Urinary dysfunction
The imperative urge to urinate causes discomfort to a person and interferes with leading a full life. This is due to the fact that after emptying the bladder, after a short time, a person feels a strong desire to go to the toilet again. There is a feeling that urination will happen immediately, and there is a fear that it will not be possible to hold it.
Sometimes this happens: in some cases, the symptom is accompanied by urinary incontinence. Typically, such phenomena are a sign of an inflammatory process of the urinary tract, less often the cause is an increase in intravesical pressure, and the disease can also be triggered by sexually transmitted infections, surgeries, and even spinal cord injuries and spinal injuries.
Daily urination rate
In the absence of any pathological processes in the body, urination is observed at least 3 and no more than 10 times per day.
At the same time, many factors influence the frequency of bladder emptying and the volume of fluid released. Thus, an increased need to pass urine may appear due to drinking too much, changes in ambient temperature, and even due to certain dietary preferences. There is a category of people for whom frequent urination is the norm. For example, women go to the toilet a little more often than men, which is explained by the structural features of their urinary system. Also, increased urination is typical for children under one year old and the elderly, which is directly related to their age.
Many people believe that constipation affects urination, which is manifested either by its absence or by increased frequency. However, changes in the urinary system are usually in no way associated with problematic bowel function. Difficulties with defecation and dysuria develop independently of each other, manifesting themselves as separate diseases.
We recommend that you read the article “Constipation in the elderly.”
Urgency
Imperative urges (urgency) constantly haunt a person with urinary disorders, preventing him from concentrating on ordinary everyday affairs. Do not confuse the usual strong urge to urinate with urgency. When it appears, it immediately becomes clear that not everything is in order in the body. It is characterized not only by incredibly strong urges, but also by their very frequent occurrence. Such symptoms cannot be controlled; they bother you constantly, regardless of the time of day, gender and age. Previously, statistics spoke of a more frequent susceptibility to the disease in older people, but now this phenomenon is increasingly occurring among young people.
There are cases when urgency is accompanied by nocturia (mainly night urination) or incontinence. Urgency often leads a person to an incapacitated state. Among urinary disorders, urgency is the most common, and among other diseases it occupies a fairly high position. If present, they speak of overactive bladder (OAB).
Frequent and painless urination
Frequent urination without pain is a symptom of a huge number of diseases. Let's try to consider some of them.
Physiological causes in adults and children
Urination may become more frequent when:
- taking large amounts of spicy, sour and salty foods, alcohol. There will be no pain, an increased volume of light urine is released, more than 200 ml at a time. Other symptoms include only mild tickling in the urethra during urination;
- stress, tension, excitement: a large daily amount of urine of normal color is released, while the single volume of urination is not increased. There may be a feeling that you need to urinate more, although the person has just gone to the toilet;
- pregnancy: in this case, other signs indicating this condition will be observed;
- along with menstruation;
- after freezing - for several hours.
Pathological causes
They can be roughly divided into those that cause predominantly nighttime and increased urination around the clock.
Frequent urination at night can be caused by:
- Cardiovascular failure. In this case, swelling will be noted in the legs, sometimes even higher (on the abdomen), interruptions in the functioning of the heart or pain in it, and shortness of breath.
- Diabetes. Increased thirst and dry mouth are also noted; the skin becomes dry, wounds and cracks easily appear on it, which do not heal well.
- Adenoma and carcinoma of the prostate. Symptoms other than nighttime urination may not be noticed. During the day, a man can feel quite well, only urinate in small portions. You can get more information about these and other male diseases that lead to frequent urination from the article: The main reasons for increased frequency of urination in men.
A person will urinate equally often both during the day and at night when:
- diabetes insipidus. At the same time, he is constantly tormented by thirst and drinks a lot, but, unlike his sugar “brother,” there is no dry mouth, dry and itchy skin;
- cystocele (prolapsed bladder): more common in women who have given birth. In addition to painless frequent urination, urinary incontinence will also be noted: when coughing, lifting heavy objects, laughing, and later during sexual intercourse;
- spinal cord injuries and tumors;
- weakness of the muscles that make up the wall of the bladder. The disease begins in childhood and is characterized by no changes in the general condition, but only frequent urination in small portions of urine, as well as a strong urge to urinate;
- uterine fibroids. In this case, painful periods, intermenstrual bleeding, and a large volume of monthly blood loss will also be noted;
- taking diuretics.
Causes
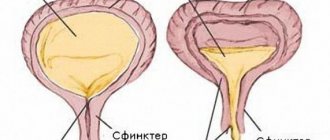
Previously, it was believed that the state of urgency was most often caused by urological and gynecological diseases, and it could also be a consequence of surgery. Now, modern research methods have made it possible to establish that the main cause of symptoms of imperative uncontrollable urges is OAB syndrome. An overactive bladder refers to abnormal bladder activity, which can be chronic. The reason for this is not fully understood, but diseases have been identified that provoke the appearance of OAB, and these are not only diseases of the genitourinary system (acute cystitis, adenoma, prostate cancer, tumor of the bladder neck). Such provocateurs include heart failure, diabetes mellitus, neurological disorders, menopause, age-related changes, and multiple sclerosis.
The main causes of constipation and pathological urination
Frequent passage of urine during fecal stagnation can be triggered by the pressure of a filled intestine on the bladder, since these organs are located close to each other.
Recipes, menus and diet products
Pain when urinating and constipation may occur due to a tumor in the prostate gland. As the tumor grows, it puts pressure on the intestines and bladder, which is manifested by problematic stool discharge and dysuria.
Common causes of constipation and problematic urination include:
- suffered stress;
- disturbances in the transmission of nerve impulses;
- diseases of the vascular and cardiac systems;
- improper calcium metabolism in the body;
- the presence of stones in the kidneys and bladder (provokes the development of pancreatitis and, as a consequence, constipation);
- diabetes.
Also, simultaneous disruption of the intestines and urinary system is observed with pathological changes in the central nervous system. Most often, people with Parkinson's disease, patients with multiple sclerosis and those who have suffered a spinal cord injury suffer from such disruptions.
Recipes, menus and diet products
We recommend that you read the article “Constipation and vomiting in a child.”
Diagnostics
People experiencing constant imperative urges are examined comprehensively, in several stages, so that the doctor can diagnose the true cause of these manifestations. To identify concomitant diseases, the patient undergoes an ultrasound of internal organs - bladder, prostate, kidneys. Next, a urine test, sediment, and culture are examined for sterility; the doctor conducts a physical examination (including a general examination and palpation).
The diary of the patient's urination is studied, on the basis of which conclusions about the diagnosis can also be drawn; OAB is diagnosed if there are more than eight urinations per day and more than one per night. To identify the causes of hyperactivity, cystometry (measurement of bladder volume), tests with water and Lidocaine are performed - a technique used to exclude neurological causes affecting the functions of the detrusor (bladder muscle).
Kidney problems
Pain after emptying the bladder can be a sign of various kidney diseases: pyelonephritis, cystinuria, nephritis, kidney cancer, etc.
Urolithiasis (nephrolithiasis)
The most common problem that causes this symptom.
Nephrolithiasis is characterized by the deposition of calculi (stones) in the kidneys.
How to recognize
The clinical picture of nephrolithiasis depends on the duration and severity of the disease. The size of the stones can vary from small deposits with a diameter of 1-2 mm to large ones the size of a golf ball. The pain in nephrolithiasis is spastic, paroxysmal, sharp, concentrated in the lumbar region. It can radiate to the iliac, inguinal and suprapubic region. In medical practice, this condition is called renal colic. An attack may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, frequent urge to urinate, discomfort after urination, and hematuria.
Diagnostics
Urolithiasis can be recognized based on the clinical picture, ultrasound, blood and urine tests, and CT.
The diagnosis is made by a urologist.
Treatment
To relieve symptoms, the patient is prescribed antispasmodics, analgesics, diet, herbal and artificial diuretics. In severe cases, surgery or other procedures are indicated to “crumple” and remove stones from the body.
Treatment
Treatment of urgency, in which urination is frequent and unbearable, should be carried out as quickly as possible. After all, it is impossible to live a full life with such symptoms; a person experiences not only physical inconvenience, but also constant stress. The goal of treatment is to control fluid accumulation in the bladder. Anticholinergic drugs are used for this. They block the nerve impulses that cause persistent urinary urgency.
In addition, antispasmodics are used in treatment to reduce muscle tone of the urinary tract. Among such drugs, Spazmex is especially popular, which does not exclude combination with other drugs and practically does not cause side effects. In addition to drug therapy, for a more effective result in treatment, Kegel exercises (alternating tension and relaxation of the muscles responsible for urination) and behavioral therapy (going to the toilet strictly according to schedule) are used.
Frequent urge to urinate and diarrhea: causes of incontinence and diarrhea
People sometimes encounter situations where diarrhea is present with a frequent urge to deurinate. Irresistible desires to empty the bladder and bowel movements indicate diseases in the intestines and urinary system. Let's look at why diarrhea occurs with urinary incontinence or pollakiuria, how to treat the disease and possible complications.
Why do problems with deurination occur?
Emerging imperative urges to visit the restroom cause many problems for a person in his social activities.
After deurination, after a short time, the need to urinate again appears. In this case, the sensation is so sharp and sudden that the person feels that deurination will occur immediately.
This gives rise to certain mental fears and complexes, the fear of not being able to get to the toilet in time. Loading …
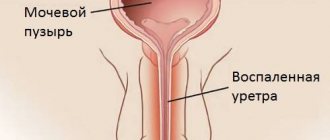
Such symptoms characterize urinary incontinence, which appears due to inflammation in the bladder and increased pressure in it, diseases of the urinary tract and infections that have entered the human body. Most often, pathogenic bacteria are transmitted through sexual contact. Incontinence is often the result of surgery, brain or spinal injuries.
Features of urgency
Urgency refers to imperative urges that exhaust the patient with an irresistible desire to visit the toilet.
No matter how hard you try, they cannot be confused with ordinary strong urges, since they arise very suddenly and cannot be consciously controlled. Symptoms appear in people of any gender and age group, day or night.
Clinical practice notes that previously this phenomenon occurred mainly in elderly patients, but now young people are also affected by this disease.
There are frequent cases of combination of urgency with nocturia, nocturnal urination, and also with incontinence. Most urgency diagnoses cause disability. This disease usually occurs with bladder overactivity and is most often encountered in the practice of urologists.
More on the topic: Causes of alkaline urine reaction
Why does urgency arise?
Until now, there was an opinion that urgency was caused by pathologies in the urological and gynecological areas. Modern medicine has proven the causes of urgency - overactive bladder (OAB). In this disease, the organ is abnormally active, and this condition is usually in a chronic stage.
The reasons for this phenomenon have not been studied, but factors provoking the pathology have been identified. These include adenoma and diabetes, heart muscle failure, sclerosis, menopause, neurological problems or age-related changes in the body.
How is urgency identified?
In patients with urgency, complex examinations of the body systems are carried out in several stages, and the doctor adjusts the preliminary diagnosis based on the results.
An ultrasound scan of the prostate and renal system, bladder is performed. Urine is examined under a microscope and by a specialist in the clinic, the presence of sediment and suspensions is determined, and cultures are performed for the presence of pathogenic pathogens.
The specialist performs palpation for a visual examination and collects an anamnesis.
The patient should keep a deurination diary, which will help with diagnosis. Urinary hyperactivity involves up to 8-10 acts of urine excretion in one night. The reasons are determined during cystometry, when the volume of the organ is measured. During the manipulation, the patient is administered Lidocaine to prevent neurological manifestations in the detrusor. The bladder is filled with clean water.
Treatment of frequent urges
The treatment is intensive and begins right in the doctor's office. This speed of action is necessary due to the patient's severe stress and problems with urination.
The goal of therapy is to restore bladder control.
The doctor prescribes anticholerergic drugs that can block the transmission of nerve impulses from the brain that causes the urge to deurinate.
To relieve muscle tone, antispasmodics are needed that act both on the urine output route and on the entire genitourinary system. The most famous medicine is Spazmex, which has no side effects and interacts well with other drugs.
Experts recommend combining drug therapy with physical activity in the form of exercises developed by Kegel. They consist of relaxing and tensing the muscles of the urinary tract in turn. Doctors also adjust and formulate behavioral therapy, when a person excretes urine on a schedule.
More on the topic: How does the human bladder work?
Frequent urge to urinate and diarrhea
Urgent urges arise not only in the genitourinary system.
If there are problems in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, the system fails, and the desire to defecate appears so acute that you want to do it immediately.
There may be situations when defecation begins without conscious control. This occurs with a sharp contraction of the muscle layer in the rectum or intestines with severe sharp pain.
When contacting the clinic, the doctor finds out that frequent urination and diarrhea accompany irritable bowel syndrome. Other symptoms of this disease: diarrhea more often than 2-3 times a day, tenesmus, flatulence, constipation for several days, abdominal pain.
After defecation, the patient feels incomplete. To relieve spasms, doctors use Dicyclomine, an antispasmodic. A person should adjust their diet by eliminating fried and very fatty foods, hot spices and other foods that can irritate the intestines. Tenesmus, a type of urge fecal incontinence, appears.
Such urges provoke strong muscle contractions and the desire to defecate, but no release of the substance occurs. Many false calls indicate the development of infections within the gastrointestinal tract or the body, acute or chronic colitis, or rectal tumors.
What is behavioral therapy?
The combination of medications and other methods significantly increases the effectiveness of treatment and in many cases restores the impaired process of urine excretion. Non-drug treatment is designed to strengthen the walls of the bladder organ and restore control over the urge to urinate.
Behavioral therapy is designed for patients with genitourinary problems.
It specifies limiting water intake, split doses, excluding coffee and alcohol from the diet, and avoiding liquids in the evening.
The optimal water for behavioral therapy is still, clean water, the volume of which is calculated by a consultant doctor based on the person’s age and underlying diseases.
The essence of behavioral therapy is to create a specific routine for going to the bathroom and excreting urine. In this case, each act must be recorded. The visit schedule is issued by the doctor and is intended to control and train the bladder muscles. Urgency is treated much more effectively in this way.
More on the topic: How does papillary bladder cancer manifest?
How effective is the Kegel complex?
A set of Kegel exercises is designed specifically for female patients suffering from frequent urges and incontinence.
Regular exercise helps strengthen the walls and muscle layer of the bladder, which helps control fluid secretion. A woman learns to control her pelvic muscles and restrain imperative urges.
The ease and accessibility of such exercises allows patients to perform them even outside the home.
Together with the muscles of the bladder, the rectum, uterus, and urethral canal are trained. During pregnancy, a woman retains urine inside in 70% of all cases of incontinence or malfunction of the urinary system.
It becomes much easier for older patients to overcome genitourinary problems associated with age-related changes in the body. These exercises can also be done to prevent hemorrhoids or during the recovery period after childbirth.
Urgency in children
In children, the causes of frequent urination in the imperative form are: vulvovaginitis in girls or balanoposthitis in boys, pyelonephritis, urethritis or cystitis. All these diseases most often occur during prolonged hypothermia of the child’s body or when an infection enters the child’s body. Congenital abnormalities of organ structure and mental disorders may also be present.
responded with an error: The request cannot be completed because you have exceeded your quota.
Rate this post: Loading…
Source: https://onefr.ru/organy/mochevoj-puzyr/pochemu-voznikayut-chastye-pozyvy-k-mocheispuskaniyu-i-ponos.html
Non-drug treatment methods. Behavioral therapy
The combination of medications and alternative treatment methods provides effective results in the fight against urinary disorders. The main directions of non-drug treatment are strengthening the bladder muscles, as well as gaining the ability to control visits to the toilet. Behavioral therapy involves limiting fluid intake if it exceeds the norm, correcting the drinking regime, eliminating alcoholic and caffeine-containing drinks, and refusing to drink before bed. The majority of the fluid entering the body during the day should be clean, non-carbonated water. The amount is determined purely individually, taking into account age and concomitant diseases. Behavioral therapy involves setting a routine for going to the toilet at a specific time to train the bladder. This approach helps cut imperative urges in half.
Anatomical features
Sometimes painful sensations can occur due to the individual anatomical features of the structure of the urinary and reproductive systems. In men, for example, this may be due to the physiological characteristics of the urethra (the presence of narrowings or bends, the large size of the canal).
How to recognize
It can be extremely difficult to recognize such a cause on your own without a medical examination. Depending on the pathology, the clinical picture and nature of pain may vary. Associated symptoms may also vary.
With anatomical defects, patients complain of difficulty emptying the bladder, problems in the sexual sphere, discomfort in the groin area and other symptoms.
Diagnostics
To identify anatomical disorders in clinical practice, the following are used: ultrasound, x-ray, MRI, CT.
Treatment
If the defect does not affect the patient’s quality of life and well-being, serious treatment may not be carried out. In other cases, drug therapy is prescribed to relieve “painful” symptoms and surgery to eliminate the defect.
Kegel exercises for women
This is a set of exercises for women designed to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. As you know, women more often suffer from incontinence, including stress incontinence (when laughing, sneezing, coughing). Regular exercise helps to reduce the urgency to stool and learn to control the pelvic muscles. The complex is very simple, easy to use and accessible to any woman.
Exercises train the muscles that are responsible for the bladder, rectum, uterus, and urethra. They help pregnant women cope with incontinence in 70% of cases and alleviate the condition of older women. Kegel exercises improve blood circulation in the pelvis and rectum, speed up rehabilitation after childbirth, and prevent the development of hemorrhoids.
Hypothermia
Pain after urination can occur due to general hypothermia of the body. Most often, this condition occurs as a result of prolonged swimming in cold water, long walks in the cold or strong winds in inappropriate clothing, as well as prolonged exposure to damp clothes and wet shoes.
How to recognize
When hypothermia occurs, discomfort occurs immediately after emptying the bladder. They are often accompanied by burning, discomfort, and pain.
Patients may also complain of pale skin, shortness of breath, “bluishness” of the nasolabial triangle, decreased body temperature, chills, lethargy, general fatigue, and decreased blood pressure.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by a general practitioner or paramedic when calling an ambulance.
Treatment
Therapy is symptomatic. At a mild stage of hypothermia, it is carried out at home. The patient is put to bed, warmed under a warm blanket, given hot broth, and provided with peace and comfort.
In case of severe hypothermia or frostbite, emergency medical care is required and the patient must be taken to a hospital.
Urinary disorders in children
The child’s frequent demands to “go potty” should alert parents, especially if urination does not occur (the urge is false). If your baby asks to go to the toilet almost every 15 minutes, this is a reason to consult a doctor to find out the cause of such manifestations and eliminate it as soon as possible. There are several reasons why imperative urges occur in children:
- balanoposthitis in boys;
- vulvovaginitis in girls;
- urethritis (inflammation of the urinary tract);
- cystitis (inflammation of the bladder);
- pyelonephritis, kidney disease.
Such diseases are caused by infections or hypothermia. But this is not the only reason; in some cases, there is an anomaly in the development of the genitourinary organs or a disease of the nervous system, including congenital defects and injuries, psychiatric diseases, and neuroses.
Dysuria and constipation: causes in women
Dysuria in women can develop due to pelvic organ prolapse. This happens when the muscles of the pelvic frame are weakened. The disease is characterized by a mixture of the uterus and rectum downwards, which causes constipation and frequent urination .
The following ailments can also be the trigger for the development of dysfunction of the urinary system and constipation in women:
- urolithiasis disease;
- cystitis;
- inflammatory processes;
- nervous fatigue;
- stress;
- changes in hormone levels (occurs due to the menstrual cycle).
Constipation and frequent urination in women can be caused by a growing uterus during pregnancy. This is often observed in the first and last trimester of pregnancy. This is explained by the pressure of the walls of the enlarged uterus on the bladder and intestines, as well as the displacement of the pelvic organs.
Sometimes the frequency of urination in pregnant women reaches up to 20 times per day. In this case, emptying the bladder occurs not only during wakefulness, but also at night. This condition does not require medical intervention, as it is considered a normal physiological process. As soon as the baby is born, the frequency of urination will return to normal.
Be sure to consult a doctor in case of urinary retention and prolonged constipation. Especially if these pathological processes are accompanied by nagging pain in the lower abdomen and deterioration in general well-being.
Recipes, menus and diet products
We recommend that you read the article “Constipation in men.”
Urge to defecate
After stool, there is a feeling of incomplete bowel movement. Antispasmodic drugs, such as Dicyclomine, are used for treatment. A prerequisite for therapy is following a diet, avoiding fatty, spicy and fried foods that irritate the intestines. One of the varieties of the disease is tenesmus. These are excessively strong imperative urges, accompanied by contraction of the rectal muscles and pain, but defecation does not occur. In this case, they also talk about false urges. The reason for this may be a tumor of the rectum, infections, chronic or acute colitis.
Diagnosis
When diagnosing a disorder, the doctor takes into account the patient’s medical history, medical examination data and data obtained during diagnostic tests (a survey of important points related to the existing problem). In addition, a number of instrumental diagnostic techniques are used.
- Anorectal manometry. To carry it out, a pressure-sensitive tube is used, the use of which determines the sensitivity of the rectum and the features associated with its functioning. This method also allows you to determine the current compression force on the part of the anal sphincter, the ability to adequately respond to emerging nerve signals.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). Due to the influence of electromagnetic waves, this method allows one to obtain detailed images concerning the studied area, soft tissue muscles (in particular, in case of fecal incontinence, the emphasis in this study is on studying the muscles of the anal sphincters by obtaining such an image).
- Proctography (or defectography). An x-ray examination method that determines the amount of feces that the rectum can contain. In addition, the features of its distribution throughout the rectum are determined, and the features of the effectiveness of the act of defecation are revealed.
- Transrectal ultrasound. The method of ultrasound examination of the rectum and anus is implemented by introducing a special sensor into the anus (transducer). The procedure is absolutely safe, without associated pain.
- Electromyography. A procedure for studying the muscles of the rectum and pelvic floor, aimed at studying the correct functioning of the nerves that control these muscles.
- Sigmoidoscopy. A special flexible tube equipped with a light is inserted into the anus (and then to other lower sections of the colon). Thanks to its use, it is possible to examine the rectum from the inside, which, in turn, determines the possibility of identifying local concomitant causes (tumor formation, inflammatory process, scars, etc.).
Frequent urination in men without pain
Frequent urination in men without pain, despite the fact that the problem is not global, but the quality of life suffers significantly from this.
For example, a man has to cancel important meetings on this occasion, night sleep suffers from the constant urge to go to the toilet, and long trips become a burden. Therefore, in order to get rid of frequent urination, you must first identify the cause, and then begin to eliminate it. And you should not hesitate to do so, since such a symptom may indicate a serious illness, and the lack of treatment can lead to complications.
Possible diseases
Causes of frequent urination in men:
- Prostatitis. It can occur acutely or chronically. You constantly want to go to the toilet, but sometimes you don’t have the strength to resist, as if the person drank a lot of liquid. But at the moment of the act of urine, little is excreted. Other symptoms associated with the disease include difficulty passing urine, accompanied by pain when urinating in men, a feeling that the bladder is still full, pain in the perineum, weakness in the genital area, in the acute stage a burning sensation appears when emptying the intestines and bladder .
- BPH. This disease is characterized by organ enlargement. The majority of people suffering from the disease are middle-aged and older men. In the initial stages of the disease, urination in men is frequent, but painless. There may be an urge to go to the toilet without results or urinary incontinence. An acute condition with prolonged urinary retention occurs as a complication.
- Infectious diseases (chlamydial infection, urethritis, cystitis, gonorrhea and other similar diseases). Pathogenic microorganisms, once in the genitourinary area, begin to irritate the mucous membranes - this is the main reason for frequent trips to the toilet. The location of the infection may vary. This happens not only to the bladder. For example, in urethritis, pathogenic bacteria are common in the urethra (urethra). A disease such as cystitis is rare for men, but if it exists, its symptoms are as follows: along with frequent urination, pain and a burning sensation appear in the penis and lower abdomen, urine becomes cloudy, white flakes and particles of pus can be found in it . In addition, a person may feel general malaise, his temperature rises, and chills appear.
- Kidney inflammation. The most common diseases are pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis. With pyelonephritis, in addition to frequent trips to the toilet, aching pain appears in the lumbar region. Additional signs of glomerulonephritis are high blood pressure, the appearance of edema, and a man may feel feverish and cold. The separated urine comes out in small portions, moreover, its color becomes darker, and admixtures of blood discharge are observed.
With pyelonephritis, in addition to frequent trips to the toilet, aching pain appears in the lumbar region
- Diabetic disease. It causes men to urinate frequently without pain. This is a disease that occurs due to metabolic disorders in the body, in particular carbohydrates. For a long time, diabetes mellitus occurs without visible symptoms, so if you start running to the toilet more often than usual, especially at night, visit a urologist and endocrinologist. Other signs of diabetes: constant dry mouth and thirst, itchy skin. A man often gets tired, his usual work becomes a burden to him, and weakness appears sexually.
- Overactive bladder. The urge to go to the toilet is very frequent and active, sometimes it is difficult for a man to run to the toilet, and there may even be urinary incontinence. The bladder is in constant tone, its muscles are tense. There are usually no deviations observed in the analyses. An overactive bladder can be caused by spinal cord injuries.
Remedies
Since there are many reasons for frequent urination, treatment options are varied, depending on the type of disease. You should first undergo a thorough diagnosis and identify the disease. Only after this will a competent specialist prescribe the necessary therapy.
If this is a diabetic disease, when men experience frequent urination without pain, treatment involves monitoring glucose levels in the body.
Infectious diseases are mostly treated with antibiotics. If you have a hypersensitive bladder, your doctor will prescribe anticholinergics, which can only be purchased by prescription.
In case of urolithiasis, surgical treatment is considered mandatory, when the stones are broken up and removed from the body during the procedure. The same applies to prostate adenoma; it is also eliminated surgically - excised using the transurethral method or removed during open surgery. Almost all diseases associated with the genitourinary area should be treated only under the supervision of a doctor.
Preventing frequent urination in men
You can avoid many diseases by following some preventive rules:
- Despite the fact that frequent drinking of water is encouraged, in case of some diseases, fluid intake will have to be reduced.
- Do Kegel exercises daily; your doctor may recommend them, or you can find the information yourself on the Internet.
- Stop taking diuretics for a while.
- Rule out prostate disease with frequent urge to urinate.
- Take a course of treatment for pathologies of the genitourinary system.
Remember that your well-being, as well as sexual activity, depends on timely treatment, which is important for men. Be healthy!
What to do if you have frequent urination
Given the large number of different causes of this condition, treatment for frequent urination should be prescribed by a doctor:
- cystitis, urethritis and pyelonephritis are treated with antibiotics, less often with antiviral agents;
- diabetes insipidus is treated with synthetic vasopressin;
- cystocele – surgically;
- for diabetes mellitus, either insulin or tableted hypoglycemic drugs are prescribed;
- for urolithiasis, the treatment of choice is stone crushing with laser or ultrasound;
- adenoma and prostate cancer are treated with surgery, only the volume of interventions will be different.
Advice! Do not limit your drinking regime under any circumstances! The body must receive at least 2 liters of fluid per day for its normal functioning. To get rid of such an unpleasant symptom as frequent urination, at home you can only introduce a diet, limiting salty, smoked foods and alcohol.
Abdominal pain when urinating - why it occurs
any sexually transmitted disease;
Causes of pain in men when urinating
The next group of diseases that can cause abdominal pain when urinating is
- urethritis,
- inflammation of the prostate
- and other similar diseases.
In addition to the pain in these cases, a burning sensation in the urethra is added. A burning sensation can occur both at the beginning of urination and at the end. If pain appears at the beginning, then most likely the urethra is inflamed. The cause of inflamed processes in the urethra can be a weakened immune system, hypothermia, sexual intercourse without protection, or the active activity of opportunistic microorganisms.
Painful sensations can also occur when urinating in men as a result of inflammation of the urethra, and its cause is infection with various sexually transmitted diseases, for example, gonorrhea, genital herpes, and so on. Microbes are able to penetrate the prostate, and thereby provoke the development of inflammation. In this case, the prostate tissue swells and puts pressure on the walls of the urethra. For this reason, pain occurs in the lower abdomen when urinating. Pain can also occur in men due to prostate adenoma. As a rule, this affects men fifty years of age and older. If you experience pain in the lower abdomen when urinating, you should go to a urologist.
Why does a woman's stomach hurt when urinating?
If a woman has a urinary disorder only at night, this indicates abnormalities in the rectum or in the cavity of the cervix. In this case, the pain may be combined with a burning sensation when urinating. This should be a reason to immediately visit a urologist for an examination and prescribe the correct treatment. If such symptoms are left unattended, the disease can become chronic. In this case, its treatment will become significantly more complicated, and other concomitant diseases may appear.
With pathology of the genitourinary system, such sensations arise. Pain occurs as a result of the inflammatory process, various infectious lesions and diseases that are transmitted sexually, as well as the appearance of kidney stones. As a rule, such pain is accompanied by such disorders as frequent urination, night urges, which increase the volume of urine. Similar pain can also appear due to innervation of the bladder, that is, cystitis. This disease must be treated to avoid all sorts of complications. To do this, it is necessary to determine the cause, and then undergo a course of treatment.
Cystitis and constipation
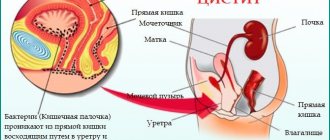
Constipation and burning during urination is most often observed in women, which is usually associated with the development of a disease such as cystitis. This disease is unique to the weaker sex, since their urethra has anatomical features that increase the risk of pathogenic microorganisms entering the bladder cavity.
An acute inflammatory process is manifested by severe symptoms, including dysuria. The chronic form of the disease is often accompanied by intestinal dysfunction, and conversely, women with complaints of prolonged constipation often have a history of cystitis. So what is the connection?
The reasons for this phenomenon may be:
- Proximity of the specified organs. When there is a large accumulation of feces in the intestine, compression of the bladder occurs, which impairs blood circulation and changes its location.
- Impaired blood circulation in all pelvic organs.
- Dysbacteriosis, especially the chronic form.
Cystitis along with constipation often worries pregnant women, which is influenced by an actively growing uterus, a sharp change in hormonal levels and a decrease in immune strength.
We recommend that you read the article “Constipation in the first trimester of pregnancy.”
Pain in the right side when urinating
One of the common complaints of patients when visiting a clinic is pain in the left or right side and frequent urination. Such a symptom may indicate a variety of diseases, different etiologies and localizations. If the patient is bothered by pain in the right side when urinating, then the causes of such discomfort may be pathologies of various organ systems.
Pathological conditions of the gastrointestinal tract can provoke the appearance of pain of various types in the right side during the act of urination:
- Gastritis – this disease is accompanied by decreased appetite, nausea, belching, and dyspeptic symptoms (constipation, diarrhea). The pain is dull, aching, and sometimes stabbing in nature and is localized in the right side of the abdomen, appearing mainly during urination and after eating;
- Duodenitis has manifestations similar to gastritis, however, pain can radiate to the scapula (right) and lower back;
- Ulcerative lesion of the duodenum - the pain is aching, spastic, stabbing, cutting in nature, intensifies with urination. The pain is periodic, and the disease is also characterized by the presence of intense heartburn, constant nausea, vomiting that does not bring relief and constipation;
- If you have hepatitis, you may experience increased pain during urination. The pathology is also characterized by general weakness, loss of appetite and emaciation, yellowness of the skin and itching, the presence of rashes, increased body temperature;
- Gallstone disease, cholecystitis and biliary dyskinesia are diseases that have similar clinical manifestations, differing in severity: sharp stabbing pain in the right hypochondrium (intensifies after eating, urinating, physical activity or changing body position), nausea, change in skin color , skin itching, dyspeptic disorders, weakness and muscle pain, sour or bitter belching;
- With pancreatitis (inflammatory process in the pancreas), the right side may also hurt when urinating. The pain is girdling in nature, intense, often accompanied by profuse vomiting, which does not lead to improvement in the condition. Right-sided localization of pain is characteristic of inflammation of the head of the gland. When the disease occurs, a change in the color of urine (“beer-colored urine”), yellowness and itching of the skin, and discoloration of feces are observed;
- Acute appendicitis - pain is localized on the right side, under the ribs, then descends to the iliac region. The pain intensifies with minimal physical activity (changes in body position, urination, defecation);
- Enteritis is a pathology affecting the small intestine (mucous membrane) and is accompanied by pain on the right, in the lower abdomen.
Infectious phenomena of the reproductive system:
- Gonococcal infection;
- Chlamydia;
- Ureoplasmosis;
- Candida lesion;
- Trichomoniasis.
Pathological processes affecting the urinary system (kidneys, bladder and ureters) are the main cause of frequent urination and pain in the right and left side:
- Pyelonephritis is a severe kidney pathology of infectious etiology. The pain has a predominantly unilateral localization, in the lower back with irradiation to the lumbar area, and is aching and intense. The disease is accompanied by an increase in body temperature to febrile levels in the evening, dry mouth and severe thirst, pale skin, darkening of the skin under the eyes in the form of circles, the appearance of facial swelling in the morning, headaches and dizziness, and the release of urine with a characteristic pungent odor. and high content of leukocytes;
- Chronic and acute forms of glomerulonephritis are an inflammatory process in the renal system that has an immune etiology. When urinating, the left and right sides hurt, the urine looks like meat slop (due to the presence of a large number of red blood cells). Patients experience shortness of breath, increased blood pressure, swelling of the face and limbs, increased body weight due to the accumulation of fluid in the tissues;
- Vesico-ureteral reflux - with pathology, there is a reflux of urine from the bladder into the ureters;
- Urolithiasis of the kidneys - in addition to strong aching, dull painful sensations in the lumbar area during urination, there is a high temperature and general weakness. Urination is frequent, and blood is present in the urine.
Pain associated with gender and age
Causes of malaise in men and boys
Representatives of the stronger half of humanity often hide the fact that they have problems, especially if they relate to the reproductive system. And in vain! After all, ignoring symptoms can lead to very serious consequences. Let's look at just a few of the most common diseases:
- Testicular torsion. It is more common in childhood; the boy becomes restless because... sharp stabbing pains in the lower abdomen, nausea, and vomiting appear. The scrotum swells and turns red.
- Varicocele. It manifests itself as burning, pulling, stabbing pain in the lower abdomen, testicles, groin, thighs, aggravated by movement and physical activity. At the same time, the size of the affected testicle changes, the kidneys begin to ache, and urinary incontinence develops at night. A characteristic feature of the pathology is that if the guy lies down or lifts his scrotum, it will become much easier and you can relax.
- Orchitis is an unpleasant pathology, its first symptom is pronounced pain in the testicle, radiating to the suprapubic bone, perineum, and lower back. An additional manifestation of the disease is a reddened, compacted, swollen scrotum. During movement, the discomfort that torments a man or teenager increases sharply. In addition, there are signs of intoxication.
- Vesiculitis - characterized by pain in the groin and above, radiating to the tailbone with a full bladder, urination, or defecation. As additional signs, the guy has: semen with pus and blood, high fever, migraine.
- With prostatitis, a disease that often occurs in men, it begins to pull in the perineum, radiating to the groin. If treatment is not started, discomfort will appear below the navel and in the back, and sexual function will decrease. When urinating, pain and aching in the lower abs will begin to occur. Therefore, if your husband regularly has pain in his lower abdomen, the first step is to consult a urologist.
- Prostate adenoma - begins with a frequent urge to urinate at night, which causes significant inconvenience. This process causes pain and burning, which reduces in the back.
- Malignant tumors can cause numerous problems. They provoke an increase in the volume of genital tissues and a change in the color of the mucous membranes. At the same time, the lower abdomen and genitals constantly and persistently hurt. Unpleasant sensations intensify upon palpation and during sexual intercourse. The lymph nodes become enlarged, the man loses weight for no apparent reason, becomes weak and lethargic.
Causes of malaise in women
There are a number of diseases characteristic exclusively of the female sex; let’s consider the main specific signs of diseases that cause pain:
- Adnexitis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries, i.e., uterine appendages) has a pronounced onset of development, which is difficult to ignore, since burning and sharp, stabbing pains appear in the lower abdomen, in the side, radiating to the perineum, back, and anus. The temperature rises to 39 C, fever occurs. There is discharge of mucus and pus from the vagina. The menstrual cycle is disrupted. The abdominal wall is tense and urination or defecation causes discomfort. The development of the disease can be triggered by cold feet.
If you catch a cold in the internal organs, but do not treat them, then after 10 days the symptoms will “attenuate” and adnexitis will become chronic.
- Endometriosis is difficult to treat. In this case, acute pain in the suprapubic region is initially cyclical, but as it progresses it becomes constant and debilitating, spreading throughout the entire pelvis. Discomfort intensifies when visiting the toilet or sexual intercourse.
- With uterine fibroids, the lower abdomen pulls. The cycle is also disrupted, and the amount of menstrual blood becomes significantly larger. Additional manifestations include: constipation and frequent urination, an increase in waist size, with unchanged weight.
- Cyst. If it's small, it usually doesn't bother you. An exception is visiting a solarium, which leads to exacerbation - the menstrual cycle is disrupted, the tailbone hurts and the lower abdomen pulls. Symptoms intensify with sexual contact, physical activity, and urination. If these manifestations are ignored, the cyst may grow rapidly, threatening to rupture. As a result, a sharp, severe pain occurs, radiating to the rectum, leg, pressure drops sharply, temperature rises, dizziness, uterine bleeding, nausea, vomiting, and possible fainting. The girl needs emergency medical care.
With all of the above diseases, the stomach may hurt more severely after electrophoresis. This does not indicate a sharp progression of the disease. This symptom means individual intolerance to electrical discharges.
- Dysmenorrhea - characterized by unpleasant sensations below the navel, which have a pulling, aching character. It can appear in girls aged 14-17 years, and in women of Balzac age. Please note that after a hot bath your stomach hurts more. The pain can radiate to the back, leg, and be accompanied by weakness, dizziness, absent-mindedness, nausea, and sleep disturbances. Physical activity makes you feel worse. Most often, treatment is not necessary, because discomfort begins about a day before menstruation and goes away after 1-4 days. To alleviate the condition, it is permissible to take antispasmodics or pain pills.
Pregnancy and postpartum period
A special group consists of women’s conditions that arise during pregnancy and after childbirth. Sometimes unpleasant sensations are physiological, sometimes they are a signal of danger. In addition, at this time the body is doubly susceptible to infections and susceptible to diseases that can negatively affect the child and the mother’s health, so you should be especially attentive to your well-being. So,
- If during pregnancy there are slight stabbing pains in the lower abdomen, this is most often explained by the fact that the muscles of the uterus are stretched, but individual fibers resist the process. If the event is rare and its intensity is low, then no treatment is required.
- If contraction of the uterus is observed after childbirth, this is usually a natural process. The spasms that arise are reminiscent of labor pains, but the intensity is much less. Normally, the disappearance of unpleasant sensations should occur within a few weeks.
- If the pregnancy test is positive, but the second line is poorly visible, toxicosis and delayed menstruation are observed, pain is felt in the suprapubic area when trying to pull in the stomach, pain occurs in the lower back, which intensifies with movement, then an ectopic pregnancy can be assumed. It is dangerous if measures are not taken in time, since the developing fetus can rupture the fallopian tube or ovary, then sharp acute colic and bleeding will occur, which threatens the death of the woman if qualified medical assistance is not provided in time.
- If during pregnancy any critical situation occurs, accompanied by bleeding from the vagina, severe pain in the lower back, in the suprapubic region, or convulsions, then urgent hospitalization is necessary, because One of the diagnoses may be placental abruption.
- If during the postpartum period there is a pulling feeling under the navel, extending to the sacrum or lower back, which is accompanied by vaginal discharge that has an unpleasant odor, fatigue, weakness, and fever, then this may be inflammation of the uterus.
- If after childbirth the lower abdomen hurts, it pulls and aches, it may be symphysitis. Discomfort manifests itself both during movement and at rest. The easiest way to move is with a “duck walk”. As it progresses, unpleasant sensations appear in the perineum, lower back, and legs.
- If 2-4 weeks have passed after childbirth, but discomfort in the form of pulling spasms below the navel and occasional uterine bleeding remains, then you need to find out as quickly as possible why this is happening. A possible reason is the presence of a placental polyp. If you ignore the body’s signals, over time, the symptoms of the pathology will appear brighter and brighter.
Causes of illness in a child
The difficulty of diagnosing diseases in children is that they cannot explain their condition, and external manifestations are not always the same as in adults. Here are just a few of the diseases that babies are most often exposed to:
- Rotavirus infection, or dirty hands disease, has a vague etiology. Against the background of increased temperature, vomiting, diarrhea, flatulence, severe general intoxication, severe stabbing in the suprapubic region begins, the throat turns red, and conjunctivitis develops.
- Worms. Their presence in the body is indicated by nighttime itching around the anus, weight loss, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps in children.
- Hirschsprung's disease is congenital and involves the absence of nerve cells in a certain part of the colon. The longer this part is, the earlier and stronger the symptoms appear, consisting of constant constipation, increased gas formation, during attacks of which the abdominal wall begins to swell, and abdominal pain. All this leads to the fact that after eating the child becomes restless, cries, and tightens his legs.
Characteristics of irritable bowel syndrome
The clinical picture of IBS can vary and is not accompanied by the manifestation of any one symptom; it is always a complex of disorders.
1) Feeling of heaviness in the stomach.
2) Flatulence and nausea.
3) Fluctuations in the consistency of fecal matter (from loose stools to constipation).
4) The feeling that during the act of defecation it is not possible to completely empty the intestines.
5) The presence of mucous discharge in the stool.
6) Defecation more than 3 times a day and less than 3 times a week.
7) False urge to have a bowel movement, as well as urges that occur spontaneously and require immediate use of the toilet.
 Exercising extra effort during defecation.
Exercising extra effort during defecation.
This, of course, is not a complete list of possible manifestations, but all of them in irritable bowel syndrome are somehow related to the digestive cycle. A diagnosis of IBS requires a combination of 2 or more of the following symptoms.
The nature of the pain is also important in the diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome.
The diagnosis of “irritable bowel syndrome” is made to a patient in the following cases:
A) The diagnosis of “irritable bowel syndrome” is made to the patient if the duration of intestinal disorders exceeds three months during the year.
B) Abdominal pain goes away for some time after bowel movement.
C) The nature of pain may change depending on the frequency of stool and the consistency of fecal matter.
In addition, irritable bowel syndrome may present with a number of nonspecific symptoms that complement the clinical picture of the disorder.
Pain associated with activities
When urinating
Usually, the discomfort that occurs means problems in the urinary system:
- Urethritis. The most pronounced symptom is that going to the toilet is accompanied by pain and burning in the suprapubic area and groin. As the disease progresses, flakes of pus may be seen in the urine. If left untreated, the symptoms may practically disappear, but the development of inflammation will continue.
- Cystitis. Its symptoms include frequent urination, accompanied by burning, itching, pain, the muscles of the lower abs hurt, and the urine becomes cloudy.
- Stones in the kidneys. Often a person finds out about their presence at the most inopportune moment. Against the background of good health, a dagger-like girdle pain suddenly appears in the lower abdomen. It intensifies when urinating, the color of the urine becomes pink. A characteristic sign of renal colic is that a person cannot find a position to relieve suffering. It is necessary to take antispasmodic medicine (2 tablets of No-shpa) and call an ambulance.
- Nephritis. It has many varieties, including alcoholic. But all are characterized by a dull pain with a full bladder, which can occur on one or both sides (depending on the extent of the damage - 1 or 2 kidneys at once), chills, sweating, fever up to 40 C, swelling throughout the body. A pulling sensation in the suprapubic area appears and intensifies after alcohol or drinking a large volume of liquid.
After bowel movement
If the lower abdomen hurts after defecation, in this case, the following abnormalities are most often detected:
- Colon ulcer - characterized by acute pain radiating to the left after defecation. In addition, there is blood in the stool, constipation alternates with diarrhea, general weakness is observed, and the temperature rises to 39 C.
- With an anal fissure of the anus, burning, pain, and itching appear, which intensify during defecation and continue after it. Referred pain may appear in the intestines in the lower abdomen, bladder, tailbone, and back. In advanced cases, bleeding develops, which means injured soft tissues.
- Diverticulitis. With this disease, discomfort is felt locally, in the left iliac region. It intensifies with coughing, laughter, active movement or palpation. The attack lasts from 1 hour to 2-3 days. Additional symptoms include: blood in the stool, nausea, fever, fever, indigestion, diarrhea alternating with constipation. A peculiarity of diverticulitis is that after bowel movement the symptoms intensify.
After physical activity
The causes of pain in this case are of a very different nature. But most often diagnosed:
- Overstrain of the abdominal muscles. The appearance of discomfort is associated with poorly developed abs; as a result, when a person performs unusual movements (frequent squats, bending, walking up stairs, etc.), pain occurs. For many patients, such overexertion can occur during a cold, which is why the question often arises: “If my stomach hurts when I cough, is it dangerous?” In this situation, there is no need to panic; pain is a side effect and does not require treatment. You can help yourself with a light massage with ointments that relieve spasms and muscle tension.
- Problems with the spine or hip joints. You can assume this problem if pain in the lower abdomen appeared after lifting weights and did not go away for the second day.
- Inguinal hernia. It manifests itself as the appearance of a tubercle under the navel on the right or left side, which begins to ache. When lying down, the symptoms disappear and the patient can relax. When straining or lifting heavy objects, the size of the swelling increases and the discomfort becomes more pronounced. The development of the disease is accompanied by constipation and urination problems.
When a hernia is pinched, the patient experiences severe acute colic and severe nausea. In this case, urgent hospitalization is necessary.
Other symptoms of IBS (not directly related to the intestines)
1) The patient may from time to time experience an unusual taste in the mouth that is not associated with the intake of a particular food.
2) The psychosomatic state changes. Feelings of depression or even depression may develop in connection with IBS.
3) IBS can be accompanied by the presence of pain not only in the abdomen, but also headaches and pain in the lower back.
4) The patient may experience functional changes in pulse rhythm (more than eighty beats per minute - tachycardia, the heart skips beats - arrhythmia). If the person does not suffer from diseases of the cardiovascular system, all this can be, among other things, a manifestation of IBS.
5) There may also be problems with urine output (urination too often, inability to completely empty the bladder, difficulty starting to urinate, etc.).
6) IBS is often characterized by sleep disturbances. Moreover, this can relate to both increased sleepiness during the day and insomnia at night.
Intestinal upset and frequent urination
Frequent urination with diarrhea is a common condition for both females and males. A number of factors can provoke pathology, including urinary tract infections. If you have a frequent urge to urinate, which is accompanied by diarrhea, it is important not to self-medicate and go to a medical facility where an experienced doctor will carry out the required diagnostics.
Pathological factors
If a patient experiences frequent urination and diarrhea, as well as additional symptoms, this indicates the presence of the following conditions:
- heart failure;
- myocardial infarction;
- diabetes mellitus of various types;
- the presence of stones in the bladder;
- inflammatory processes in the bladder;
- kidney diseases;
- diabetes insipidus;
- disturbances in the activity of the urinary tract;
- renal failure in the acute or chronic stage, in which destruction of organ cells is observed.
Kidney disorders
Since the kidneys are responsible for urination in the human body, increased urge and accompanying diarrhea are observed along with pain in the projection area of this organ. Such unpleasant symptoms may indicate the development of the following conditions:
Taking a large dose of medication can provoke symptoms of poisoning.
- Food and drug poisoning. If a person eats low-quality, expired or insufficiently processed foods, there is a risk of pathogenic bacteria entering the body, which cause poisoning. In this case, the patient complains of acute pain and diarrhea. In addition, you can also be poisoned by medications by taking an increased dosage or due to individual intolerance to the components that make up the medications.
- Diseases and disorders in the functioning of organs. Kidney failure and inflammation are often accompanied by diarrhea, pain and frequent urination. In addition, such symptoms are also observed in cases of injury due to blows, falls and other injuries.
Reasons of a physiological nature
Frequent urination and loose stools are caused by the following non-dangerous factors:
- Pregnancy period. In the first trimester, the uterus increases in size, subsequently beginning to put pressure on the urinary cavity and its valve. Along with this, diarrhea is also observed. Loose stools and frequent urge to defecate may also indicate impending labor.
- The beginning of critical days. Hormonal disruptions that occur during menstruation affect the muscles of the vagina and anus, which is why girls complain of an increased urge to defecate and frequent bowel movements.
Diagnostic procedures
If a patient has diarrhea and frequent urination, it is important not to delay visiting a healthcare professional. These symptoms may not indicate the development of pathologies, but you should still make sure that they are absent. To begin with, the specialist conducts a visual examination of the patient and palpates.
Then he begins to interview the patient, finds out what the person is complaining about, and how long ago the unpleasant symptoms arose. After this, the patient is sent for tests that are required to clarify the intended diagnosis.
When the results are ready, the generalist sends the patient to another doctor who is treating the problem directly that the research showed.
Treating Frequent Urination and Diarrhea
Therapy for frequent urge to defecate and loose stools is based on eliminating the cause that contributed to the development of these undesirable reactions.
If frequent urination is caused by infections, then a medical professional will prescribe antibacterial pharmaceuticals. If the problems are associated with impaired bladder muscle tone, then the doctor prescribes medications that help cope with this problem.
In addition, experts recommend using exercises that will help improve muscle tone.
Specific training for better muscle control
Kegel exercises are considered the most effective. The patient will need to take a comfortable sitting position and imagine the process of emptying. During this, it is important to pay attention to which muscles are tensed. You will need to remember them and resort to alternate relaxation and tension. This gymnastics should be done 3 times a day, gradually increasing the duration of classes.
Mostly, Kegel exercises will need to be done for 6 months, until the muscle tone of the bladder returns to normal.
Conservative approach
Treatment of frequent diarrhea involves the consumption of low-fat foods, which are recommended to be prepared by stewing. In addition, prebiotics are used that inhibit intestinal motility, for example, Loperamide, Diara, Imodium.
They also resort to antibiotics, the most popular of which is the drug Amoxicillin. It is important to remember that the right medicine and its correct dosage can only be prescribed by the attending physician, depending on the individual characteristics of the patient and the cause of diarrhea.
If diarrhea is provoked by the use of medications and intoxication, then their use is stopped.
Source: https://kishechnikok.ru/problemy/rasstroystvo-kishechnika/rasstrojstvo-kishechnika-i-chastoe-mocheispuskanie.html
Causes of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Specific reasons that could cause this far from pleasant condition have not yet been identified, and doctors and scientists have conducted numerous studies regarding the nature of IBS and examined patients suffering from this disease.
However, what is characteristic of irritable bowel syndrome is that during the study of the patient’s medical history, as a rule, no concomitant pathologies (for example, an inflammatory or tumor process) are revealed that could lead to such pronounced and long-lasting intestinal disorders.
Some scientists argue that IBS is associated with a disruption of the neuroendocrine connections between the intestines and the brain, as a result of which the intestines receive the wrong signal from the brain structures and, as a result, a functional disorder occurs. However, this assumption has equal parts supporters and opponents.
In some cases, IBS can also occur for arbitrary reasons, namely:
1) Due to regular violation of diet.
2) Systematic consumption of low-quality food.
3) Disturbances in the general hormonal background of the body.
4) Long-term treatment with drugs (mainly antibiotics) that negatively affect the intestinal microflora.
Pain associated with various conditions
Constipation
The appearance of this additional sign indicates the following deviations:
- Spikes. In this case, a person experiences pain in the lower abdomen, which becomes intense after eating, physical activity, or raising his legs. At rest, the sensations become pulling. With this disease, there is increased gas formation, constipation, and the abdominal cavity begins to swell.
- Genital prolapse. Most common in older women. In this case, a pulling sensation appears in the suprapubic region, a sensation of a foreign object in the vagina, urinary incontinence, and lack of stool.
- Irritable bowel syndrome. Its symptoms are: chronic constipation, swelling, mucus discharge from the anus. The stomach swells when you try to pull it in, and after eating there is discomfort. After defecation, there remains a feeling of incomplete emptying, but relief comes.
Diarrhea
In this case, the following diseases are most likely to develop:
- Dysentery - at first, a dull pain spreads throughout the entire womb, then descends to its lower part and becomes sharp and cramping, intensifying before the urge to go to the toilet. The stomach swells, diarrhea, weakness, dizziness are observed, the temperature rises to 38 C, and appetite disappears.
- Enteritis. The main symptom is spasms that appear several hours after eating and are localized in the right iliac region or closer to the navel. When defecating, mushy, liquid stools are observed, which contain poorly digested food. Increased gas formation occurs in the intestines.
Bloating
Increased gas formation (flatulence) indicates indigestion and the onset of putrefactive processes. This is typical for the following diseases:
- Obstruction of the large intestine. With its development, gradual stool retention, bloating and spasmodic pain in the lower abdomen are observed. With palpation, you can easily feel the space-occupying formation.
- Dysbacteriosis - a cutting spasm occurs in the suprapubic area and is accompanied by increased gas production, belching, and an allergic reaction to familiar foods. In addition, diarrhea begins, which alternates with constipation. The development of the disease is often preceded by taking antibiotics and eating fast food.
Nausea and vomiting
Typically, with the help of these signals, the body reports intoxication, which can occur due to:
- Excess of vitamins. In this case, in addition to nausea and vomiting, fatigue, irritability, sleep problems are observed, muscle spasm in the suprapubic area is combined with diarrhea.
- Poisoning. The lower abdomen hurts for this reason, mainly due to eating expired foods. In addition to the above symptoms, diarrhea, weakness, dizziness, and fever appear. Coughing and sudden movements bring discomfort. After defecation, the condition improves briefly.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract that no longer fully cope with their functions. One of the most common diseases in modern society are gastritis and stomach ulcers. In the first case, a pain occurs after eating in the right hypochondrium, radiates to the left, back, under the navel and provokes sour vomiting. To normalize the condition and reduce pain, you need to lie quietly for several minutes. For the second, it is not uncommon to experience discomfort in the morning on an empty stomach, but after eating, the state of health returns to normal. If the ulcer grows, involving the pancreas, heartburn appears in the evening.
First aid
You should not self-medicate if unpleasant symptoms occur, as this will only harm your health. Before visiting a specialist, the following will help alleviate the condition:
- taking noshpa;
- tea with rosehip;
- a strict diet with the exclusion of any allergenic foods, pickles, hot spices from the menu;
- taking an antihistamine (Zodac, Loratadine, Zyrtec);
- rest and peace;
- exclusion of stress factors and physical activity.
What not to do:
- take any antibacterial drugs and NSAIDs on your own;
- warm up the lower abdomen using heating pads;
- visit the swimming pool, bathhouse, sauna;
- to harden;
- attend physiotherapeutic procedures;
- have sex.
Prevention
To avoid the occurrence of pain associated with disorders of the urinary organs, it is necessary:
- carefully monitor the cleanliness of the genitals;
- strengthen immunity;
- Healthy food;
- avoid stress and hypothermia;
- empty the bladder in a timely manner, preventing it from overflowing;
- drink at least 1.5 liters of liquid per day.
Once every 12 months, it is necessary to undergo a preventive examination by a nephrologist or urologist and do an ultrasound of the urinary system. This will allow you to identify possible pathologies at an early stage of development, carry out timely treatment and prevent the occurrence of complications.
Symptoms of dark urine
A healthy person secretes a light yellow liquid that has no odors or impurities. But there are different causes of dark urine, and the type of disease that develops depends on the shade. Changes in the color of urine are sometimes associated with a person’s age, because after 50 years, damage to the genitourinary system occurs in both men and women. Moreover, each syndrome is characterized by urine of a certain color.
- If the color of the urine has changed to dark yellow, while the liquid is cloudy and of high concentration, then the patient has experienced dehydration, resulting in nausea, vomiting and loose, light-colored stools.
- Brown discharge indicates hemolytic anemia.
- Black urine is a sign of melanosarcoma, alkaptonuria, and acute hemolytic kidney is also diagnosed.
- Red, almost burgundy thick urine with blood indicates tumors, cystitis and urolithiasis.
- Glomerulonephritis is the reason why the color of meat slop appears.
- A greenish-brown tint (beer-colored urine) means that the patient is developing parenchymal jaundice.
- If there is a gray tint, which is almost white and discolored, it is said that there is fat or purulent discharge in the discharge, and the urine smells unpleasant.
Clinical manifestations of diarrhea are usually characterized by a standard set of complaints and objective examination data. For some of its types, there are specific distinctive features that can be used to accurately determine the specific nature of the disease.
But it also happens that even additional laboratory and instrumental data do not always turn out to be informative. In order not to miss anything, you need to be very attentive to everything that happens to the body, accompanying diarrhea.
High temperature with diarrhea
Gynecological pathologies
Gynecological pathologies are diseases of the female genital organs that arise as a result of injuries, hormonal disorders, and infectious processes. Most of them are accompanied by difficulty urinating, pain and pain during and after emptying the bladder.
How to recognize
Pain in gynecological diseases is localized at the very bottom of the groin area. It can be permanent, “dull” in nature, or occur abruptly only during and after urination, and then go away.
Often accompanied by a “pulling” sensation in the lower abdomen, pain, cloudy or clear vaginal discharge (sometimes with an unpleasant odor), cloudy urine, and general malaise.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is carried out by a gynecologist. The diagnosis is made based on the patient’s complaints, ultrasound results, gynecological examination, and laboratory test results.
Treatment
Treatment tactics depend on identifying the cause that led to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms. In case of infectious processes and detection of STDs, antibiotics are necessarily prescribed, as well as drugs to strengthen women's health, restoratives, analgesics, etc.