability and cost.
A patient can undergo ultrasound diagnostics at a clinic in his area. The compulsory medical insurance program provides free research. The social quota also allows MRI examinations free of charge, but the number of referrals is very limited. Patients of regional inpatient departments undergo magnetic resonance imaging free of charge. In an outpatient setting, MRI is a paid examination, and to undergo it you must receive a referral to a large diagnostic center or visit a commercial clinic. If you study the price list for paid medical services, the cost of ultrasound will be an order of magnitude lower than that of tomography.
| Ultrasound | Kidney MRI |
What is magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging is a unique diagnostic study that allows the doctor to obtain high-quality layer-by-layer images of any place in the human body. The MRI method is quite complicated. It is based on the ability of the nuclei of hydrogen atoms contained in all living tissues to generate electromagnetic signals after exposure to radio waves and a magnetic field. They differ in healthy and diseased cells, thanks to which an MRI machine can accurately “examine” internal organs and identify pathologies in them.
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is another name for the MRI method.
An MRI image of the kidneys is similar to that obtained with a CT scan, but differs from it in greater contrast
Operating principle of a magnetic resonance imaging scanner:
- A magnet of a certain strength arranges the hydrogen atoms in the organ that needs to be examined.
- A radio wave pulse passes through a magnetized network of these particles.
- Excited hydrogen atoms line up along the axis of the magnetic field and produce an electrical signal.
- The latter is caught by a ring-shaped receiver.
- As the hydrogen atoms return to equilibrium, the signal decay is continuously recorded.
- The electromagnetic response is converted using equipment into digital values, which are then displayed on the tomograph display in the form of an image of the organs being examined.
The return to a state of equilibrium is called magnetic relaxation and is a characteristic of any type of living tissue. In an MRI examination, the duration of relaxation periods affects the image contrast and the intensity of the electromagnetic signal. The latter is an energy emission that depends on the number of hydrogen atoms. It is different for each type of fabric.
The human body is 70% water. Therefore, hydrogen atoms are present in varying quantities in all organs.
The design of modern tomographs allows you to change the strength of the magnetic field affecting human organs and tissues. MRI of the kidneys alternately uses high, medium and low fields.
Tesla (T) is a unit of magnetic field induction.
Combining information from images obtained with weak, medium and strong magnets results in a clear picture of the kidney structures. In terms of reliability and accuracy, MRI is far superior to other diagnostic methods, such as CT or ultrasound.
The tomograph is a hollow cylinder with a retractable table on which the patient is located
Table: Types of Magnetic Field Created by a Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanner
| A magnetic field | Field induction, T |
| Super weak | 0,01–0,1 |
| Weak | 0,1–0,5 |
| Average | 0,5–1,0 |
| Strong | 1,0–2,0 |
| Super strong | 2,0 |
Video: what is MRI
To kid
Kidney MRI has no age restrictions. The procedure can be performed on children from the first days of life.
Magnetic resonance imaging is performed on children under anesthesia so that physical activity does not affect the quality of the images. Most commercial clinics do not have permission to perform diagnostics using anesthesia. Such medical institutions accept children from the age of seven.
The difficulty of performing an MRI on a child is that he is frightened by the unpleasant sounds inside the tomograph, and the limited space of the scanning capsule provokes panic and a high level of anxiety. In this case, it will be better to undergo examination using an open-type device. Parents can be present nearby and reassure the child.
The presence of implanted electronic devices prohibits magnetic resonance imaging; there are no other contraindications to MRI for children.
Photo
| Healthy kidneys on MRI |
| Kidney hematoma |
| Kidney cyst |
| Cystic kidney cancer |
| Kidney cancer |
Price
On our website, many clinics list prices for MRI, including MRI of the kidneys.
To see prices, you need to go to the list of clinics in your city. To do this, select your city on the “Addresses” page.
On the page for the list of city clinics, in the form for selecting a clinic based on parameters, in the “Research area” field, select “Kidney MRI”.
The list will be filtered and the clinics will be sorted by increasing price, which will allow you to find out where to get a kidney MRI cheaper.
| List of clinics filtered by MRI of the brain using the example of the city of Moscow |
If prices are not indicated on the website, then you need to call all the clinics and find the best price for you yourself.
When talking with the operator, be sure to ask if there are any promotions or discounts. For example, some 24-hour clinics offer discounts on MRIs at night.
You can get an MRI with compulsory medical insurance or VHI insurance. To do this, you need to find out which clinic does MRI under insurance, using the information on the website or calling the clinics yourself if there is no information on the website. In the form for selecting a clinic by parameters, there is a field “MRI under insurance”. Next, you need to find out the list of documents that the clinic operator will tell you, collect them and you will be able to undergo an MRI with insurance, which will allow you to save a lot.
How is an MRI performed on children?
This type of research is contraindicated for school-age children. After all, it’s quite difficult for kids to sit in one place. But during the procedure it is strictly forbidden to move.
For certain indications, MRI can also be performed on children.
But if the child can boast of perseverance and is not afraid of confined spaces, the doctor may well prescribe a referral for an MRI. In this case, the procedure will be similar to that described above. There will be no differences in the process itself.
Reviews
On our website, people leave reviews for clinics about their MRI experience.
To read patient reviews, you need to go to the list of clinics in your city. To do this, select your city on the “Addresses” page.
The list in the block of each clinic will show a button to go to the list of reviews, if there are reviews, or a button to go to write a review, if there are no reviews yet.
| This is what review buttons look like, using the example of the city of Moscow |
You can also leave a review about your MRI experience so that other people can choose the most suitable clinic.
To leave a review, you need to click the “Your review” button and you will be taken to the review writing form. Or if there are already reviews, then you need to go to the end of the list of reviews and there will be a form for writing a review.
To open the review writing form, click the “Leave a review” button.
Fill out the form and send it for moderation.