An unpleasant odor emanating from urine is not the main sign of the disease, however, it is what people most often pay attention to when cystitis has reached the chronic stage. Many patients note that the fumes emanating from the liquid resemble ammonia. Such changes are caused by the presence of ketone bodies in the biological fluid, which contain acetone and bilirubin.
In cases where the pathology is progressive or the patient does not receive proper treatment, a putrid odor may appear. It is provoked by the presence of pathogenic microorganisms and their waste products in the urine.
Causes leading to problems
The basic rule that must be followed, regardless of the pathological or non-pathological cause, is to contact a specialist if there is a prolonged presence of an altered odor, since timely diagnosis followed by therapeutic intervention in many cases helps to avoid dangerous complications. Often the causes of a strong smell of urine in women are diseases of the urinary system.
When an unpleasant smell of urine appears in women, one can suspect the presence of a number of diseases in the body:
Women who are not too picky when choosing sexual partners may complain about an unpleasant aroma - in this case, the cause is often infections transmitted through sexual contact. Taking into account the fact that the reproductive system is anatomically located very close to the urinary system, a change in the properties of urine is observed. The most common pathologies that change the odor of urine include:
In women, the occurrence of a strong odor of urine is a frequent accompaniment of other unpleasant phenomena:
- Changes in the properties of urine are observed against the background of intoxication of organs by parasites - their influence is diagnosed in seven out of ten people in accordance with statistical data.
- If the liquid has an unpleasant aroma combined with a dark color, you can suspect an increase in the amount of bilirubin, which indicates problems with the liver.
- When dehydrated, the state of urine also changes. The reason sometimes lies in an incorrectly selected or constantly disrupted drinking regime, the use of certain pharmaceuticals, increased blood loss, diarrhea and other factors. Excessive dieting can have a similar effect.
- Changes are also possible with diabetes; an unnatural aroma of urine indicates hyperglycemia; the next stage may be the development of a diabetic coma. An accompanying symptom is drying out of the oral mucosa, a feeling of thirst, and weight changes.
- Failures in metabolic processes can also change the state of urine.
However, a change in the characteristics of the contents of the bladder does not always indicate the presence of pathologies; sometimes the symptom in question develops against the background of hormonal changes due to bearing a baby. Moreover, the problem usually occurs in the 2nd half of pregnancy. The smell will become more unpleasant if you hold back the urge to visit the toilet for a long time - the liquid in the bladder becomes more saturated, literally “infused” and turns into a concentrate.
Nutrition can also change the contents of the bladder for the worse; spicy, excessively fatty foods, pickles, garlic and carbonated drinks, asparagus can negatively affect the fluid. Antimicrobial drugs and B-group vitamins can also have a negative effect. An extraneous aroma can also appear with active consumption of drinks with added alcohol, especially beer.
When the sense of smell gives a distress signal
When urine has a strong, unpleasant odor, you should be wary, and if this phenomenon persists, the best solution is to contact a specialist. It is also worth mentioning the differences in olfactory sensations - a disgusting-smelling liquid, depending on the predominance of one or another shade, may indicate very specific pathological processes in the body. Let's look at what a certain smell can tell you:
- If the urine stinks of acetone, you can suspect the presence of stomach cancer, diabetes mellitus, an incorrectly composed menu in which proteins and fats predominate, chronically elevated temperature, exhaustion of the body due to diets, fasting, and excessive physical stress. Interestingly, acetone in small quantities is constantly excreted by the kidneys from the body as part of urine, but if the aroma becomes strong, we can talk about a pathological excess of the permissible limit.
- Another constant component of urine is ammonia. However, if its odor increases, it is necessary to consider possible influencing factors. We can talk about the use of medications containing iron and calcium, abuse of proteins, less often, ammonia stench accompanies inflammatory processes occurring with cystitis or pyelonephritis. Ammonia can form due to stagnation of urine, dehydration, and liver pathologies.
- The pungent odor of urine may be sour, reminiscent of spoiled milk or sauerkraut. In this case, fungal infections of the genitourinary system are first suspected - usually candidal urethritis or vaginal pathology. Additionally, there is turbidity in the urine, itching, white discharge that resembles flakes or a suspension and appears in the genital area, a whitish coating on the vaginal mucosa and on the labia. A sourish tint also indicates problems in the functioning of the organs of the digestive system - this could be intestinal dysbiosis, high levels of acidity of gastric juice and other painful conditions. Taking certain medications - usually antimicrobial agents - also provokes the appearance of sourness, since taking such drugs upsets the balance of microflora.
- In fairly rare cases, the fluid from the bladder itself smells like spoiled fish, but vaginal discharge can get into it after sexually transmitted infections enter the body, hence a similar effect. Thus, the venereal pathology of trichomoniasis causes damage to both the genital organs and the urethra, and the causative agents of the pathology, actively multiplying, secrete a yellowish leucorrhoea that specifically smells like fish.
These are the most common changes, but there are many other pathologies. For example, phenylketonuria, which refers to a hereditary failure of protein metabolism, “smells” like mold. The rare disease trimethylaminuria is accompanied by the stench of rotten fish, and not only urine smells like that, but the whole body.
An aroma of maple syrup or burnt sugar may occur, which indicates the presence of leucinosis. This hereditary disease is characterized by disturbances in the production of enzymes that break down certain amino acids. As a result, the latter begin to accumulate in the tissues, causing intoxication of the body. Symptoms of the pathology also include vomiting, seizures and problems with coordination of movements.
In case of infection of the urinary system or genital organs with E. coli, the urine smells like rotten eggs, the same phenomenon accompanies the formation of pyelonephritis or rectal cancer. If a similar symptom occurs in girls, the development of infectious processes occurring in the kidneys and bladder can be suspected.
Do men suffer from cystitis discharge?
You can determine the onset of cystitis in yourself by characteristic signs:
- change in urine color or cloudiness;
- the appearance of discomfort and pain when going to the toilet;
- signs of intoxication of the body (weakness, fever, pain);
- urge to urinate frequently;
- deterioration in performance;
- sleep disorders.
Due to cystitis, the quality of life deteriorates, psychological disorders and neuroses appear. Patients have to give up all their usual activities; due to frequent urges to go to the toilet, they stay at home. All of these symptoms characterize the acute stage, when cystitis may cause discharge of different smells and colors. They require separate treatment when the cause is a disease of the genital tract.
A woman suffering from cystitis may experience a small amount of clear or whitish discharge from the urethra. They have a mucous consistency, do not have a specific odor and are explained by damage to the urinary canal - urethritis.
With this inflammation, blood is detected in urine tests, so its inclusions can be found in traces on underwear or a pad.
If there is vaginal discharge during cystitis, this indicates a pathology of the genital organs, which has caused inflammation of the bladder.
Examples could be:
- Purulent, unpleasant-smelling discharge due to lesions of Trichomonas, Chlamydia, Treponema pallidum.
- A pink or brown tint indicates ulcerative processes in the lower urinary tract.
- The yellow, greenish color of a moderate amount of discharge with an unpleasant odor characterizes trichomoniasis.
- White, scanty or copious discharge that may smell like fish indicates a fungal infection, bacterial vaginosis, or mycotic cystitis.
The bloody nature of the discharge accompanies purulent cystitis. This pathology is caused by infection with E. coli, which enters the urethra due to poor hygiene.
Streptococcal infection also leaves a bloody trail. It affects women and men suffering from blood diseases.
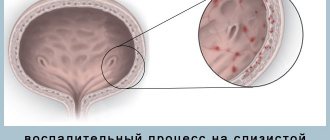
The mucous surface is so called because the lining layer of the epidermis is capable of producing a thick viscous secretion. This mucus is needed in order to envelop and remove dangerous substances, bacteria, allergens, etc. from the organ. With the development of inflammation, this secretion begins to be produced in large quantities in order to remove from the bladder not only the pathogens themselves, but also the products of their vital activity, the results of the body’s fight against them.
Inflammation of the bladder can be both a consequence of problems of the genital organs and their cause. That is, pathogens of vaginosis, thrush, colpitis, and STDs can enter the urethra and penetrate the bladder cavity along the ascending path. And at the same time, pathogenic bacteria, viruses, and allergens from the urethra can enter the vagina and cause inflammation in the genital tract.
In the presence of other symptoms of cystitis, such as pain, frequent urges, general malaise, a woman may not pay due attention to the presence and nature of the discharge. It is even more difficult to understand where exactly they come from. However, it is worth being careful, since the secretion can vary in color, consistency, smell, and each variety signals a particular inflammatory agent.
From the urethra
It is logical to assume that most of the secretions leave the bladder during urination and noticing them, much less assessing the consistency and color, is an almost impossible task. All that remains is to record the presence of suspensions in the urine, changes in its color and odor. However, a small amount of secretion is released from the urethra in the intervals between trips to the toilet, and then characteristic marks remain on the underwear, as well as immediately after the end of the emptying process.
So, what are urethral discharge and what does it mean:
- Abundant transparent mucous. A small amount of colorless mucus is normal. If it is present in large quantities, this indicates irritation of the inner layer of the bladder and urethra, and incipient inflammation.
- White thick. Secretion that resembles cottage cheese in consistency and color indicates the proliferation of a fungal infection.
- Yellow or green. A change in the color of the discharge towards yellow or green indicates the presence of pus, and, accordingly, a strong inflammatory process.
- Bloody. Red or brown discharge with cystitis occurs when the capillaries of the mucous layer are damaged. Usually, in this case, the urine also changes color, acquiring different shades of red or brown. The reason for this may be ulcerative, necrotic processes in the bladder, as well as the appearance of cracks in the epidermis due to severe inflammation.
From the vagina
Due to the very close location of the urinary canal and genital organs, cystitis is often accompanied by vaginal discharge. They remain in sufficient quantities on underwear and for an attentive woman it will not be difficult to determine their consistency, color and smell.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2_CgHO6rbPo
Vaginal discharge may be:
- white curdled ones. This secretion has a sour odor and indicates the development of a fungal infection. The most common pathogens are fungi of the genus Candida;
- red or brown. A change in the color of leucorrhoea occurs as a result of blood entering it from the cervix, uterus, ovaries, or when the inner layer of the vagina is damaged. The cause may be the development of a severe inflammatory process with deep damage to the tissues of the genital organs;
- yellow-green. The coloring of leucorrhoea in various shades of yellow and green indicates the presence of sexually transmitted infections: trichomonas, chlamydia, and other STDs. Itching and burning appear in the labia and vagina;
- white or grayish with a fishy smell. This secretion occurs as a result of vaginosis, that is, an imbalance of microflora in the vagina;
- purulent. Leucorrhoea containing pus, causing severe itching, and having an unpleasant putrid odor is a symptom of bacterial colpitis.
Women suffer from inflammatory processes in the bladder very often. This is facilitated by the structural features of the body: a wide but short urethra, located in close proximity to the vagina, serves as a convenient “bridge” for pathogenic microorganisms.
Hypothermia greatly weakens the female body and thereby contributes to cystitis: sometimes it is enough to sit on a bench for a few minutes in winter to get the entire symptomatic “bouquet” of the disease. It should be understood that discharge is not considered a typical sign of cystitis, and usually it indicates concomitant ailments. Often, inflammation of the bladder “neighbors” with urethritis and pathologies of the genital organs.
| Nature of the discharge | What does discharge indicate? |
| Discharge from the urethra | |
| Transparent slime | It is considered a variant of the norm. Sometimes it turns out to be a symptom of slight inflammation in the urethra. |
| Pus | The inflammatory process affected the bladder and urethra. The pathology is clearly expressed. |
| Brown discharge | Damage to the capillaries, which often accompanies severe damage to the mucous membranes or ulcerative process in the lower urinary tract. |
| White discharge | Fungal infection of the skin of the urethra, candidal cystitis. |
| Vaginal discharge | |
| Light slime | In the absence of any discomfort - the norm. |
| Yellow-green pus | Sexual infections. If there is additionally a strong burning or itching, then colpitis (inflammation of the vagina) is possible. |
| Brown discharge | Damage to the uterus (inflammation, erosion). Problems with the ovaries, as a result of which the balance of female hormones in the body is disrupted. |
Female cystitis is almost always associated with vaginal discbacteriosis, thrush or colpitis. Therefore, the doctor must prescribe treatment that is effective against concomitant diseases: if these ailments remain “in force,” then inflammation of the bladder will constantly worsen. With good urine tests and the presence of discharge, it makes sense to suspect the presence of tumors in the ovaries or uterus: an increase in these organs provokes inflammation process in the bladder.
The smell of discharge can tell a lot about the state of the body, because it clearly characterizes the presence of certain bacteria and ongoing processes.
A woman should know that:
- discharge with a slight fishy “aroma” is a direct symptom of gardnerellosis (also called bacterial vaginosis, or vaginal dysbiosis). Gardnerella itself is considered conditionally pathogenic and is present in almost every female body. But if there is a hormonal imbalance or an imbalance in the acid-base balance in the vagina, a pathological process starts;
- a sourish odor indicates the presence of fungus. Vaginal candidiasis often occurs as a result of the use of certain medications: for example, if a woman tried to treat cystitis on her own and received the wrong antibiotic therapy. Increased acidity of the vaginal environment also contributes to the development of fungal infections;
- a frankly unpleasant, fetid odor of discharge accompanies the purulent process occurring in the body. Almost always the cause of such a pathology is sexually transmitted infections.
Since seeing a doctor is mandatory, the patient needs to remember (or write down) some parameters of the discharge - based on this information, the specialist will be able to prescribe the most appropriate tests and make an accurate diagnosis. Important features of the discharge include:
- Volume. Depending on the nature of the pathological process, discharge can be scanty, moderate or abundant.
- Consistency. This information often helps determine the type of disease. For example, with thrush there is usually a cheesy discharge.
- Duration and frequency. How often does discharge occur? Are they typical in the morning or are they observed throughout the day? Does it happen that a symptom disappears for a few days and then returns again?
Other reasons for changes in the properties of urine
Quite often, changes in the properties of urine do not occur as a result of the development of diseases. For example, the liquid may smell like garlic, sulfur, or ampicillin due to the consumption of certain foods or the use of antimicrobials. Regular cabbage, due to the sulfur compounds it contains, can enhance or worsen already unpleasant aromas. Seasonings, especially garlic and curry, cardamom or cumin, can also change the properties of the contents of the bladder.
Changes also appear when a woman is carrying a child. However, the reasons may be factors that existed before pregnancy. During this period, it is very important to carefully monitor any unusual nuances. For example, it is considered most dangerous for pregnant women when the liquid has a sweet aroma, a hint of rotting apple or acetone. Such symptoms may indicate the development of diabetes mellitus in pregnant women, the occurrence of eclampsia or nephropathy.
It has been noticed that during the process of bearing a child, inflammatory processes most often occur in the bladder or kidneys, resulting in the appearance of fluid with a purulent or sour spirit. In the third trimester, it is possible that the ureter may be compressed by the enlarged uterus, which causes stagnation of the contents and increases the ammonia smell. Another reason why a pregnant woman’s own urine may not smell very pleasant is the increased blood supply to the mucous layers of the body, including the nasal membranes. As a result, even the most ordinary urine and natural discharge can seem foul.
Quite often, discomfort is caused by poor hygiene, partial urinary incontinence, cystitis and other reasons.
How to get rid of pathology
Having determined why the urine began to smell atypical, they move on to eliminating the influencing factors or begin treatment to get rid of the disease accompanied by this unpleasant phenomenon. The main proposals for eliminating the pathological phenomenon include:
- Visit a specialist if you have persistent symptoms that do not disappear even after eliminating all possible influencing factors. The doctor will determine the necessary examination and develop subsequent treatment.
- At home, you can use decoctions of knotweed, cranberry or lingonberry - they are recommended to be consumed instead of tea.
- A review of the diet will be required, eliminating foods that provoke an unpleasant phenomenon.
- It is necessary to adhere to the correct drinking regime, consuming at least two liters of purified liquid during the day.
- Control over intimate hygiene should be tightened, given the proximity of the anus to the vagina. Ideally, washing is carried out after each bowel movement, which avoids the penetration of pathogenic microflora into the urethra.
Treatment using pharmaceuticals becomes possible only after an accurate determination of the disease causing the phenomenon in question. If the problem is in the kidneys, diuretics are required. Kidney failure may require hospitalization. In case of infection of the genitourinary system, treatment should be comprehensive with the use of antifungal agents and antibiotics. Most often, therapy is carried out against the background of a diet in which it is necessary to limit the consumption of flour, fatty and sweet foods, focusing on fresh fruits and vegetables.
You should remember that self-medication is inadmissible, which will avoid unnecessary complications.
venerbol.ru
Treatment of the disease
Based on a number of reasons why cystitis occurs, there are various courses of treatment that have a specific effect on the source of inflammation. That is why treatment in any case should take place according to the recommendations and under the supervision of a doctor, in a hospital setting. Do not neglect your health and self-medicate.
Taking medications
Complex therapeutic measures to eliminate cystitis consist of taking tablets and solutions. These can be antibiotics of various effects, drugs that have an antiviral threshold and improve the body's immune system, anti-inflammatory drugs.
At the same time, treatment of vaginal discharge occurs. The prescription of drugs is carried out taking into account the pathogen. Antibiotics are prescribed to patients in the presence of discharge that occurs due to sexually transmitted infections. They are also prescribed if the causative agent is a fungus, for example, Candida. In these cases, the use of various antifungal agents is indicated.
Restoration of the natural microflora of the vagina
To restore the microflora, doctors collect smears. This makes it possible to determine the number of bacteria and fungi, as well as their exact types. After collecting data, a course of treatment is prescribed.
The first thing to start with is getting rid of bacteria. To eliminate all pathogenic flora, the doctor prescribes suppositories or special tampons. Antifungal drugs are rarely prescribed as an adjunct to treatment.
After the bacteria from the vagina are eliminated, it should be equipped with lactobacilli, which can restore the microflora. This stage is controlled by a gynecologist based on test results.
Physiotherapy
To improve the patient’s condition (reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process and eliminate pain), the doctor additionally prescribes physiotherapy, or, in other words, a physiotherapy procedure. It is carried out using ultrasound, electricity or magnetic radiation. Each of these methods is selected individually.
Physiotherapy procedures are carried out in this way: electrodes are fixed above the pubic part, through which a weak electric current is passed. Thus, the effect of the current is on the muscles of the bladder, which contract, eliminating painful sensations. To completely improve the patient’s condition, it is recommended to complete the full course of treatment.
Why does the smell of urine change?
Inflammation is caused by more than ten different causes. In case of infectious infection, E. coli, staphylococci and streptococci can provoke an exacerbation of the condition. The waste products of pathogens get inside. Bacteria and germs decompose in urine. All of the above leads to a change in the smell of urine due to inflammation of the bladder.
It is worth noting that a strong aroma does not always indicate an infection. A fishy smell may indicate a malignant tumor developing in the genitourinary system. It is important to conduct clinical studies to determine the cause of the deviations.
Unpleasant odor of urine during cystitis is also caused by:
- bilirubins;
- urobilinogens;
- red and white blood cells.
Normally, all these components should not be present. Urine is sterile. Foreign cells enter urine only as a result of pathologies and injuries caused by inflammatory processes and malfunctions of the kidneys. An unpleasant, pungent odor of urine after cystitis can be caused by antibiotics that affect the chemical composition of waste fluids. It is imperative to carry out differential diagnosis in order to establish what exactly caused the changes.
What does urine smell like with cystitis?
One of the characteristic signs of inflammation of the bladder is a sharp change in the chemical composition of the fluid secreted by the body. Urine usually smells like ammonia or ammonia. The stronger the intensity of the aroma, the more advanced and acute the form of cystitis. Acetone in the urine indicates that the liquid contains a large number of pathogenic microorganisms.
Clinical studies will show changes in urine to the acidic or alkaline side, which creates an optimal environment for the growth of bacteria. The unpleasant, sharp ammonia smell of urine is precisely evidence of such transformations.
Types of discharge
Based on the color of the discharge, doctors determine the degree of influence of cystitis on certain organs:
- Vaginal discharge with cystitis, which has not changed much and still retains the consistency of mucus, is transparent or white in color with a slightly specific fishy odor, in which case the microflora is not significantly disturbed. To avoid additional problems after this, you should take care of personal hygiene of intimate organs. Change tampons and pads (daily and regular) more often.
- Discharges that are yellowish or greenish in color indicate that the microflora has already become infected and has made significant changes.
- The worst signs in this case will be a brown or bloody discharge (sometimes red or pink). Such discharge occurs when the cervix is damaged and there is a significant imbalance of hormones in the woman’s body.
Causes of urine color change
During inflammation, the color of the discharge fluid changes along with the odor. The color of urine with cystitis should be brown, red, greenish and yellow. At the same time, the density of urine increases.
The cause of metamorphosis is the processes in which the genitourinary system is involved. You should only worry in cases where the color of the fluid is persistent and is accompanied by high temperature (above low-grade fever), pain, and a feeling of incomplete evacuation after going to the toilet.
What color is urine with cystitis?
During a clinical examination, the first step is to visually inspect the fluid sample. A change in the shade of urine indicates possible complications of inflammation:
- Urine is reddish in color - ranges from pink to burgundy. Cause: damage to the epithelium and mucous membrane of the bladder due to inflammation. Red coloration of urine may indicate internal bleeding or the development of microhematuria. Less commonly, the symptom is caused by taking antibiotics and certain medications. Burgundy color is observed during etiotropic therapy using uroantiseptics.
- The greenish color of urine indicates that purulent inflammation has begun. An infection in the genitourinary system causes the body to send a large number of leukocytes to the affected area. By absorbing cystitis pathogens, blood cells die and decompose, which leads to the formation of purulent discharge.
- Bright yellow color - appears during the period of antibacterial therapy. The reason for the changes is taking medications. Yellow colored urine is considered normal and is not a cause for concern. After stopping the course of antibiotics, the color of the discharge fluid becomes the same.
The attending physician should explain to the patient that urine may be bright orange due to the effect of medications on the chemical composition and acidity of the liquid. This way you can avoid excessive worrying of the patient when he detects stained urine.
Causes of discharge
Often complicated cystitis in women is accompanied by a change in the nature of the discharge (consistency, color, smell), which occurs due to the fault of the same pathogenic bacteria. The causes affecting discharge can be both pathogens of genitourinary system infections and other microorganisms that are not directly related to cystitis (for example, E. coli). Diseases distant from the genitourinary system, such as tuberculosis or measles, or pathologies of the endocrine system, have a special impact on the occurrence of the disease.
No less important reasons include disorders in the tissues of the urinary system and reproductive organs, taking aggressive medications that directly affect the mucous membrane, and even pregnancy. Complications that arose after chemotherapy should not be excluded.
What causes urine to be cloudy and flaky in cystitis?
In addition to the effect of inflammation on color and odor, metamorphoses occur in urine associated with an increase in density and the appearance of foreign bodies, observed during visual inspection of the liquid. You should be wary and immediately consult a doctor if you detect any foreign inclusions.
Cloudy urine with white flakes indicates that cystitis is caused by an infection. This is an alarming symptom. If timely treatment is not prescribed, the inflammation will go up to the kidneys and cause pyelonephritis. Sediment in the urine with flakes is the result of mucus and bacteria entering the urethral canal. The sign may indicate infection with a sexually transmitted infection.
Cloudy urine with cystitis is the result of protein compounds entering the urethra. Due to inflammation, the renal pelvis and canal walls are damaged. Tissue particles enter the outgoing liquid. If antibacterial therapy is prescribed, flakes in the urine disappear within 3-4 days.
The attending physician will pay attention not only to the density of the liquid and the presence of foreign bodies in it, but also to other characteristics:
- Cloudy urine at the end of urination most often indicates acute inflammation of the bladder caused by an STI. The symptom does not appear every time you go to the toilet. Flakes and cloudiness occur every now and then. The frequency of precipitation depends on the stage of the inflammatory process.
- Cloudy urine at the beginning of urination indicates that the inflammation has spread to the urethral canal. Occurs in chronic cystitis. The symptom manifests itself with scanty urine discharge caused by pathological processes that have spread to the neck of the bladder. The appearance of mucus occurs with complications of inflammation: urethritis (severe irritation and injury to the urethra), prostatitis, pyelonephritis.
Changes in the chemical composition of urine, manifested in a pungent odor, transformation of density and color, should not be ignored. Only a urologist, after receiving the results of clinical tests and examining the patient, will be able to make an accurate diagnosis. If a woman gets cystitis, she often requires a consultation with a gynecologist.
Bladder inflammation does not go away on its own. Without the necessary treatment, the disease becomes chronic and leads to serious complications.
ponchikov.net
Urine smells like fish - what should I do?
Normally, urine emits a characteristic odor, but without a specific specific shade.
If your urine smells like fish and this smell persists for a long time, then this is a serious reason to contact a medical specialist.
Causes of unpleasant odor
The reasons for the appearance of foreign odor in urine are different and do not always come down to pathological processes, so it is important to determine it before treatment.
Not pathological
A healthy person may experience the problem of a fishy odor after eating food shortly before going to the toilet. Products that can create odors include:
- peppered dishes;
- eating asparagus;
- over-salted foods.
In both men and women, this problem is eliminated after giving up such food after about two days.
Sometimes, to maintain the body, people take B vitamins. They can cause a foul odor, so you should tell your doctor if you are taking such vitamins. Antibiotics also contribute to the appearance of odor.
The smell goes away after stopping the use of the drugs.
In women, the smell of fish occurs after eating protein foods in large quantities. Women often notice the smell of fish with reduced immunity, especially after illness.
During pregnancy, a smell may appear and indicate hormonal changes in the body.
In men, the smell appears after therapeutic fasting and eating fresh herbs.
A child’s urine smells like fish due to sexually transmitted infections transmitted through household contact or from a sick mother.
Dehydration can lead to a concentration of chemical elements in the urine and, as a result, an unpleasant odor in men and women.
If a man is struggling with the problem of prostatitis, then the smell of fish is characteristic of the disease, but in any case it is necessary to consult a urologist. If a man plays sports and experiences frequent physical activity, the smell of urine may change because there is not enough water in the body.
If, after stopping physical activity, medications and products that provoke the smell of fish, the urine still smells foul, then you should not delay visiting a specialist.
What affects the smell of urine?
Normally, only those products that are broken down in the human body. By the way, even completely healthy people’s urine smells completely different, and this is also due to their diet. Also, the smell of urine is influenced by those microorganisms with which this secreted substrate came into contact in the body. After all, urine accumulates in the bladder, but during a full cycle it also comes into contact with the membrane of the kidneys and urethra. Going through such a complex path, the liquid accumulates those substances that settle on the walls, and it is they that can affect the change in “aroma”.
Urine changes its smell very strongly even when taking medications. A huge part of them is processed by the kidneys and excreted through the urination organs. Perhaps all people have noticed this fact. Various medications add their own scents to the already familiar smell of urine.
Finally, the liquid excreted by a person with decay products has a particularly strong odor in the morning, and during the day these “aromas” are somewhat muted. This is due to the fact that during the night hours a person normally does not visit the bathroom, but “saves” everything until the morning. The longer urine stays in the genitourinary organs, the more “flavors” it will collect from the inside. By the way, this also applies to the color attribute. It is almost impossible to achieve the same high color urine as in the morning during the day.
What is urine
Urine is a light-straw-colored liquid that is released by the body through the urinary system.
Excretion occurs at a microscopic level within the kidneys. There are microstructures there that filter the blood.
During the filtration process, liquid, metabolic products and some electrolytes are removed.
Acidic and alkaline electrolytes are removed in equal amounts, which ensures constant neutral acidity. These electrolytes form the specific gravity of urine, which is normally 1.015 - 1.025.
From the kidneys, urine passes through the ureters into the bladder - a reservoir for accumulation. Then, through the urethra it is removed from the body.
The composition contains cylinders, leukocytes, and erythrocytes. The presence of leukocytes provides protection against bacteria, and red blood cells enter there during the filtration process, since the permeability of the renal capillaries is high.
Casts are exfoliated epithelial cells. Separation is considered a normal process, since the mucous membrane is constantly regenerating.
What does urine smell like with cystitis?
Most often, this smell reminds patients of ammonia. The fumes that come from the emitted liquid have a very pungent and unpleasant odor, which often makes people wince. If a significant portion of pathogenic bacteria and their secretions enter the urine, it acquires an unpleasant odor of pus. Such cases concern only fairly advanced situations, when the patient’s cystitis is usually already identified.
What influences such changes? It is known that with cystitis, the acidity of urine increases greatly, and it is this factor that is largely responsible for the change in odor. Ketone bodies can be found in urine, and their basis is acetone and bilirubin. These components have a pungent odor that cannot be confused with anything else.
When the permeability of the walls of the bladder and urethra increases, protein is found in the urine, which also has a strong odor. Finally, when analyzing urine in a patient with cystitis, an increase in components such as nitrites, salts of nitrous acid, can be detected. These breakdown products smell bad and significantly affect the overall odor that a patient with cystitis feels in the toilet.
Cystitis affects the composition of urine
Human urine is often the determining factor in making a diagnosis.
It contains elements that must correspond to proportions: their violation becomes a sign of the development of pathology. When analyzing urine, it is important to quantify each change: this allows the doctor to more accurately diagnose the disease. For example, a significantly elevated protein level most likely indicates pyelonephritis. In the case of cystitis, this element goes beyond the normal range, but not much.
The qualitative characteristics of urine are also of great importance in determining the disease. In other words, the appearance of this biological fluid can tell a lot.
Color is important
A healthy person's urine is clear and straw-colored. Pathological changes in it are visible to the naked eye. Upon examination, it is noticeable that urine differs from the normal state, first of all:
- becomes opaque and becomes cloudy;
- may be white or brown, sometimes reddish in color - depends on the presence of blood in the urine;
- there are traces of pus (this indicates an advanced inflammatory process);
- there are flakes;
- mucus is present.
The provocateurs of changes that occur in biological fluid are bacteria and their metabolites. It is pathogenic microorganisms that cause the inflammatory process. Its progress, in turn, leads to the appearance of blood in the urine, desquamation of the epithelium in the bladder, and pus. With hemorrhagic cystitis, urine completely takes on the appearance of “meat slop”.
If qualitative changes can be detected at the first examination of the liquid, then the situation with quantitative and structural characteristics becomes clear only within the framework of laboratory studies.
Complications of cystitis that increase the unpleasant odor of urine
Here it is customary to divide the reasons by gender. Thus, with cystitis, the unpleasant odor of urine in the fair sex may increase as a result of:
- Changes in the microflora of the genital organs. If previously a woman was diagnosed only with an inflammatory process in the bladder, now the patient should take a closer look at the vagina, cervix and uterine cavity, where invisible changes also occur.
- Activation of other pathogens during cystitis in women, which previously only lived in the body, but did not pose a strong threat to it.
In men, the strong odor of urine may increase in the following cases:
- With the progression of genitourinary tract infection. The number of pathogenic bacteria in his body not only does not decrease, but constantly increases, and this directly affects the smell of urine.
- With the development of acute renal failure. Such cases with cystitis are not uncommon. This can happen both when a man’s existing disease worsens, or due to improper treatment. In the latter case, we are talking about the side effects that many medications for cystitis have. Renal failure often appears in the annotation, and therefore the patient needs to closely monitor his health and promptly inform the attending physician about changes in well-being.
- When the body is dehydrated. In other words, if a man has drunk little liquid over the past few hours, then his urine will be more concentrated. At
- When infection penetrates into the prostate gland. So, with prostatitis, the smell of urine takes on a rotten hue. A change in the smell of urine during prostatitis can also be affected by an increase in a man’s body temperature, as well as local hyperemia in the genitourinary organs.
- For kidney infection. A fairly common occurrence is when men quickly develop pyelonephritis as a result of cystitis.
In children with inflammation of the genitourinary organs, the smell of urine most often resembles ammonia. It is not as strong and sharp as in adults, but this signal of changes occurring in the child’s body also needs to be heeded.
Pediatric cystitis
Alas, the disease has not spared the younger generation. It’s more difficult for a child than for an adult. He feels bad and in pain, but he cannot explain exactly where it hurts. Of course, we are talking about a preschooler. An older child is able to tell what is bothering him. The kids get off with the phrase “the tummy hurts.”
What parents should pay attention to:
- The baby has frequent urges to go to the toilet. When urinating, he begins to cry and complain of pain.
- The child sits on the toilet for a long time, citing the fact that he cannot pee.
- The child becomes capricious and irritable. He cries constantly, and when asked to go to the toilet, he reacts with panic.
- A child’s urine smell with cystitis is fishy. Its color changes, the discharge becomes darker.
- The temperature often rises to 38 degrees.
If your child has these symptoms, take him or her to the doctor immediately.
What else can influence the worsening odor of urine during cystitis?
Deterioration of the olfactory sign of urine does not always indicate progression of the disease. This is often influenced by those foods that were recently in the patient’s diet: horseradish, garlic, onions, asparagus. Alcohol intake has a particularly strong effect. Even a small dose of an alcohol-containing drink, when broken down, produces changes that frighten patients, and this applies even to absolutely healthy people. Many seasonings also change the smell of urine, not for the better, but traditional herbal remedies usually do not affect the “aromas” of the fluid secreted by a person.
What to do if the smell of urine changes?
Of course, visit a doctor. But is a specialist obliged to pay attention to a patient based only on the fact that his urine has begun to smell sharp? Of course, this is his direct responsibility. Even such an indirect sign of inflammation in the genitourinary organs, such as the appearance of an unpleasant odor when urinating, should suggest a series of tests.
Perhaps the inflammation will ultimately not be detected, and then a qualified urologist will refer the patient to other specialists - a gastroenterologist, gynecologist or even an oncologist. It is always possible to treat the disease in the early stages. If after this no disturbances in the functioning of the body are found, perhaps it’s all to do with the diet. If this fact - a change in the smell of urine - bothers a person so much, he should eliminate a number of foods, and the problem will be solved.
So, the importance of timely consultation with a doctor, even due to the unpleasant smell of urine, is very high. A patient who notices changes in his body and comes to a specialist in a timely manner is likely to live healthy for a long time.
uroguru.com
When does urine smell like you need to see a doctor urgently?
If a person suffers from diabetes mellitus, he has a pronounced sweet smell of urine, then this is the first sign of the imminent development of hyperglycemic coma.
It is urgent to administer insulin, call an ambulance for further treatment or hospitalization.
The presence of a fetid cadaverous odor, which is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, the presence of purulent-hemorrhagic impurities, indicates the beginning of the disintegration of the tumor, which is localized along the urinary tract.
Lack of medical care leads to the progression of bleeding, which will lead to hemorrhagic shock and death.
Darkening with the appearance of an unpleasant odor indicates severe liver pathology, which is accompanied by a lack of function. This condition requires immediate hemodialysis or plasmapheresis, otherwise the outcome will be unfavorable.
A change in the smell of urine is characteristic not only of cystitis and diseases of the genitourinary system. The phenomenon is observed in pathologies that affect other organs.
It is worth noting that the nature of the discharge from the body can tell more than some laboratory tests.
It was not for nothing that zemstvo doctors, to diagnose diseases, made do with examining urine and feces, and accurately made a diagnosis.
Characteristic signs of the inflammatory process
Urine accumulates in the bladder, but during the full cycle of its formation and excretion in the body, it comes into contact with the kidneys and urethra. Therefore, the unpleasant odor of urine should cause concern in a woman and necessitate a visit to a medical facility.
The cause of the unpleasant odor of urine can only be determined after examination. With cystitis, the urine becomes cloudy, with sediment, and the smell resembles ammonia.
Such consequences may appear after taking medications. This happened because the bladder mucosa was exposed to chemicals, and cystitis began to develop. The urine will have a specific chemical smell.
Only after carrying out the necessary tests will the doctor be able to make an accurate diagnosis. It is necessary to find out the cause of the disease. Very often this is E. coli. The infection enters the bladder and infectious cystitis develops.
The smell of urine indicates the course of the disease. At the same time, secretions may get into the urine, this could be pus. Even during the period of cystitis, urine will be exposed to bacteria, which affects the change in its odor. The liquid will also contain secretions of microorganisms that caused the disease.
Causes
In a healthy body, the urethra, which connects to the bladder, is sterile. This state is maintained thanks to the work of the immune system.
When the urodynamic process is disrupted, urine stagnates in the bladder and at the same time immune reactions weaken (trauma, vitamin deficiencies, hypothermia), the risk of the addition of an inflammatory pathogen increases. If it turns out to be viruses or bacteria, cystitis takes the form of an infectious disease.
Pathogenic microorganisms are able to penetrate the bladder through blood, lymph, descending in case of kidney diseases and ascending in pathologies of the rectum and genital organs.
If the provoking factors are allergies, hormonal disorders, chemical, toxic, thermal effects, the pathology is classified as non-infectious cystitis.
Each woman may secrete 1-2 ml of uncolored secretion from the vagina during the day. This condition corresponds to its healthy microflora. If we exclude diseases, then the first sexual intercourse, frequent change of sexual partners, abortion or pregnancy can also upset its balance.
Then the type and composition of the discharge changes, its quantity increases, itching and a strange smell appear. Bacterial vaginosis develops, which is characterized by white or green discharge.
Ascendingly, from the affected reproductive system, the infection enters the urinary system. This is facilitated by the short and wide female urethra.
Of course, discharge in men during cystitis is less common than discharge in the female half of humanity. The fair sex suffers from such manifestations or consequences of cystitis more often. This is due, as already mentioned, to the fact that pathological formations are explained by exacerbations of diseases of the genital area.
Potential causes of discharge:
- Fungal infection - it develops against the background of inflammation;
- Reduced immunity - it can provoke herpes, candidiasis and other pathologies;
- Insufficient or improper hygiene of the genital organs - pain in the groin and discharge due to improper hygiene will not keep you waiting;
- Treatment of the disease with antibiotics - they can lead to vaginal dysbiosis.
If you have previously been diagnosed with cystitis, but there was actually no discharge, you should definitely find out the nature of the discharge. It could be colpitis, or it could be sexually transmitted infections, which could themselves cause cystitis.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z_JHuRJCDgo
Many women are interested in whether there is vaginal discharge during cystitis and what its nature is. Inflammation of the urinary system can be accompanied by the release of a substance of varying consistency, color and odor. This indicates the addition of a secondary infection and the rapid development of pathogenic flora.
With cystitis there may be discharge:
- transparent or with a white tint in small quantities, not accompanied by an unpleasant odor and itching are the norm;
- purulent, greenish, gray indicate the presence of a sexually transmitted infection. In this case, the cause of cystitis is also an STI;
- Bloody and brown discharge with cystitis indicates damage to the cervix.
If there is a pathological process in the genitals, then it becomes the main cause of cystitis. And treatment should consist of eliminating the factor that provoked inflammation of the bladder.
Discharge due to cystitis is more common in women than in the male half of the population. This is due, first of all, to the fact that pathological formations are associated with exacerbation of existing pathologies of the genital area. Inflammation of the bladder worsens the situation, causing the rapid development of diseases (for example, erosion, bacteria).
The main causes of discharge include:
- A fungal infection that develops against the background of inflammation.
- Decreased immunity, which provokes herpes, thrush and other pathologies.
- Poor hygiene associated with poor health and soreness of the genital organs.
- Taking antibiotics to treat cystitis, leading to vaginal dysbiosis.
Inflammation in the body often causes pathologies in the female genital area. Against the background of cystitis, hormonal levels are disrupted and the microflora of the mucous membranes changes. All this provokes vaginal discharge due to cystitis.
What pathologies and infections provoke the appearance of discharge during cystitis? Let's list them:
- bacteria that are transmitted through sexual contact: mycoplasma, gardnerella, chlamydia, gonococcus;
- infections of a nonspecific nature: fungi, E. coli, streptococci, staphylococci, Proteus;
- severe infections: septic diseases, diphtheria, measles, tuberculosis;
- tumor pathologies;
- defects in the nutrition of the tissues of the external surfaces of the bladder and genital organs, caused by chronic constipation and the inability to empty the bladder frequently;
- endocrine system disorders that reduce local protective factors and regenerative stages (thyroid disease, diabetes mellitus);
- the use of immunosuppressants, as well as conditions after radiotherapy and chemotherapy;
- long-term use of medications that chemically irritate mucous tissues;
- local irritation by salts of the bladder mucosa in case of urolithiasis and insufficient fluid intake.
The first symptoms of cystitis
It is possible to assume that cystitis has begun to develop based on the characteristic signs. But you cannot make a diagnosis based on these symptoms alone.
The patient will have:
- The need to go to the toilet very often.
- The bladder will not empty completely.
- When urinating, pain will appear, quite strong and sharp.
- The lower abdomen will pull and hurt.
- Body temperature will be elevated.
- Deterioration in general health.
- Nausea and vomiting may occur.
A urine test reveals an increased number of leukocytes and red blood cells. It may also contain bilirubin, urobilinogen and an increase in ketones. Because of these processes, the specific smell of urine appears. Ketone bodies are formed in the liver and are a combination of three substances - acetone, acetoacetic and betahydroxybutyric acid. Therefore, the smell of urine appears, which will be rotten in nature. In the absence of an inflammatory process, ketone bodies are not present in urine.
Certain medications can affect the process of changing the odor and color of urine. If a patient takes medications and is examined by a urologist, it is imperative to take into account the effect of medications on urine.
oprostate.com
Prevention measures
It is necessary to take preventive measures to avoid the disease at any age. Firstly, you should avoid hypothermia: do not sit on a cold stone, floor, or swim in ice water. Secondly, select things according to the season: that is, do not wear skirts and thin tights in winter, and outerwear should reliably cover your back and butt.
It is recommended to drink plenty of water, thus cleansing the kidneys and bladder. A good alternative would be rosehip tea. You should take care of your immunity, avoiding colds. And undergo regular medical examinations, including from a gynecologist.
Other tips are practically the same as those for cystitis in men: an active lifestyle, protected sexual intercourse and a balanced diet. Personal hygiene is important, especially during menstruation. You should not endure the urge to go to the toilet; it is better to go more often. In this case, the risk of getting cystitis is reduced.
A woman who discovers symptoms of the disease and specific discharge should not undergo treatment. It is worth remembering that cystitis during pregnancy is especially dangerous. If treated in a timely manner, the attending physician will be able to provide qualified assistance while preserving the woman’s reproductive function.