There are 2 common types of diseases: pyelonephritis and cystitis. These pathologies relate to inflammatory processes and also have a similar symptomatic picture. But the treatment will be slightly different. They are often confused, which leads to incorrect diagnosis and adverse consequences. To distinguish cystitis from pyelonephritis, you should know the difference between the two diseases.
There are 2 common types of diseases: pyelonephritis and cystitis. These pathologies relate to inflammatory processes and also have a similar symptomatic picture.
How to identify cystitis yourself
Despite the fact that the signs of inflammatory reactions in the bladder organ have characteristic features, the symptoms of the disease are quite similar to the manifestations of other urological pathologies.
Therefore, even if there is complete confidence that the patient has independently identified the manifestation of cystitis, it is not recommended to begin independent treatment.
In order to have 100% confidence in identification, we will consider the main signs of cystitis and its differences from the manifestations of other, most common diseases.
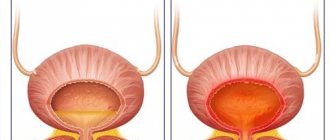
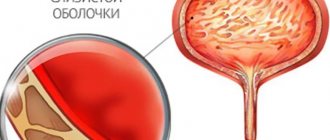
The clinical picture of cystitis is characterized by the manifestation of the classic triad of symptoms - dysuria (difficulty urinating), terminal hematuria (blood in urine) and pyuria (purulent inclusions in the urine). They can appear either individually or in combinations.
The acute process is characterized by the rapid development of bladder dysfunctions, manifested by:
- frequent micturition (urination) – pollakiuria,
- constant desire to urinate,
- sharp urges to perform sexual intercourse,
- pain, cutting and burning in the urethral canal during voiding,
- frequent night trips to the toilet - nocturia,
- fetid odor and turbidity of a fresh portion of urine.
Increased body temperature and chills with cystitis are not a mandatory sign of pathology, but can appear along with other symptoms. If signs of fever and chills appear, this may indicate the involvement of the renal tissue structure in the inflammatory process and the development of the acute stage of pyelonephritis.
In the first days of the disease, disorders in the urination process rapidly progress.
The intervals between movements are reduced (up to 5 – 15 minutes). Urine does not have time to accumulate in the cavity of the reservoir, so the mictions have a very small volume. The urge to urinate does not stop even at night. In most cases, they cannot be controlled, which causes urinary incontinence (patients do not have time to run to the toilet).
Pain syndrome accompanies movements at their beginning or end, or constantly. Sometimes the pain is not associated with urination. Pain in the pubic area or perineum can cause constipation due to cystitis, caused by compression of the inflamed urinary reservoir with feces.
The manifestation of the painful syndrome does not depend on the severity of the inflammatory process. Sometimes superficial inflammation of the structural tissues of the bladder causes acute unbearable pain, and with extensive inflammatory reactions, the pain is insignificant. Inflammatory processes in the bladder tissues can manifest themselves as an independent disease and be combined with other pathologies in the body.
This must be taken into account. For example, difficult bowel movements or diarrhea due to cystitis often appear simultaneously, especially in women during pregnancy. Once manifested, the disease may never occur again, but if signs of bladder inflammation appear repeatedly over the course of a year, this may mean a relapsing course of the disease.
As a result of research work, a new version has emerged, due to the fact that the manifestation of repeated inflammatory processes in the bladder is a newly emerging disease, and not a relapse of cystitis, which requires mandatory additional examination.
Professional diagnostics will help you understand that you have cystitis. Self-comparison of symptoms alone is not enough. Their differentiated analysis with similar signs of other pathologies is necessary. In addition, quite often, the clinical picture of the disease has a hidden course, and delay in treatment leads to chronicity of the inflammatory process and the development of undesirable consequences.
Features of prevention
The development of cystitis and pyelonephritis can be prevented if the patient adheres to certain rules:
- Empty your bladder in a timely manner.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Adhere to hygiene measures.
- Maintain water balance in the body.
- Increase and strengthen immunity.
When the first signs of pathology appear, you should immediately visit a doctor and undergo treatment. This will prevent the occurrence of a chronic form of the disease, a malignant process and cancer.
Methods for diagnosing cystitis
The diagnostic examination begins with identifying the background of the disease (history) and assessing the present symptoms.
An integral part of diagnosis is laboratory monitoring of urine:
- General, bacterial.
- Microbiological – tank seeding for flora.
- Antibiotic resistance.
- Monitoring of non-centrifuged urine using a hematocytometer.
- A special rapid test for cystitis is carried out - leukocyte and esterase.
Possible instrumental methods include ultrasound, cytoscopic and x-ray examination, uroflowmetry and biopsy.
Women are advised to undergo examination by a gynecologist to rule out sexually transmitted infections.
Laboratory and instrumental examination indicators help doctors differentiate cystitis from other diseases (pyelonephritis, prostatitis, urethritis, urolithiasis and other urological problems). But based on a number of key points in the manifestation and localization of symptoms, it is possible to independently suspect the development of an undesirable pathology. Let's take a closer look at their differences.
Antibacterial therapy
Antibacterial drugs are used to treat diseases of the urinary organs. The main goals of antibiotic therapy are to prevent the development of complications, prevent the transition of an acute process to a chronic one, quickly relieve symptoms and restore ability to work.
Antibiotics for pyelonephritis and cystitis are prescribed depending on the identified pathogen. To clarify the pathogen, urine culture is performed to determine the flora and sensitivity to antibiotics. The causative agents of these diseases can be various microorganisms.
| Causative agents of cystitis | Causative agents of pyelonephritis |
Nonspecific flora
Specific flora
| Nonspecific flora
|
We treat pyelonephritis
According to the latest recommendations, fluoroquinolones are the first-line drugs for uncomplicated pyelonephritis. Most often it is recommended to take cefixime 400 mg per day or levofloxacin 0.5-0.75 once a day. In previously untreated patients, ciprofloxacin or norfloxacin may be used. Second-line drugs are amoxicillin in combination with clavulanic acid. It is used at 625 mg (1 tablet) 3 times a day.
In severe cases of pyelonephritis, treatment is carried out in a hospital with parenteral administration of drugs. Antibiotics from the carbapenem group are prescribed - meronem, ertapenem. Amikacin and levofloxacin can be used. In pregnant women, it is recommended to use the drugs cefibuten, cefixime, cefotaxime or ceftriaxone. For fungal infections, fluconazole and amphotericin are used.
Antibiotic therapy is carried out for 7-14 days, depending on the severity of the disease.
We treat cystitis
In case of cystitis, it is necessary first of all to exclude specific flora. If the disease is nonspecific, drugs of the fluoroquinolone group, protected penicillins or third-generation cephalosporins are prescribed. The most commonly used fluoroquinolones are levofloxacin and ciprofloxacin. Among penicillin drugs, amoxicillin is preferred in combination with clavulanic acid. Of the cephalosporins, preference is given to cefixime and ceftibuten.
For a specific infection, macrolides, metronidazole, tetracyclines and fluoroquinolones are preferred. When chlamydia is detected in tests, macrolide antibiotics are used. Trichomonas are most often sensitive to metronidazole. Treatment of ureaplasma is carried out with macrolides, tetracyclines or fluoroquinolones.
Treatment with antibiotics for cystitis is carried out in short courses of 3-5 days. The exceptions are pregnant women, patients with concomitant diabetes mellitus, patients over 65 years of age, the specific nature of the disease, and a chronic form of infection. In these patients, treatment usually continues for 7-10 days.
In the treatment of pregnant women, it is best to use cephalosporins or ampicillin in combination with clavulanic acid. The use of fluoroquinolones is contraindicated. To treat chlamydia in pregnant women, macrolides can be prescribed, and in the second trimester, azithromycin.
After completing the course of antibacterial therapy, herbal preparations with anti-inflammatory properties continue to be used for a long time.
For urinary infections, herbs that have a diuretic and antibacterial (uroseptic) effect are used. Herbs also help normalize microflora after the destructive effects of antibiotics.
- Herbs that have a diuretic effect: corn silk, bearberry, black currant, horsetail, juniper, flax seeds, rose hips.
- Herbs that relieve inflammation and have antibacterial properties: bearberry, oats, yarrow, parsley root, cornflower, calendula, corn silk, knotweed.
Kidney tea, which contains orthosiphon, is often used to treat infection. Orthosiphon staminate is a herb that grows in Southeast Asia, the Caucasus and Australia. It has a diuretic and potassium-sparing effect, and is a good antispasmodic. Other urological fees, Brusniver, Canephron, etc. may also be used. Many herbs are found in traditional medicine recipes.
What are the differences between cystitis and pyelonephritis?
Both diseases are characterized by damage to the genitourinary system. Their signs are quite similar. How to distinguish cystitis from pyelonephritis is helped by their severity and localization.
- With inflammatory damage to the urinary bladder, the severity of general symptoms, in most cases, is insignificant. The prevailing local symptoms are dysfunctions in the urinary system: dysuria, disturbances in mictions and detrusor functions, causing additional pain, a portion reduction in urine output per miction, the presence of false (imperative) urges, etc.
- Signs of the development of renal pathology - pyelonephritis are characterized by the severity of general symptoms - high temperatures, chills and the manifestation of hyperhidrosis (sweating), clear signs of intoxication (loss of strength, extreme tiredness and fatigue, insomnia, insomnia and poor appetite) due to the influence of pathogenic toxins. Painful symptoms of various types (paroxysmal, aching or dull) are localized in the lumbar area in the projection of the affected kidney. Acute pain syndrome, in the form of renal colic, can provoke stones that block the urethral lumen.
Dysuric signs appear only in the case of secondary development of inflammatory processes in the bladder.
Difference in treatment principles
To treat pyelonephritis, diuretics, painkillers and antiseptics are used. The principle of treatment for cystitis is the same, but antispasmodic medications are additionally prescribed.
Medicines
Drugs for the treatment of cystitis:
- Antibiotics: Ceftriaxone, Monural, etc. Destroy pathogenic microflora. The most commonly used medications are the cephalosporin group.
- Anti-inflammatory: Cyston, Phytolysin, etc. Relieve inflammation in the bladder, providing an antiseptic effect.
- Diuretics: Nephrosten, etc. Increase diuresis, accelerating the elimination of pathogenic microflora.
- Antispasmodics: No-shpa, Spazmalgon, etc. Relax smooth muscles.
- Antiprotozoal: Metronidazole, Trichopolum, etc. They affect protozoa and are used to treat Trichomonas and other intracellular parasites.
- Antifungals: Diflucan, Mycomax, etc. Get rid of candidiasis infection, which often penetrates through the urethra into the bladder.
Medicines that are used to eliminate pyelonephritis:
- Uroantiseptics: Furadonin, Furagin, Palin, etc. Have an antimicrobial effect.
- Anti-inflammatory and improve kidney function: Canephron, Urolesan, etc.
- Loop diuretics: Furosemide and others have a diuretic effect.
- Painkillers: Tempalgin, Baralgin, etc. Relieve severe symptoms.
Traditional methods
Herbal medicine is used as an auxiliary method of treatment. For cystitis, bearberry is used, which has an anti-inflammatory and diuretic effect. Additionally, chamomile and oregano are used. All ingredients should be mixed and taken in the amount of 1 tbsp. l. Then pour 300 ml of boiling water and leave for 1 hour. After filtration, you need to take 100 ml of infusion 3 times a day.
Birch buds and horsetail are most often used to treat pyelonephritis. 2 tbsp. l. the mixture of raw materials must be poured with 450 ml of boiling water and left for 50 minutes. Then filter and take 100 ml daily 4 times a day. The course of treatment is from a week or more.
To improve the condition of the kidneys, a mixture of St. John's wort and oregano, which should be taken in the amount of 1 tbsp, is also suitable. l. and pour 400 ml of boiling water. You need to infuse the liquid for an hour. After filtration, take 200 ml 2 times a day.
For cystitis, bearberry is used, which has an anti-inflammatory and diuretic effect.
Diet
For cystitis and pyelonephritis, it is necessary to follow a protein diet. It is recommended to reduce the consumption of salt, chocolate, fatty and fried foods. It is important to drink more fluids and include fermented milk products, cereals, fresh vegetables and fruits in the menu.
It is useful to enrich the diet with cranberry juice, which increases diuresis and helps cleanse the kidneys and bladder.
It is advisable to steam all dishes and add a minimum of oil. It is necessary to include vegetarian borscht, fish and Lenten cookies in the menu.
Distinctive signs of bladder inflammation and prostatitis
The nature of the clinical state of both diseases will tell you how to distinguish cystitis from prostatitis. Often, especially in older men, these two pathologies provoke each other, since the organs (MP and prostate gland) are in close proximity.
So, the symptoms may have identical manifestations. To make the most accurate diagnosis, you need to pay attention to special points.
- Dysuric signs of bladder damage are accompanied by frequent voiding with cutting symptoms at the beginning and end of urination. However, the volume of urine may not always decrease. Pain during movements intensifies, localizing in the area of the lower triangle of the abdomen. Body temperature occurs very rarely. It is possible for the infection to spread to the overlying parts of the urinary system.
- With prostatitis, dysuric problems are expressed by frequent false urges with a sharp reduction in the volume of urine output - a weak stream, urine output drop by drop. Soreness manifests itself in the rectum, groin or scrotum area. An increase in temperature indicators is not typical. The infectious process does not spread, but can cause the development of prostate cancer, adenoma, or the formation of stones. Therefore, it is very important to determine in time whether cystitis or prostatitis is the cause of the patient’s illness.
Medicines
Drugs that are most often used in the treatment of pyelonephritis and cystitis:
- antibiotics: Monural, Palin, Nolitsin, Ciprofloxacin, Nitroxoline (destroys fungi);
- urological antiseptics: Monurel, Furadonin, Cyston, Canephron, Fitolysin;
- painkillers: Pentalgin, Tempalgin, Uropirin, Butadione;
- antispasmodics: No-shpa, Drotaverine, Papaverine, Duspatalin;
- anti-inflammatory drugs: Nurofen, MIG, Meloxicam, Nimesulide, Voltaren;
- antipyretic medications: Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Ibuklin, Nurofen;
- detoxification agents: Enterosgel, Polysorb, Filtrum;
- diuretics: Hypothiazide, Veroshpiron, Furosemide, Lasix;
- immunomodulators: Timalin, Uro-Vaxom;
- drugs that activate blood circulation in the kidneys: Heparin, Curantil;
- suppositories: Voltaren, Papaverine, Betiol, Sintomycin;
- probiotics: Linex, Bifiform, RioFlora Immuno, Acipol, Bifidumbacterin.
Among the drugs used in the treatment of pyelonephritis and cystitis is the urological antiseptic Monurel.
The urologist (or nephrologist) prescribes medications, taking into account the form, severity of pyelonephritis and cystitis, age, weight, and gender of the patient. The drug Biseptol has been popular for a long time, but today there are many drugs that are more effective than this drug from the sulfonamide group.
Complex herbal preparations Monurel, Cyston, Canephron N have proven themselves to be excellent.
Differences between the symptoms of cystitis and urethritis
Both diseases are characterized by the development of focal inflammatory reactions in the mucous membrane of organs - the reservoir cavity of the bladder and in the cavity walls of the urethra. In addition, the causes of the disease and symptoms are almost the same. But there is still a difference between cystitis and urethritis, and their timely identification will significantly reduce the duration of therapy.
The signs of one and the other pathology are largely identical. In both cases, similar dysfunctions in the processes of urination are noted.
Attention should be paid to the fact that with urethritis, urine does not have a specific odor, pain is local in nature, manifests itself mainly in the pubic area, mucous purulent discharge from the urethral canal is noted and inflammation can spread to the mucous membrane of the vaginal cavity, and the addition of bacterial flora often provokes the development of bacterial vaginosis.
It is difficult even for a specialist, let alone a patient, to independently identify a disease based on signs alone. The pathology is usually clarified using a diagnostic method.
Why are antibiotics needed?
Pyelonephritis and cystitis are diseases that have long been known to mankind. It can be caused by different types of organisms - viruses, bacteria or fungi. In the vast majority of cases, the causative agent of the disease is a bacterial bacillus, and therefore with a high degree of probability we can talk about bacterial cystitis. A fungal infection can also cause inflammation, but this usually occurs against a background of reduced immunity. Finally, penetration of viruses into the urinary organs is only possible through unprotected sexual contact from a partner who is himself a carrier of the infection. In this case, most often we are talking about a sexually transmitted disease, and cystitis is only its complication or consequence.
Distinctive signs of urolithiasis (urolithiasis) and cystitis
These two diseases are closely related, as they develop as a result of inflammatory processes provoked by stone formation and spreading from the bladder reservoir to the kidney tissue. It is changes in the clinical picture that will tell you how to distinguish cystitis from urolithiasis.
- Inflammation of the parenchymal renal tissue causes failure of its functions, manifested by an increase in capillary capacity and the accumulation of minerals that form stones in the pelvic cavities of the kidneys. The opposite scenario is also possible - a traumatic one, when the removal of stones from the kidneys causes an irritating effect on the mucous tissue, its thinning and inflammatory reactions, manifested by signs of inflammation of the bladder.
- Clinical symptoms for both pathologies are very similar. It manifests itself with the same cutting and burning pains during mictions, caused by irritation from moving stones and sand, structural changes in the urine and blood impurities in it. The main distinctive symptoms of these pathologies are due to the manifestation of the symptom F.I. Pasternatsky. Light tapping in the lumbar area in the projection of the kidneys, with urolithiasis, is reflected by pain, which is not typical for cystitis.
- Concretions can also form in the reservoir cavity of the bladder, causing its inflammation. The same cutting pains occur, but they can radiate - in women to the groin area, in men to the groin and head of the phallus. Pain syndrome can occur in both pathologies, due to blockage of the urethral cavity by stones, abruptly interrupting the process of urination and a feeling of incomplete urine output.
- In case of urolithiasis, changing the position of the body can correct the situation by resuming acts of miction, which is impossible with inflammatory lesions of the bladder.
As you can see, distinctive signs of diseases exist. At first glance, differentiation is simple. But recognizing the disease in reality can be very difficult. Doubts and comparisons will take a lot of time. Self-diagnosis will lead to incorrect treatment, significantly worsen the condition and increase the risk of developing dangerous complications. Trust your health to a specialist.
Treatment
Only complex treatment of cystitis and pyelonephritis can most effectively eliminate inflammatory processes. For this purpose, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are used. Also, in the treatment of pathology, doctors use symptomatic remedies.
Medicines for the treatment of cystitis and pyelonephritis
Photo from the website apteka.rozetka.com.ua
The basis of drug treatment is antibacterial drugs. For pyelonephritis and cystitis, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used. The doctor may prescribe one of the following remedies:
- Ceftriaxone. Refers to cephalosporins. Taken once a day, 0.5-1.0 g. Administered intramuscularly. For pain relief, it is better to dilute the medicine in a 1% lidocaine solution. In severe cases, intravenous injections are used.
- Spiramycin. Effective tablets for pyelonephritis and cystitis. This macrolide has a wide range of effects on bacteria. You need to drink 1-3 tablets 3 times a day at regular intervals.
Non-steroidal drugs are used to relieve inflammation. The most popular suppositories for pyelonephritis and cystitis are Indomethacin. To relieve pain, use 1 suppository twice a day. To enhance the therapeutic effect of suppositories, treatment is supplemented by taking the tablet form of the drug.
Antispasmodics will also help eliminate discomfort. For this purpose, No-shpa and Spazoverin are prescribed. Congestion in the kidneys and bladder is treated with Cystenal or Canephron.
Diet for cystitis and pyelonephritis
Nutrition for pyelonephritis and cystitis differs from the usual diet. For successful therapy, the amount of proteins is reduced (to 70 g per day). The consumption of table salt is also sharply limited, pickled foods, flour products and spices are excluded. Read more about diet for pyelonephritis→
Nutrition for cystitis and pyelonephritis in women and men consists of:
- vegetable soups;
- lean varieties of meat and fish;
- milk and fermented milk products, with the exception of cheeses;
- eggs;
- side dishes of cereals and pasta;
- vegetable salads;
- fresh fruit.
The diet for cystitis and pyelonephritis also concerns the method of preparing the dish. All food can only be boiled, stewed, baked and steamed. Avoid eating canned and smoked foods, as well as any fast food.
Folk remedies for cystitis and pyelonephritis
With the permission of the attending physician, therapy can be supplemented with traditional methods. For cystitis and pyelonephritis, it is recommended to drink such effective herbs as:
- bearberry;
- lingonberry leaves;
- bear ears;
- violet;
- hop cones;
- flax seeds.
Herbal medicines for pyelonephritis and cystitis should also not be taken on your own. Before using them, it is necessary to consult with a specialist so as not to aggravate the course of the pathology and lead to complications. Read more about herbs for pyelonephritis→
Physiotherapy for cystitis and pyelonephritis
During the convalescence period, physiotherapy methods are used to speed up the healing process. Usually prescribed:
- UHF or microwave;
- exposure to weak direct currents;
- pulse therapy;
- baths;
- massage.
During the recovery period, it will be useful to use mineral waters, such as Essentuki No. 20, Naftusya, Berezovskaya. Spa treatment is also indicated.
ethnoscience
Medicinal herbs are popular in the treatment of pyelonephritis and cystitis. The following products are prepared from them:
- Bearberry decoction: 25-30 g of dry leaves per 0.5 liter of water. Boil in a water bath for 15-20 minutes, filter. Take 2 tablespoons 5-6 times daily with alkaline mineral water.
- Decoction of lingonberry leaves: 4 tbsp. l. raw materials per 1 glass of water. Boil also for 15-20 minutes. Drink 1-2 tbsp every day. 4-5 times.
- Cranberry or lingonberry juice: 0.5 kg of fruit per 3 glasses of water. Cook the pureed berries for 10-15 minutes, strain and sweeten. You can drink up to 3-4 glasses a day.
Diet
Patients are prescribed salt-free dietary table No. 7 (in the remission stage - No. 15). Main principles of nutrition:
- Drink plenty of fluids - up to 2-3 liters of urological decoctions, fruit drinks.
- Maximum carbohydrates, minimum proteins, animal and vegetable.
- Small but frequent meals (up to 6-7 times).
- Priority goes to boiled, stewed and steamed dishes made from lean meat, fish, and vegetables.
- Daily inclusion of fresh vegetables, herbs, and fruits in the diet.
- Complete abstinence from alcohol, fried foods, smoked foods, pickles, marinades, hot spices, chocolate, cakes, coffee, soda.