Thursday, October 24, 2019
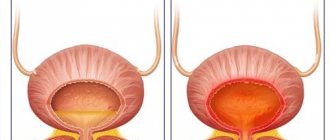
Cystitis is a disease in which inflammation affects the bladder. Due to its anatomical features, it affects women more often than men. The disease can be caused by various reasons, but in general it is provoked by bacteria, viruses or fungi. The disease is quite painful, reducing the quality of life and causing significant discomfort. Therefore, it is important to know how to prevent the occurrence of pathology and whether cystitis is transmitted from an already sick person.
basic information
Before we tell you whether cystitis is transmitted from woman to man and back, it is necessary to tell you what this disease actually is.
In the medical literature, cystitis refers to inflammation of the bladder, and in urology this term is used as the name for a urinary infection, as well as disruption of the said organ and changes in urine sediment.
Due to the fact that the mentioned disease is caused by certain types of bacteria and is an inflammation that occurs on the walls of the bladder, it is logical to assume that these same microorganisms can spread to another organism.
What is honeymoon cystitis?
Defloration cystitis, or honeymoon cystitis, is a form of the disease that develops after the first sexual intercourse. Both partners may be virgins, but unpleasant symptoms appear immediately after coitus. To understand whether a man can infect a woman with cystitis, we need to take into account the peculiarities of intimate physiology.
In women, the disease is associated with a violation of the vaginal microflora, the act of defloration, microcracks in the skin and mucous membranes during coitus, and mixing of microflora. So it is quite possible to contract cystitis from a man, or rather, from sexual intercourse itself.
In men, cystitis can occur during contact even with a virgin partner. Often inflammation is a consequence of congestion, diseases of the genital organs, stones in the urethra or on the walls of the bladder.
Honeymoon cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder walls that occurs in a young girl after her first sexual experience.
The main symptoms appear a few hours after intimacy. The reason for this is the penetration of microorganisms into the area of the genitourinary system, since the obstacle (hymen) has disappeared.
The disease cannot be ignored; the likelihood of becoming chronic increases. In the future, intimacy has a chance to be accompanied by symptoms of cystitis, which may affect the psychological level.
Penetration of infection
Is cystitis transmitted from woman to man? As mentioned above, the disease in question is inflammatory in nature. And, as you know, inflammation itself is not contagious, since it can only harm the patient in whose body it developed. However, a disease such as cystitis is caused by bacteria that have the ability to pass into the body of another person.
So is cystitis transmitted from woman to man? According to experts, under favorable conditions, microorganisms that provoke inflammation of the bladder can be transmitted from one patient to another.
How does infection occur?
Is cystitis transmitted from woman to man? It is known that the female half of the population is more susceptible to this disease. This is due to the characteristics of the female reproductive system.
The urethra in women has a different structure from that of men, and the likelihood of pathogenic microorganisms entering it is much higher. The infection process begins with bacteria entering the vagina. Hence, there is a high probability that microorganisms pass into the urethra. Infection occurs if the bacterial background of a woman’s reproductive system has been disrupted.
In men, infection occurs differently. Most often, after infection, the disease does not manifest any symptoms, but transmission of cystitis to another woman is possible. This means that the man becomes a carrier. When having sexual intercourse with a healthy woman, there is a possibility of transmitting the pathology.
What bacteria can trigger the development of cystitis?
There are several types of opportunistic flora that can cause cystitis and are sexually transmitted:
- staphylococcus;
- mycoplasma;
- coli;
- candida;
- ureaplasma;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- Proteus;
- Trichomonas;
- gonococcus;
- chlamydia.
In women, these pathogens, after entering the vagina, can cause vaginitis, colpitis, cervicitis or an inflammatory process in the urethra. Only after this does the infection reach the bladder and can trigger the development of cystitis.
It is worth noting that if the immune system is in good condition, inflammation can be avoided, but there is a possibility that the infectious focus will persist in the body for a long period of time.
Often, patients who have recently changed partners or have changed several sexual partners in a short time face a relapse of the disease, due to the likelihood of transmission of pathogenic flora from a partner. Using a barrier method of contraception (condoms) significantly reduces the risk of transmitting pathogens.
There is a possibility of cystitis occurring when the necessary hygiene measures do not take place after anal sex. That is, if vaginal sex is immediately practiced after anal sex, there is a risk of E. coli entering the vagina, one of the causes of bladder inflammation.
What factors contribute to the spread of bacteria?
Factors that allow infections to spread throughout the body include:
- hypothermia;
- failure to comply with the rules of basic personal hygiene;
- suppression of the immune system;
- acute or chronic diseases of the genitourinary system;
- promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- dysbiosis.
What are the risks of getting infected? What is the danger?
The question of whether cystitis is contagious has been sorted out. In addition to knowing whether cystitis is contagious or not, it is important to understand that frequent changes of sexual partners and the presence of a chronic form can trigger the acute stage of the disease.
Therefore, promiscuity is one of the contributing factors: pathogenic microorganisms will be passed on to you from your partner. However, the presence of an infectious pathogen alone is not enough for the occurrence of a disease.
If there are no structural, as well as morphological and functional changes in the walls of the bladder, infection does not occur: bacteria are transmitted, but this does not affect health in any way.
Women become infected if there are active inflammatory processes, as well as disturbances: phagocytic activity of the mucous membranes, hydrodynamic protection, mucus production by the periurethral glands, urine osmolarity, antibacterial activity of some urine ingredients. Infections + presence of “vulnerability” = damage to the least protected and nearby organs.
The situation gets worse if a woman:
- weakened immune system;
- constant hypothermia occurs;
- presence of chronic infectious diseases;
- stress;
- the period before/after menstruation (when the ascending tract is most vulnerable);
- pregnancy;
- synthetic underwear;
- complete disregard for personal hygiene;
- There is a lack of vitamins and poor nutrition.
Answering the question of whether it is possible to become infected with cystitis, one cannot help but say that the probability of infection by bacteria is very high, because the peculiarity of the female body is a thick and short urethra, and therefore bacteria from the vagina, which can be sexually transmitted, enter the bladder through the urethra .
Features of the structure of the female body
Is cystitis contagious for a man, or more precisely, how does pathogenic microflora spread? Representatives of the stronger half of humanity can get cystitis through sexual intercourse extremely rarely, because the ascending route of infection is not typical for them (the infection does not spread upward).
This depends on the anatomical features of the structure of the urethra: it is narrow and long, and microorganisms are not able to pass through it unhindered. Therefore, the question of whether cystitis is transmitted from a woman to a man has a negative answer, but one should be wary of pathogens.
Fact! The possibility of contracting bacteria that cause cystitis is affected by a sudden or severe weakening of the immune system (for example, HIV, oncology, taking strong antibiotics, immunosuppressants).
Features of the structure of the male body
What is the danger of the disease? The disease can occur in the form of isolated episodes that can be easily stopped, or it can have serious complications. With cystitis, kidney damage often develops.
Plus, a feature of inflammatory processes in the lower organs of the urinary system is a close relationship with diseases of the reproductive system. And this can lead to the mutual occurrence of urethritis in women and men.
Every 4th woman who has suffered more than 3 exacerbations of the disease is subsequently diagnosed with bladder cancer.
Types of uropathogens
When considering the causes of the disease, two main groups of infectious processes that cause cystitis can be distinguished:
- specific – caused by sexually transmitted infections;
- nonspecific – caused by conditionally pathogenic and pathogenic nonspecific microorganisms.
Separately, postcoital cystitis can be distinguished - it is caused by nonspecific microflora and is associated with congenital or acquired abnormalities in the anatomical structure of the genitourinary system.
Nonspecific cystitis
Most often, the causative agents of this species are: Escherichia coli, Proteus, Klebsiella, staphylococci, streptococci.
In addition, ureplasma and mycoplasma are of no small importance. They are not classified as sexually transmitted diseases, but are opportunistic microorganisms that cause recurrent cystitis.
Also, E. coli is a conditionally pathogenic bacterium, since it is a normal representative of the intestinal microflora. But this is the most common causative agent of genitourinary tract infections. This occurs due to poor personal hygiene or due to the anatomical structure. It enters the lumen of the urethra, then penetrates the bladder and provokes inflammatory symptoms.
The following factors contribute to the penetration of E. coli into the urinary tract:
- Hormonal imbalance due to taking hormonal drugs, diseases of the endocrine system.
- Hypothermia of the body, especially local.
- A diet with insufficient fruits, vegetables, proteins and an excess of saturated fats and carbohydrates.
- Clothes and underwear are smaller in size, which impairs blood supply.
- Using panty liners and not replacing them in a timely manner. Pathogenic microflora forms on their surface. There should be a change every 1-2 hours.
- Abnormal stool, frequent dysbacteriosis.
- Neglect of personal hygiene rules.
- A sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work, which causes congestion in the pelvic organs.
- Unconventional types of sex.
The route of infection can be not only through the urethra, but also through the blood and lymph.
Local hypothermia is one of the most common causes of nonspecific cystitis
This type of cystitis accounts for 60-80% of cases. This is the most common type of UTI - urinary tract infection. With proper and timely therapy, this disease quickly stops without causing harm to the body or leading to complications.
It is impossible to become infected with a nonspecific type of cystitis.
Specific cystitis
This type occurs due to infection with sexually transmitted diseases.
If specific cystitis is detected, then the probability of contracting it through sexual contact is about 80%. The main infections that cause inflammation in the urinary canals:
- Chlamydia is one of the common STDs. The course of the disease is asymptomatic, there are practically no clinical manifestations. The main symptom is the appearance of discharge with an unpleasant odor and genital itching. Patients with a genetic predisposition to the disease may develop asymmetric arthritis and uveitis.
- Gonorrhea - the main symptoms of the disease are purulent discharge of a thick consistency from the vagina and urethra, itching, burning, pain during sexual intercourse.
- Trichomoniasis - it is accompanied by symptomatic discharge: watery or foamy in a large volume, yellowish in color. In men they can come from the urethra, women tend to have vaginal secretions. Patients complain of itching and ulcerative manifestations on the mucous membranes of the genital organs.
- Mycoplasmosis.
Only specialists, a gynecologist and a urologist, after a series of examinations, can accurately distinguish sexually transmitted infections from cystitis, which is caused by them.
Prevention of cystitis
Since the infection that causes cystitis is most often transmitted during sexual intercourse, in order to prevent infection, special attention must be paid to sexual culture and safety in this area. Of course, sex life is an important aspect in a relationship and should not be neglected, but it is still necessary to adhere to certain rules of sexual behavior.
First of all, it is necessary to be selective in choosing a sexual partner, remain faithful to him, and refuse promiscuous sexual contacts. It has been proven that people who actively change sexual partners become infected much more often than those who adhere to monogamy. In addition, protection is very important, for example, the use of barrier contraception (condoms), which not only prevent unwanted pregnancy, but also protect against possible infections.
It is important to observe the rules of hygiene immediately before sex. And if a couple practices unconventional types of sex (for example, anal), after such contact it is also necessary to perform hygiene procedures.
If certain circumstances occur, for example, during menstruation or in the presence of microflora disorders (thrush), infectious diseases of the reproductive system, it is recommended to refrain from intercourse until these problems are resolved.
Other preventive measures deserve no less attention, such as:
- Intimate hygiene, in particular, regular washing of the genitals, frequent change of underwear.
- Timely elimination of sources of infection (for example, caries).
- Regular visits to the toilet when there is a urge to urinate (at least 5 times a day).
- Be careful when visiting public toilets and showers.
- Thorough hand washing after returning from the street or contact with a potential source of infection.
- Protection against hypothermia.
- Active lifestyle, giving up bad habits.
- Proper and varied nutrition.
By regularly following the rules stated above, the likelihood of developing cystitis is significantly reduced.
Risk factors
Most often, cystitis is transmitted from a man to a woman during coitus, especially if intimate intercourse took place before the onset of menstruation or immediately after it. Symptoms of this disease in a representative of the fairer sex may occur after sexual relations with a sick man during a period when her immunity was reduced.
It should also be said that signs of cystitis are often observed in pregnant women after sex with an infected man.
How often does cystitis become infected during sexual intercourse? According to experts, this happens in 8 cases out of 10. As a rule, bacteria begin to actively multiply in a woman’s urogenital canal in the presence of the following unfavorable factors:
- insufficient strict adherence or non-compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- the presence of several partners at the same time or their frequent change;
- a casual love affair with a person diagnosed with cystitis.
To avoid such infection, experts recommend using first-level contraceptives (condoms) during sexual intercourse.
Sexual life during illness
It is recommended to refrain from sexual contact while fighting cystitis, since viruses and bacteria can enter the partner’s body, causing him to develop a similar problem.
In addition, cystitis is accompanied by pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen. An exacerbation of the disease may also occur if hygiene rules are not followed before and after sexual contact.
Cystitis is accompanied by pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen.
It is strictly forbidden to have sex during the acute course of the disease, when it is necessary to take antiviral and antibacterial drugs.
Prevention measures
If sex with cystitis does take place, you need to adhere to several mandatory rules:
- before sex, you need to wash yourself thoroughly (it is advisable not to use soap; it can be replaced with special gels for intimate hygiene or folk remedies based on calendula and chamomile);
- do not use intimate lubricants and gels;
- you should choose a position in which the pressure on the bladder will be minimal;
- it is necessary to use barrier contraception;
- Immediately after sex, you need to take a shower and perform hygiene procedures for the genitals.
Compliance with these rules will help to avoid discomfort and exacerbation of the disease after sexual intercourse.
Main causes of the disease
Cystitis is polyetiological, that is, multi-cause. The reasons may be different:
- Pathogenic intestinal microflora: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, enterococcus, staphylococcus.
- Causative agents of sexually transmitted infections: chlamydia, ureplasma, Candida fungi, herpes virus.
- Infectious process after surgical/instrumental intervention, due to damage by streptococci, salmonella, herpes virus, adenoviruses.
- Exposure to toxins and non-infectious agents (chemical, cold, radiation, allergic, neuropsychic, metabolic, parasitic).
Fact! As a rule, the primary disease without complications is infected with the same groups of microorganisms, transmitted in different ways, but the chronic form is a mixed pathogenic flora.
Favorable factors for the development of the disease are injuries to the mucous membranes of the bladder, impaired normal blood circulation, hypothermia, fatigue, and hormonal imbalances. In addition, cystitis can be caused by infrequent urination, which leads to stagnation. Based on the main causes and factors, you can answer the question and understand how cystitis is transmitted.
Is cystitis transmitted from woman to man?
To know for sure whether cystitis is transmitted from woman to man, it is necessary to take a closer look at this disease, which is what we will do in this article.
Cystitis is accompanied by an inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the bladder, making it difficult to urinate. It becomes more frequent and very painful (the pain that accompanies it in the lower abdomen is nagging in nature).
Reasons for the development of cystitis
Cystitis can be either an independent disease or a consequence of others: kidney disease, inflammatory processes in the ureters, prostate dysfunction.
The form of the disease is:
- acute - accompanied by an increase in temperature, appearing and disappearing symptoms of cystitis, requires immediate help, treatment lasts 7-10 days;
- chronic - exacerbations are periodic, frequent and often painful urination is an almost constant concern. During the period of exacerbation, the symptoms are the same as in the acute form.
Symptoms
The disease manifests itself by the presence of characteristic symptoms:
- pain in the lower abdomen (pulling or aching);
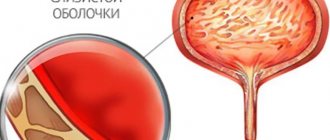
- blood after urination. Blood in the urine can be invisible to the eye (with a small number of red blood cells) and noticeable to the eye (due to a significant admixture of blood, the urine changes color). This symptom is associated with injury to the cervical canal of the affected organ.
- sharp pain at the end of urination. Pain occurs when urine passes through the urethra, and pain occurs due to pinching of the nerve endings located in its walls.
- frequent urge to urinate. Frequent urges arise due to the high excitability of nerve cells (swelling as a result of inflammation compresses the nerve fibers, the tone of the bladder increases, and the volume decreases).
- a feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied.
Urine analysis reveals microorganisms: streptococci, staphylococci, gonococci.
Routes of infection
These pathogens usually penetrate the bladder through the ascending route, and when it is not completely emptied, the bacteria in it begin to actively multiply. With viral cystitis, the viruses present in the body are activated. Cystitis can be caused by:
- coli;
- Trichomonas;
- fungal infection;
- Proteus;
- chlamydia;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- viruses.
Pathogens can enter the body in several ways, the main ones being:
- urethra;
- chronic pyelonephritis;
- kidney tuberculosis;
- defloration;
- rough sex;
- diseases that have no connection with the urethra (tonsillitis, dysbacteriosis, furunculosis).
In some cases (approximately 20%), cystitis can be non-infectious and develop: as a result of a burn with a rinsing solution; under the influence of foreign bodies (urinary stone); under the influence of drugs.
Cystitis in men
There is a misconception that cystitis only affects women, but this opinion is erroneous. Men suffer from this disease less often due to peculiarities in the anatomical structure; the symptoms are not pronounced.
According to statistics, every fifth woman suffers from cystitis, and one in two hundred men suffers from cystitis.
In most cases, the infection enters the bladder of men hematogenously (through the blood), and the causes may be:
- hypothermia;
- stagnation of urine;
- alcohol abuse;
- spicy food;
- stress;
- reduced immunity;
- neurosis;
- poor hygiene.
Development mechanism
Once the body’s protective properties are weakened, susceptibility to infection increases. Microorganisms entering the urethra, and from there into the bladder, cause inflammation.
- During sexual intercourse with a partner suffering from bladder inflammation, microorganisms enter the healthy body. However, it is more difficult for men to contract cystitis: their urethra is longer and it is more difficult for microorganisms to reach the bladder.
- Sometimes it happens that a woman suffering from cystitis undergoes a course of treatment and takes all the medications prescribed by the doctor. After treatment, the signs disappear, but after several sexual acts the symptoms of the disease reappear. In this case, the sexual partner is the source of infection.
- The disease becomes chronic, as the man is constantly infected with a bacterial (possibly fungal) strain. First, there is a bacterial imbalance in the vagina, which can be triggered by pregnancy, stress and poor hygiene.
The next stage is the development of bacterial vaginosis (often it is chronic, when periods of exacerbation alternate with periods of remission).
After this, colpitis and vaginitis (inflammation of the vagina) are observed. In this case, there may be purulent discharge and pain in the lower abdomen and external genitalia.
Next, the cervix is involved in the process, and after that urethritis and cystitis develop.
So is cystitis sexually transmitted?
If one of the sexual partners is a carrier of any sexually transmitted infection, then he can transmit the pathogen to the other partner.
And this will provoke cystitis or its exacerbation, although cystitis itself is not sexually transmitted.
Bacteria that cause diseases of the urinary organs can be transmitted through sexual contact if one of the partners is a carrier of the infection. However, cystitis is not sexually transmitted and this is obvious.
Attention:
Source: https://udietologa.ru/tsistit/peredaetsya-li-tsistit-ot-zhenshhiny-k-muzhchine/
Signs of cystitis
Inflammation of the bladder can be acute or chronic. The occurrence of pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Changes in urination, frequent urination;
- Pain when passing urine;
- The genitals hurt and itching;
- It feels like the bladder is not completely emptied;
- Bloody discharge in the urine;
- Pus and mucus in the urine;
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
With cystitis, the bladder is affected, so any changes in urination and pain are a reason to visit a doctor.
What is the connection between cystitis and STIs?
This disease is not classified as an STD. It is a consequence of the transmission of infectious agents that can cause inflammation of the bladder from one partner to another.
When there is no appropriate treatment, the virus or bacteria quickly spreads in the urinary tract, resulting in symptoms of the disease.
To avoid the unpleasant consequences of inflammation due to STIs, it is necessary to treat existing diseases in a timely manner.
If there are initial signs, consult a doctor to prescribe adequate therapy.
It is imperative to be tested for the presence or absence of pathogens of various kinds of infections inside the body, especially in a situation where there has been a recent change of partner.
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) can cause inflammation of the bladder mucosa in women. Cystitis in this case is accompanied by a number of characteristic symptoms: burning in the vagina, pain when urinating, pain behind the pubis, pathological discharge.
Cystitis due to STDs in women may not appear immediately; it depends on the length of the incubation period of the disease.
Diagnostics
When a man and a woman come to you with signs of cystitis, the specialist will prescribe to both partners:
- Take a general blood and urine test. An increased level of leukocytes and red blood cells indicates inflammatory processes in the body. A blood test makes it possible to assess the general condition of the patient.
- Biochemical analysis of urine is carried out to diagnose the content of nitrates, salts, protein and other indicators important in making a diagnosis.
- A bacteriological analysis of urine is carried out to determine the type of pathogen and its resistance to antibacterial drugs.
- Ultrasound diagnostics and x-rays are two methods of instrumental research to determine the size, structure, condition of the bladder and other organs of the genitourinary system. Both methods allow you to confirm the diagnosis and identify possible complications.
- Cystoscopy and biopsy is a laboratory examination of bladder tissue to determine the cause of inflammation. It is used when other methods have failed to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe therapy.
The structure of the human reproductive system
Cystitis is inflammation of the genitourinary system. To understand what this pathology is, it is necessary to consider how exactly this system is structured in men and women.
Female genitourinary system
The pathology most often manifests itself in the fair sex, so cystitis is considered to be more of a female disease. This is due, first of all, to the structural features of the female genitourinary system. Thus, the urethra in women is shorter and wider, which means that it is easier for bacteria to penetrate through it into the bladder area.
Male genitourinary system
In a man, the urethra is much longer and has a rather narrow lumen. Therefore, it is much more difficult for the pathogenic infection to move through it and reach the bladder.
How is cystitis different from sexually transmitted diseases?
Other sexually transmitted diseases are transmitted through sexual contact, but cystitis has a slightly different method of infection. How is cystitis transmitted? It is possible to get the disease through sexual intercourse, but infection occurs indirectly.
Pathogenic microorganisms transmitted indirectly are not chlamydia or gonorrhea, which can be transmitted due to fusion, but bacteria of a different nature: staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli and others. In order to provoke their pathogenic action, special conditions are needed. They can remain in the patient’s body and not make themselves felt.
What is the difference from an infection?
The disease cystitis has many causes, but the main role is played by infections. Infectious diseases can be very different and manifest themselves in different ways. Bacteria that cause sexual pathological conditions include:
Infectious penetration into the body occurs as a result of sexual contact. When transmitting inflammation, the provoking factors are microorganisms: streptococci, Escherichia coli, staphylococci. They settle in the body and do not manifest themselves in any way until the appropriate conditions arise.
The structure of the genitourinary system in women
Most often, the question of whether cystitis is transmitted from woman to man is asked by representatives of the fairer sex. What is this connected with? The fact is that in most cases it is women who suffer from this disease. This is explained by the structure of their urethra. It is quite short and wide, which allows various bacteria and fungi to enter the bladder. As for men, their urethra is much longer and thinner. Therefore, they suffer from cystitis very rarely.
Infectious cystitis
To answer the burning question of whether cystitis is sexually transmitted, you need to know the nature of this disease. The difference between infectious inflammation and all other diverse diseases is that the cause is always the entry of pathogenic bacteria into the bladder.
Infectious cystitis is provoked by chlamydia, E. coli, herpes viruses, staphylococci, gonococci and many others. In nature, there is a huge variety of microorganisms that cause inflammation, but the bodies of many people successfully fight this disease - when viruses or bacteria enter, many men and women do not get sick due to strong immunity. People with weak immune systems suffer from cystitis very often.
Is it possible to get infected
Cystitis is an inflammatory process and is therefore not contagious. The infection that initiates this process and against which inflammation occurs is contagious. Among the possible ways of infection are:
- hematogenous (when pathogenic microorganisms are introduced into the bloodstream, for example as a result of surgical interventions);
- lymphogenous (when microbes enter the body through lymphatic vessels);
- ascending (microorganisms enter the body from the bottom up, that is, through the urethra to the bladder);
- descending (microbes enter the bladder from inflamed internal organs);
- contact (during direct contact during medical procedures (for example, installation of a catheter), including those aimed at examining the inner surface of the bladder).
Escherichia coli is a microorganism that acts as a causative agent of cystitis.
Among the possible microorganisms that act as causative agents of inflammation, the following are most often identified:
- coli;
- chlamydia;
- gonococcal infection;
- Trichomonas;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- Proteus;
- fungus.
Less commonly, the causative agent can be an adenovirus that affects the upper respiratory tract and is transmitted by airborne droplets, as well as parainfluenza and herpetic infections. Their presence in the body predisposes to impaired microcirculation in the bladder. This creates a favorable background for the development of subsequent bacterial inflammation.
Thus, the routes of infection with possible diseases against which cystitis occurs are diverse and depend on the pathogen that triggers the disease mechanism. This can be sexual, household, or even airborne transmission of a disease that will cause cystitis.
The causative agent of cystitis can be an adenovirus that affects the upper respiratory tract and is transmitted by airborne droplets.
Women
Women are most susceptible to inflammatory manifestations due to their different body structure from men. The anatomical structure of the female urethra is such that pathogens can easily and quickly penetrate through it to the inner surface of the bladder.
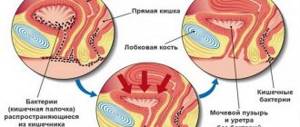
Thus, the ascending route of infection in women is most common. This happens due to the introduction of pathogenic microbes as a result of disruption of the microflora of the vagina or from the anus.
Men
In men, inflammation of the urethra and bladder is not as common as in women, and it is most common in the form of a descending mode of infection, i.e. transfer of infection from internal organs to the urinary tract. Despite this, there are cases of inflammation being transferred from a partner, so an ascending route of infection cannot be completely ruled out.
Children
Childhood cystitis is most common in preschool and early school age. Infection with pathogenic microorganisms occurs mainly due to non-compliance with personal hygiene rules. When favorable conditions for reproduction are created, microbes enter the urethra and cause severe inflammation.
Ways of transmission of the disease
Cystitis is a conditionally infectious pathology. That is, the inflammatory process itself is not transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one, but the bacteria that trigger this mechanism can easily migrate from one organism to another. Most often this happens during sexual intercourse, especially if a person is promiscuous, practices unprotected and unconventional sex (for example, switching from anal to vaginal penetration).
At the same time, we should not forget about household methods of infection.
Thus, a bacterial infection that provokes the development of cystitis can be transmitted through:
- standing water (for example, in a public swimming pool),
- contaminated dishes and household items,
- paper money,
- plumbing (toilets, showers, bathtubs).
It is also important to understand how an infection that enters the body can spread throughout the body and reach the bladder area.
The following ways of spreading pathogenic microflora are distinguished:
- Contact - during certain medical procedures, such as catheterization or cystoscopy.
- Rising. Initially, the infection enters the body through the external genitalia, then, as the number of the pathogen grows, the inflammatory process rises, and bacteria penetrate the bladder through the urethra.
- Descending. This method of spread often occurs with existing inflammatory diseases of other organs of the urinary system, for example, with pyelonephritis, when the infection “descends” into the bladder from the affected kidneys.
- Lymphogenic, when there is a focus of inflammation, from where the infection spreads throughout the body along with the lymph flow.
- Hematogenous, in which pathogenic microflora spreads through the bloodstream, for example, if a person has infectious diseases such as bronchitis, caries, sore throat.
The most common route of infection is upward. This option occurs in almost 70% of cases.
Is it possible to have sex with cystitis?
Doctors do not recommend having sex with this pathology. This is due to several reasons.
Firstly, a woman does not experience pleasure during contact, but rather experiences pain. Sexual interactions cause pain and itching in the lower abdomen and genital area.
Secondly, with regular intercourse, the treatment process can be complicated. During therapy, it is advisable to refrain from frequent sexual intercourse. This is due to the entry of pathogenic microorganisms into the urethra from the vagina.
Is cystitis transmitted from woman to man?
It is quite possible to infect your partner with cystitis. Most often, men become infected with cystitis during prolonged and regular sexual intercourse with a woman in whom this disease occurs in a chronic or acute form. It should be noted that if the immune system of the stronger sex is very strong, then they are not in danger of developing such a disease, since the bacteria die in the urethra, never reaching the bladder.
Now you know whether cystitis is transmitted from woman to man through sexual contact. It should also be said that if a woman continues to actively engage in sex during the acute or chronic course of this disease, then curing it will be problematic, even despite taking potent antibacterial agents. Therefore, many specialists recommend that their patients abstain from sexual intercourse during treatment and for several weeks after it.
Can a man infect a woman?
We told you above whether cystitis is transmitted from woman to man through sex. However, some representatives of the fair sex are also interested in whether this disease can be passed on to them from a partner. Most doctors give a positive answer to this question.
If a man’s genitourinary system contains bacteria that cause inflammation of the bladder, then during sexual intercourse they can easily enter the woman’s body. This is again due to the special structure of their urethra. Therefore, if a disease is detected, a man needs to undergo a full course of therapy with antibacterial and other agents. It is also advisable to abstain from any sexual intercourse or use contraceptives during treatment.
Cystitis during oral or anal sex
The spread of bacteria that cause inflammation occurs during lovemaking, these include:
- gonococci;
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasma;
- Trichomonas;
- coli.
It matters what type of sex partners have. If this is normal vaginal penetration, which occurs between trusted intimate partners, or the act is protected, then bacterial infection does not occur, and therefore pathologies in the urethral area do not occur.
It is not recommended to practice anal and vaginal intimacy in one act of intimacy if you have a weakened immune system, the presence of sexually transmitted infections and dysbacteriosis, as well as while taking antibiotic therapy. This practice can lead to mutual penetration of pathogenic flora and ultimately cause inflammation of the genitourinary tract. In this case, the catalyst for the onset of the disease will be E. coli.
Oral sex can lead to small microtraumas on the head of the penis, which will further contribute to the penetration of infection and the development of the inflammatory process.
Therefore, plunging into the abyss of passions and in pursuit of fleeting pleasure, you should not forget about your health.
Current issues
Is cystitis transmitted? Can you get infected through ordinary household items or not? The answer to these questions is simple. This disease is not transmitted through household contact. The toilet, personal hygiene items (razors, washcloths), soaps, and cutlery are not a means of transmitting the disease.
But it should be noted that through everyday life it is possible to become infected with various infections, which can provoke cystitis.
Is cystitis sexually transmitted or not? Although signs of the disease often appear immediately after sexual intercourse, it is impossible to catch inflammation of the bladder “through bed”. Why then do doctors advise abstaining from sex during the acute period of the disease? Sexual intercourse has only an indirect significance in infection.
Important! A patient with an acute form is more susceptible to irritation and damage to the urethra due to damage to the mucous membranes. And damaged or injured mucous membranes are an open door for microorganisms.
In this way, you can only acquire or transmit bacteria/infections to your partner, and only if there is a favorable situation, these pathogenic microorganisms will multiply, leading to illness.
In other words, if one of the partners has a chronic or acute stage of the disease and unprotected sexual intercourse occurs, then the likelihood of bladder inflammation in a healthy partner increases.
A natural question arises: is cystitis transmitted from men to women, and more precisely, are infections that provoke the disease transmitted? Of course, there is a risk of infecting a partner and has the following stages:
- penetration of bacteria into the vaginal microflora,
- irritation of the vaginal mucosa, and after the urethra,
- ascending infection,
- development of cystitis.
However, it all depends on the condition and functioning of the woman’s immune system. If a woman is healthy and leads a healthy lifestyle, the risks are reduced. In cases where the disease cannot be avoided, treating the woman alone is not enough.
Since the man remains a carrier of sexually transmitted infections or bacteria, and during the next act he will “share” them with his partner again. Therefore, it is important for both men and women to undergo a comprehensive course of treatment for infections.
Speaking about non-infectious causes of cystitis, it is worth saying that the disease is not transmitted from one person to another. This is an “artificially” produced inflammation.
Is cystitis transmitted through household contact?
When wondering about the possibility of transmitting cystitis through household means, one should remember the possibility of infection entering the body, the causative agents and the development of the disease.
Cystitis can also be caused by allergens, toxins and other non-infectious agents. But this type of disease is much less common.
Due to the infectious form of the disease, it can be said that it is impossible to contract cystitis through household means. But at the same time, it is possible to become infected with certain diseases that cause it. In particular, you can pick up certain bacteria when visiting a public toilet if they remain on the toilet seat. To avoid this, you should use special backing sheets on the seat.
Infection can occur through common personal hygiene items - towels. It is also possible for pathogenic microflora to remain on them. Therefore, using a single towel is not recommended; each family member should have their own.
Can a woman infect her partner?
There is every chance of transmitting cystitis to a partner through sexual contact. Most often, the stronger sex is exposed to cystitis during a period of long-term and systematic intimate relationships with a woman who has this disease, which has a chronic or acute form. However, with good immunity in a man, cystitis will not be able to develop, since the bacteria die in the urethra before they have time to enter the bladder.
Treatment of infection
Treatment is aimed at reducing pathogenic bacteria, so drug therapy is used, namely antibiotic treatment. During the recovery of the body, you should carefully monitor hygiene so as not to provoke the entry of other harmful microorganisms, and you should also abstain from sexual intercourse for some time.
Exposure to provoking factors should also be avoided during rehabilitation, when the body is most susceptible to negative influences. Irritation of the mucous membranes can provoke the appearance of other diseases of the reproductive system or the occurrence of complications.
It is difficult to say for sure whether cystitis is contagious or not. At its core, this disease is not transmitted through sexual acts, but often it is after sex that a woman begins to feel signs of cystitis. In men, the disease does not manifest itself, but after sexual intercourse the infection can spread to a woman. This only happens if the girl’s body is suitable for the spread of infection. Low immunity, hypothermia and other factors can increase the chances of developing pathology.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy includes the prescription of broad-spectrum antibiotics, uroseptics, antispasmodics and diuretics.
Several of the most effective pharmaco-clinical groups of drugs are used, such as:
- penicillins – Amoxiclav, Ampicillin, Flemoxin;
- nitrofurans – Furadonin, Furazolidone;
- cephalosparin series - CefIII, Cedex, Cefuroxime.
The dosage is selected individually, based on the course of the disease and other factors that only a doctor can correctly assess.
Uroseptics help relieve pain and improve urination; they are completely safe, since the main active ingredient is of natural origin.
Drugs that reduce spasms help relax smooth muscles - No-shpa, Baralgin, Papaverine.
The action of diuretics is based on increasing the amount of urine produced, thus maximizing the accelerated washout of pathogenic microflora and reducing inflammation of the entire urinary system as a whole.
With an integrated approach to patient therapy, remission occurs within 1-3 weeks, depending on the general condition of the body.
Traditional methods
Treatment using traditional medicine is only auxiliary, you must remember this and follow the recommendations of your doctor.
Traditional medicine recipes are very diverse, the most effective ones are presented in table form.
| Main component name | Description and dosage |
| Cowberry | Pour a handful of crushed lingonberry leaves into 600 ml of boiling water, then boil for 10 minutes. Leave in a warm place for about an hour. You need to drink half a glass of the composition throughout the day. The next day we prepare a new batch. Action – diuretic, antiseptic, antibacterial. |
| Bearberry | A decoction is made from this herb in a ratio of 1:10. The course of treatment is more than a week. The effect is anti-inflammatory and disinfectant. |
| Dill seed | Pour 200 ml of boiling water over a tablespoon and leave for 30 minutes. Course intake – 1/3 cup 5 times a day. Impact – relief of spastic pain, flatulence. |
| Cranberry | 500 gr. Grind the berries, a meat grinder is better for this purpose, pour the resulting mass with two liters of water and bring to a boil over low heat, add honey. Drink fruit juice throughout the day. Has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. |
| Yarrow | Grind the grass, 2 tsp. raw materials pour a glass of boiling water. Leave for an hour and drink 50 grams. three times a day. |
| Millet | For a tablespoon of millet you need one glass of boiling water. You need to simmer the mixture of millet and water over low heat for about 10 minutes, let it sit for 5 minutes and eat a tablespoon every hour. On the second day you need to consume 3 tbsp. spoons at a time. From the third day, the dose is increased to half a glass. Therapeutic course is one week. |
| Juniper | The crushed raw materials are poured with boiling water in a proportion of three to two. Infuse and drink instead of brewing tea. You need to drink about a liter per day. Helps even with advanced forms. |
| St. John's wort | For the best therapeutic effect, it is better to take only inflorescences; take a glass of water per glass of water. spoon of flowers, leave for about 20 minutes. Take 50 ml three times a day. |
IMPORTANT! Both partners must undergo the course of therapy, otherwise relapses in the future cannot be avoided.
Treatment methods
When an intense clinical picture develops, the patient requires competent treatment. So, if the symptoms of the disease manifest themselves acutely and cause the patient significant discomfort, it is recommended to remain in bed for several days until the patient’s condition stabilizes.
Throughout the treatment you must follow a special diet. In particular, avoid spicy and salty foods and dishes high in fat. Consumption of these products leads to fluid retention in the body and only aggravates the course of the disease. It is important to establish a drinking regime and drink drinks that have a diuretic effect.
The patient is prescribed mandatory drug therapy, which includes taking diuretics (most often herbal). In case of severe pain, the patient is prescribed antispasmodics (for example, Drotaverine, Papaverine), in addition, in this case, warm sitz baths and heating pads are useful. However, it is important to observe moderation: prolonged use of heat can only intensify the inflammatory process.
The patient also requires antibacterial therapy. However, the use of certain antimicrobial drugs is prescribed only after the specific type of pathogen has been determined. To reduce the risk of developing dysbiosis caused by taking antibiotics, the patient is also prescribed drugs that normalize the microflora (for example, Linex). In addition, therapy includes taking immunomodulators to strengthen the body's natural defenses, as well as vitamin complexes. An important point in treatment is to eliminate the cause of cystitis.
How to avoid cystitis? Main recommendations
All the methods described above for “getting” cystitis will be “useless” if a person is in good health and does not react to “simple” pathogens. To become immune to bladder inflammation, you just need to follow these tips:
- Avoid hypothermia. Freezing of the body is considered the main cause of cystitis. Therefore, you should not sit on benches in winter, wear short jackets in severe frost, or swim in cold water.
- Eat properly. Too hot, overcooked, spicy dishes should be completely prohibited. You should also limit your alcohol consumption. Vegetables, fruits and plenty of water will be beneficial.
- Treat all diseases noticed in yourself. Since cystitis can be “born” from any inflammation in the body, it is better to eliminate the infectious source as early as possible.
- Avoid underwear that is too tight. Such “clothing” compresses blood vessels, disrupting normal blood flow. For the same reason, sedentary work is harmful.
- Go to the toilet on time. The need to urinate should be satisfied as quickly as possible: stagnant urine is an excellent “platform” for the active reproduction of pathogens, which sooner or later cause inflammation.
It is important to understand that cystitis is only a “by-product” of an unhealthy lifestyle. It is impossible to become infected with it unless the body “joyfully” accepts the infection and contributes to its development. With a strong immune system and a moderately active lifestyle, such a scenario is almost unrealistic.
How to avoid sexual transmission of cystitis?
Condoms will help prevent the transfer of pathogenic microflora from a partner, which over time can lead to the development of an inflammatory process in the bladder. The barrier method of contraception protects against the penetration of foreign microorganisms, which reduces the risk of developing inflammation.
To prevent cystitis, both men and women are also advised to reduce stress levels, maintain a strong immune system, wear comfortable underwear made from natural materials and avoid hypothermia. The absence of bad habits plays an important role.
When an inflammatory process of the bladder is detected, it is important to find out the cause of its occurrence. If the cause is pathogenic microflora, then the partner should get tested.
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician. For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors!
Prevention
Cystitis in men is rare. It occurs as a complication of prostatitis and, like women, causes a lot of painful sensations.
However, it is not recommended for a woman to have sex during cystitis. This is due, first of all, to the painful sensations that accompany this disease. During sexual intercourse, strong pressure will be exerted on the walls of the bladder, which, of course, will negatively affect the healing process. During sexual intercourse, there is a risk of additional infection, which can aggravate the course of the disease.
If cystitis is not treated, the disease may recur later. So, for example, if inflammation of the bladder is caused by a candida fungus (causing thrush), then it may not manifest itself in any way when transferred to a partner. Whereas during subsequent sexual intercourse, if it enters the vagina, it will again cause inflammation of all organs of the woman’s genitourinary system.
Petting
To prevent the development of cystitis and its transmission to a sexual partner, it is recommended:
- dress warmly and avoid hypothermia;
- eat right and lead an active lifestyle;
- drink 2 liters or more of pure water daily;
- empty the bladder in a timely manner and prevent stagnation of urine;
- do not wear tight synthetic underwear;
- undergo preventive examinations;
- timely treatment of other infectious and inflammatory diseases.
Is cystitis transmitted between sexual partners? Answer: no. Only infection, fungi or viruses that lead to the development of inflammation in the bladder can be transmitted. An infection transmitted to a sexual partner may not always lead to cystitis; urethritis, vesiculitis, thrush and other infectious diseases of the genitourinary organs may develop against their background.