Congenital malformations (CMD) are the most dangerous complications of pregnancy. As a result of congenital malformation of the fetus, the child may become disabled, and in severe cases this can lead to death. Congenital malformations of the fetal central nervous system include:
- anencephaly (no brain);
- spina bifida (open form of spinal cord herniation);
- CDF of the fetus;
- pathological changes in the cardiovascular system (heart disease);
- limb defects – atresia (limb missing);
- Maxillofacial deformities – cleft palate or cleft lip.
Causes of congenital malformation of the fetus
The development of fetal defects can occur under the influence of many factors. Most of them remain unclear. The etiological signs of all congenital malformations of the fetus are divided into:
- hereditary - deviations in the chromosome sets of the parents;
- teratogenic - the fetus or embryo has been damaged by the action of pesticides, infections, medications, and so on;
- multifactorial - the joint influence of genetic and environmental factors on the fetus, which separately cannot be the cause of the defect.
There is evidence that biosphere pollution is the cause of seventy percent of cases of disease, sixty percent of cases of development with pathologies and more than fifty percent of deaths of children. The birth of children with subsequent abnormal development is associated with professional activity: emotional stress, exposure to high and low temperatures or dust, contact with chemical industry products and heavy metal salts.
There is a higher risk of congenital malformation in the fetus in women with significant obesity. This can cause abnormalities in the development of the neural tube. But such changes in the fetus’s body are caused not only by excess weight of the pregnant woman, but also by a sharp decrease in weight in the early stages of pregnancy.
Pregnancy after congenital fetus
You can plan a pregnancy after an abortion due to the development of congenital malformation in the fetus as early as six months after the previous one. In some cases, the couple is advised to wait a year. During the planning process, future parents undergo a series of studies, based on the results of which the doctor recommends when they can conceive a child. In preparation for the next pregnancy, the couple needs to lead a healthy lifestyle, avoid the influence of negative factors, take vitamins and other beneficial substances to strengthen their body.
NPP GA, even if the 2008 edition is a non-existent document of a non-existent department of a non-existent country. This document is not registered anywhere in the new Russia.
The amazingness of our country is manifested in the fact that, having FAPs, we accept points from the NPP and include them in the RPP, despite the differences between the NPP and FAP. I'm not even talking about the fact that pilots are deprived of their coupons on the basis of violations of the NPP of the USSR Civil Aviation, issued by the MGA for Aeroflot.
FAP Flight operations in the Russian Air Force:
33) “decision altitude” - the altitude established for a precision approach at which the missed approach maneuver must be initiated if, before reaching this altitude, the pilot-in-command has not established the necessary visual contact with landmarks to continue the approach the landing or position of the aircraft in space, or the parameters of its movement do not ensure safe landing (hereinafter referred to as VPR);
95) “precision approach” - an instrument approach with navigation guidance in azimuth and glide path, generated using electronic means;
56) “minimum descent altitude” - the height established for a non-precision approach, below which the descent cannot be made without the necessary visual contact with landmarks (hereinafter referred to as MAF)
57) “non-precision approach” - an instrument approach without navigation guidance along a glide path generated using electronic means;
Here someone wrote about visual approach:
21) “visual approach” - an approach when the spatial position of the aircraft and its location are determined visually by the crew using the natural horizon, earthly landmarks, as well as in relation to other material objects and structures;
Visual approach according to GMP is a mixture of a hippopotamus and a crocodile, and is more similar to Circling Approach with its visual maneuvering zones established for aircraft categories.
By the way, in FAP PiVP, FINALLY, they separated “visual approach” (almost like according to Doc 4444), and “circling approach” (practically, Circling Approach)
11.5.14. A circling approach is performed:
with continuous visual contact with the runway threshold or approach lighting aids; during the day and at dusk at airfields for which such an approach is provided. At dusk, the approach is carried out with the runway lighting equipment turned on. The flight crew ensures that the aircraft remains within the established visual maneuvering zone. An approach to land from a circle at a controlled aerodrome is carried out after receiving permission from the ATS unit in accordance with the procedure developed by the operator using aeronautical information collections (based on flight instructions or an air navigation passport). The instrument descent according to the established circling approach pattern is carried out to the altitude established at the start point of the approach along the prescribed trajectory or indicated by the ATS unit.
11.5.15. The descent of the aircraft in the visual maneuvering zone after the start of the turn onto the pre-landing straight and on the pre-landing straight is possible if there is visual contact with ground landmarks and the runway. If visual contact with the runway is lost at any point in the visual maneuvering zone, the flight crew stops descending and performs a flight towards the runway with a climb and entering the aborted approach (missed approach) pattern using instruments.
11.5.16. A visual approach to landing is carried out in accordance with the procedures defined in the aeronautical information book or with the flight operations instructions (air navigation passport) of the aerodrome, or in other established order. A visual approach may be initiated at any point on the arrival route or at any point on an instrument approach pattern, provided that the necessary visual contact is established with landmarks and the runway. At a controlled aerodrome, permission from the ATS unit is required to perform a visual approach. The flight crew reports to the ATS unit that visual contact with the runway has been established. A visual approach is carried out provided that the height of the cloud base is not lower than the minimum flight altitude at the initial stage of the approach, and the visibility is not less than:
5 km – at an airfield located in a flat, hilly or mountainous area with a relief height of up to 1000 m;
8 km – at an airfield located in a mountainous area with a relief height of 1000 m or more.
When two aircraft of the same type are making a simultaneous visual approach, the aircraft flying ahead, to the left or below has priority in the approach. The flight crew of the lighter aircraft allows the heavier aircraft to land first.
A visual approach cannot be conducted unless the flight crew is familiar with the terrain and landmarks on which the approach procedure is based.
Do you feel the similarity between a visual approach according to the GMP and a “circling approach” according to the FAP PiVP?
Application
to the order of the Ministry of Industry and Trade of Russia
from "__" _________20 No. ____
FEDERAL AVIATION RULES
FLIGHT OPERATIONS
IN EXPERIMENTAL AVIATION
Chapter
I. _
GENERAL PROVISIONS 1. Federal aviation rules for flight operations in experimental aviation (hereinafter referred to as the Rules) were developed in accordance with the Air Code of the Russian Federation (Collection of Legislation of the Russian Federation, 1997, No. 12, Art. 1382), decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated March 11 2010 No. 000 “On approval of the Federal Rules for the Use of the Airspace of the Russian Federation” (Collection of Legislation of the Russian Federation, 2010, No. 14, Art. 1649) and in pursuance of Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 01.01.01 No. 000 “On the Federal Rules for the Use of Airspace and Federal Aviation Rules” (Collected Legislation of the Russian Federation, 1998, No. 14, Art. 1593; 2000, No. 17, Art. 1875, 2010, No. 28, Art. 3705).
2. The rules determine the procedure for conducting flights in flight test units of experimental aviation organizations.
3. The rules are mandatory for all subjects of legal relations, regardless of their organizational and legal form and form of ownership, which are subject to the air legislation of the Russian Federation governing relations in the field of experimental aviation, including legal entities engaged in development, production, repair and testing of aviation and other equipment and having a license to operate in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
4. For the purposes of these Rules, the following terms and definitions apply:
Conducting flight tests without formalized and approved flight test programs, estimates (agreements) for them and logistics plans is not allowed.
40. Test programs for experimental aircraft and programs for the most complex types of flight tests (high angles of attack, spin, flight safety equipment, etc.) are discussed at the Experimental Aviation Methodological Council for Flight Tests and, after their consideration, are approved by the head of the aviation organization.
All other flight test programs are reviewed by methodological councils of flight test units of experimental aviation organizations and approved by the heads of these aviation organizations.
41. Submission, acceptance and periodic tests of serial aircraft in aviation organizations - aircraft manufacturers are carried out in accordance with the methodological instructions of the aircraft developer on the basis of test programs specified in the current technical conditions, manuals (guidelines) for testing aircraft, aircraft flight operating manuals (crew instructions).
Specific test flights are carried out according to profiles and methodological recommendations (techniques) for their implementation, developed by the aviation organization-manufacturer of the aircraft based on the methodological instructions of the aircraft developer.
Profiles and methods of test flights are agreed upon with the customer's research institute, the customer's senior representative in the aviation organization, the aircraft developer, and the aircraft manufacturer and are approved by the head of the aviation organization that manufactured the aircraft.
When changing technical specifications programs, manuals for testing aircraft, manuals (instructions) for the flight operation of aircraft, agreed upon changes are made to the guidelines and test flight profiles accordingly.
42. For each test flight, the leading aircraft flight test engineer (head of the test team), together with the test pilot and test team specialists, develop a task for the test flight and draw up a flight sheet.
43. The test flight assignment specifies:
flight purpose;
flight profile and route;
sequence and methodology for completing the task;
flight duration;
weather conditions under which the task is permitted;
the procedure and duration of switching on on-board measurement systems;
safety precautions (in addition to those specified in the flight manual) specific to this mission;
questions that the crew must answer in the mission report;
measures to counter foreign technical intelligence and ensure secrecy requirements;
the minimum amount of fuel and distance from the airfield, which ensures landing on it with a specified fuel balance;
the in-flight responsibilities of each crew member;
The test flight task is signed by the leading engineer, specialists who took part in its development, and supervisory persons.
Crew members sign off on the task after it has been completed.
The test flight assignment is approved by the head of the flight test unit or an official who has such right in accordance with the order of the head of the aviation organization.
44. The completed flight sheet and test flight assignment are signed by the deputy head of the flight test unit for flight service (senior test pilot), the leading aircraft flight test engineer and the specialists who took part in its development.
The flight sheet when performing the first runs (approaches) on an experimental (modified) aircraft, when performing the first test flight, vertical takeoff and landing, from the deck of a ship and during the first departure from a hydroairfield of an experimental amphibious aircraft is approved by the general (chief) designer aircraft.
The flight sheet for the first test flight of the lead serial aircraft, as well as when conducting tests of an increased degree of complexity on serial aircraft, is approved by the head of the aviation organization-manufacturer of the aircraft.
For other types of tests, the flight sheet is approved by the head of the flight test unit (deputy head of the flight test unit for flight service) or an official entitled to do so in accordance with the order of the head of the aviation organization.
45. When developing guidelines and profiles for presentation, acceptance and periodic tests of serial aircraft, developing and completing a test flight task and flight sheet, it is recommended to be guided by the Instructions on the procedure for preparing and maintaining documentation for flight test work and technical operation of aircraft in flight test units of experimental aviation organizations.
46. In cases where ground work is performed on an aircraft, as provided for in the test program, the leading engineer for experimental work and flight tests in his specialty develops a task for performing the specified work, which is approved by the head of the flight test unit.
Test team
47. Test teams in aviation organizations - aircraft developers, flight research institutes and research institutes are formed from flight and ground personnel, as a rule, from one aviation organization.
The test crew includes flight personnel, in-flight test participants, and ground engineering personnel.
The head of the testing team is a leading engineer for flight testing of aircraft (in some cases, a leading engineer for experimental work and flight testing in his specialty), who has a valid certificate in his specialty.
The flight personnel of experimental aviation include test pilots, test navigators, on-board test engineers (mechanics), on-board test engineers of flying laboratories, on-board test technicians, on-board test radio operators, on-board test electricians, and on-board test operators.
In-flight test participants include aviation personnel performing their duties in flight in accordance with the test flight assignment and on the basis of the flight test (research) program at specially equipped workplaces not provided for in the aircraft flight manual, but ensuring forced exit from the aircraft vessel.
48. The composition of the test team is appointed by order of the head of the aviation organization for the entire period of flights under the test program. Replacement of members of the testing team is allowed in exceptional cases (except for backups appointed in accordance with the established procedure) and is formalized by order of the head who approved the original composition of the team. Newly assigned flight crew members must be given the necessary flight test training.
49. Flight personnel and specialists of other aviation organizations are included in the test team in accordance with the test program and on the basis of orders (instructions) of the heads of these organizations. In this case, the composition of the test team is appointed by order of the head of the parent aviation organization by agreement.
50. In aviation organizations - aircraft manufacturers, flight crews, in-flight test participants and ground engineering and technical staff to conduct presentation, acceptance and periodic tests of serial aircraft are appointed by order of the head of the aviation organization
51. The testing team in its work is guided by:
these Rules;
aviation regulations (airworthiness standards for civil aircraft);
Air Force General Technical Requirements (Air Force GTR);
flight test programs;
aviation equipment testing manuals, aircraft flight operation manuals, technical operation manuals and regulations;
other regulatory documents on flight test work and its support.
Experimental aircraft crew
52. The crew of an experimental aircraft consists of flight personnel and in-flight test participants and is appointed by order of the head of the experimental aviation organization.
53. A test pilot who has a valid test pilot certificate, as well as the training and experience necessary to perform a flight mission on an aircraft of this type, is appointed as the commander of an experimental aircraft.
54. Flight personnel and flight test participants must have valid test certificates for their specialties, as well as the training and experience necessary to perform the flight mission.
55. Flight personnel of other aviation organizations of experimental aviation, as well as civil and (or) state aviation
tions are included in the crew of an experimental aircraft if they have valid test certificates in their specialties, have the training and experience necessary to perform the duties of a crew member of this type of aircraft, and in accordance with the flight test program.
Aircraft used to support flight tests (auxiliary aircraft) are permitted to be flown by flight personnel of state or civil aviation authorized to fly the specified types of aircraft in the prescribed manner.
When performing flights with a mixed crew, the tasks and responsibilities of each crew member are determined by the aircraft flight manual (crew instructions) and the flight assignment.
56. Flight personnel of foreign states are included in the crew of an experimental aircraft:
when conducting joint flight tests (research) on the basis of a resolution (order) of the Government of the Russian Federation, an intergovernmental agreement, a contract - in accordance with the joint flight tests (research) program;
in the joint production of an aircraft in aviation organizations of the Russian Federation and in aircraft manufacturing companies of foreign countries - in accordance with the joint testing program;
when displaying aviation equipment at shows (exhibitions) abroad and demonstration flights with a foreign customer - with the permission of the head of the delegation of the Russian Federation;
during demonstration flights of aircraft with a foreign customer under contracts - with the permission of the head of the enterprise developing aircraft;
during displays of mass-produced aircraft in the Russian Federation - by the head of the experimental aviation organization in agreement with the Department of Aviation Industry of the Ministry of Industry and Trade of the Russian Federation;
when training flight personnel of a foreign customer - in accordance with the contract for the supply of aviation equipment;
when conducting acceptance (bearing) tests of an aircraft manufactured in accordance with the terms of the supply contract - by the head of the experimental aviation organization in agreement with the Department of Aviation Industry of the Ministry of Industry and Trade of the Russian Federation.
57. Flight personnel of foreign countries are included in the crew of an experimental aircraft after the necessary training conducted by specialists of the flight test unit in accordance with standard programs for training and performing familiarization flights on dual-control aircraft. Preparation for flights must correspond to the flight task and ensure the safety of its execution.
Permission to perform a joint flight with a representative of a foreign customer is drawn up in a preparation certificate and signed by the head of the aviation organization (the head of the delegation of the Russian Federation or the head of a team of specialists - when flying abroad) and the foreign citizen allowed to fly.
Admissions to flight tests and other types of flights
58. Flight personnel and in-flight test participants who have valid certificates in their specialties, as well as flight personnel performing flights, are allowed to conduct flight tests
on multi-seat aircraft under the commissioning program (under the training program as a tester).
59. Admission of test pilots and crew members to various types of flights and the conditions for their performance is carried out by order of the head of the aviation organization based on the results of inspections by type of flight training and is recorded in the flight record book.
Test pilots and crew members are allowed to fly on a type of aircraft that is new to them by order of the head of the aviation organization after they have passed the ICC tests on knowledge of aviation equipment, the characteristics of stability and controllability of the aircraft, the Flight Operation Manual of this aircraft, and the completion of training exercises on operations in special cases, for forced abandonment of a given aircraft with ratings not lower than “good” and performing control flights on a given type of aircraft with a rating not lower than “good”.
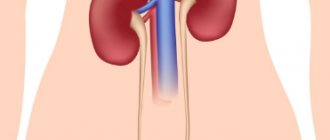
The organs of the urinary system are divided into kidneys and urinary tract. The kidneys filter the blood and excrete toxic waste products in the urine. If there is a block in the urinary tract, fluid secreted by the kidneys cannot be eliminated from the body, and unilateral or bilateral hydronephrosis develops.
Translation from Latin “hydronephrosis” means “water in the kidneys” (hydro - water and nephros - kidney).
This specific pathology is not a separate disease, but rather a consequence of other diseases of the genitourinary system. Therefore, treatment of hydronephrosis is based on eliminating the primary pathology.
Characteristics
Benign cystic formations can form on almost any organ, and the kidneys are no exception. The mechanism of cyst formation, regardless of their location, is standard. Under the influence of external or internal negative factors, a cavity gradually forms in the intercellular space, which is subsequently filled with interstitial fluid. As it develops, the cavity forms boundaries, which are represented by a connective tissue capsule consisting of collagen fibers.
Depending on the cause of the cyst, the internal contents of the tumor may be serous fluid, pus or blood.
The formation of kidneys in the fetus begins at 10-11 weeks of gestation. The formation of renal cysts at the stage of intrauterine development can occur during the formation of renal tubules or blood vessels. As a rule, until the renal tubules begin to function, cystic neoplasms are very difficult to identify, since their size remains constant.
There are also clinical situations in which polycystic kidney disease is diagnosed in the fetus, characterized by the formation of multiple cysts located over the entire surface of the paired organ. This serious condition can cause serious complications that require qualified assistance in a short period of time.
Causes
Single renal cysts or cystic renal dysplasia are congenital conditions that were formed at the stage of the formation of a paired organ. With cystic kidney dysplasia, a characteristic change in the size and shape of the organ is observed, which is deformed due to the formation of multiple tumors.
In 70% of cases, the true cause of the development of this pathology is gene mutations that occurred at one of the stages of the child’s intrauterine development. Other, no less probable reasons for the development of this kidney pathology in the fetus include:
- Heredity factors. If a similar condition was previously diagnosed in close relatives, the child, even at the stage of intrauterine development, is at significant risk of developing single or multiple renal cysts.
- The impact of external adverse factors on the body of a pregnant woman and the developing fetus. A common cause of this pathology is the use of certain medications that have a teratogenic effect, unfavorable environmental conditions in the area of residence, exposure to ionizing radiation on the body of a pregnant woman, drinking alcohol and smoking during pregnancy, as well as frequent use of household chemicals, which includes its composition of acid and chlorine.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases previously suffered by a pregnant woman, including sexually transmitted infections.
In addition, there are so-called idiopathic cysts, the true reason for the formation of which remains poorly understood.
Why and under what conditions does a cyst form in the fetal kidney?
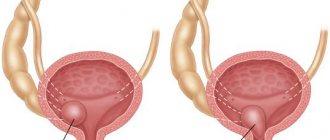
A fetal kidney cyst is a benign tumor on the kidney or in the renal pelvis, which includes walls and a hollow space containing serous fluid. This tumor is located in the upper or cortical layer of the kidney. The shape of a cyst can be spherical, ellipsoidal, and cysts are classified into single-chamber, simple and complex.
Causes of cystic tumor formation
When a cyst forms in the fetus, the following etiological factors are mainly identified:
- Pathologies during intrauterine development due to exposure to environmental factors - irradiation of the mother's body, poor ecology, drug abuse at the stage of formation of the organs of the fetal urinary system, harmful addictions of the mother and exposure to household chemicals on the mother's body.
- Hereditary factors. When pathology is detected in relatives, the fetus develops the disease very often. Based on the manifestation of the disease in family members, fairly accurate predictions can be made.
- Pathologies of the body at the cellular level that occur during fertilization of the egg. This becomes possible due to non-compliance with contraceptive rules or during an unplanned pregnancy.
- Infectious pathologies or inflammations suffered by the mother during the formation of excretory organs in the fetus.
Sometimes the reasons for the formation of a cyst in the fetus cannot be determined.
How is kidney damage in the fetus diagnosed?
Modern medical equipment makes it possible to detect a cystic tumor as early as the fifteenth week of fetal formation. The main diagnostic method is ultrasound examination. The doctor determines the number of cysts, their location, size, and is also able to analyze the safety of kidney function.
Signs of disease development in the fetus also include:
- Compensatory kidney hypertrophy.
- Violation of the homogeneity of the contours of the organ.
- Hyperechoic tissue between cysts.
- Low water.
After the baby is born, he immediately undergoes an ultrasound to clarify the diagnosis or analyze kidney function. A month later, another ultrasound is performed.
Basic methods of prevention
- Pre-pregnancy planning. The entire female body must be prepared for bearing a child, and acute and chronic diseases must be treated.
- Timely registration of a pregnant woman - this should be done at 12 weeks of pregnancy.
It also requires constant visits to the gynecologist, and at least three ultrasound scans during the entire period of gestation, usually at the following stages:- 10 - 14 weeks;
20 - 24 weeks;
- 32 - 34 weeks.
- Refusal of a woman from harmful factors.
Such as drinking alcohol, smoking, taking medications, the influence of household chemicals, stressful situations. - Doctors recommend avoiding abortions and promptly treating inflammation of the genital organs.
- Also, during pregnancy, it is necessary to prevent any infectious damage to the body.
It is important! According to statistical data, at present, cystic tumors in the kidneys of the fetus are rare, and multiple cysts are generally considered isolated unique cases. If such a diagnosis has been made, it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Modern medical science makes it possible to effectively resist this pathology, and when diagnosing the disease in the early stages, the doctor can monitor the progress of the process and intervene when the need arises.
Prognosis and complications of renal cyst
When single small formations form in one of the kidneys, the prognosis remains favorable. Doctors monitor that the cyst does not grow and does not affect the flow of nutrients to the kidneys.
Children can be safely born with this disease and most often do not require additional treatment. All that is needed is regular diagnostics, prevention of child injuries and infections in his body.
In case of polycystic disease, experts advise the woman to terminate the pregnancy. This kidney damage can cause kidney failure, especially if both kidneys are diseased.
It becomes possible to maintain pregnancies provided that treatment is immediately organized immediately after birth. An additional negative side of polycystic disease is the tendency to affect several organs simultaneously.
When a diagnosis is made, cysts can also be diagnosed in the liver and gallbladder.
It is important! The most unfavorable prognosis is established when the fetal kidneys are affected by multicystic disease. The bilateral form is incompatible with life and the pregnancy is terminated even at long terms.
Complications can develop immediately after the birth of the child or in adulthood. The most common complications are the growth of the cyst, pressure from the neoplasm on the surrounding organs, hemorrhage into the cyst cavity, and degeneration into a malignant tumor.
(Not yet )
Source: https://TvoeLechenie.ru/urologiya/pochemu-i-pri-kakix-usloviyax-obrazuetsya-kista-v-pochke-u-ploda.html
Diagnostics
If a pregnant woman does not neglect a routine medical examination, including ultrasound diagnostic techniques, then the timely detection of single or multiple cysts in the fetus will not cause difficulties. Ultrasound diagnostic method is the main way to assess fetal development at the intrauterine stage.
From a statistical point of view, multicystic dysplasia of the left fetal kidney is detected more often than a similar right-sided lesion (as of 2020). Using the ultrasound method, it is possible to detect cysts, accurately count them, determine their location and size. In addition, this method allows you to assess the degree of decrease in the functional ability of a paired organ in the fetus. The main ultrasound signs of the development of this pathology include:
- Decreased amniotic fluid volume (oligohydramnios).
- Increased echogenicity of the renal parenchyma located between the cysts.
- Change in the homogeneity of the renal contours.
- Compensatory hypertrophic changes in the paired organ.
In addition, every newborn is shown an ultrasound examination of the kidneys immediately after birth. A repeat study is performed 1 month after birth.
Treatment
The tactics of medical specialists when diagnosing this pathology in a developing fetus directly depends on factors such as the number and size of cysts, as well as the degree of functional failure of the damaged organ.
If the fetus has been diagnosed with a single cyst on one of the kidneys, then doctors prefer to conduct observational tactics, assessing the dynamics of the pathology using ultrasound examination.
If the fetus has been diagnosed with multicystic dysplasia of both kidneys, the woman is advised to terminate the pregnancy, since this anomaly can be fatal in a short period of time.
After the child is born, if characteristic clinical symptoms are present, the child can undergo a procedure for draining the cyst, followed by the introduction of a sclerosant. The degree of renal impairment in this pathology is assessed through laboratory techniques such as measuring the level of potassium, urea and creatinine in the body.
If a newborn develops chronic renal failure against the background of a cystic lesion, he is prescribed a hemodialysis procedure or transplantation of a damaged organ.
If the size of the neoplasm exceeds 50 mm in diameter, the child may be prescribed radical removal of the damaged organ (nephrectomy). As a rule, this intervention is not performed in the neonatal period. The optimal age for nephrectomy is from 1 year to 1.5 years. Children with a similar diagnosis undergo removal of the damaged kidney through endoscopic retroperitoneal access, which does not involve dissection of the muscle layer.
Danger of pathology for the fetus
When the fetus has enlarged renal pelvis, this situation is dangerous due to the development of the following complications:
- Enlargement of the ureters may occur - this pathology develops due to strong pressure inside the bladder. Among other things, spasms can also provoke expansion.
- Narrowing of the ureteric orifice - this deviation very often leads to the formation of a cystic or spherical protrusion in the ureter, and as a result of this pathology, the outflow of urine is disrupted and pyelonephritis can develop.
- The occurrence of cystitis is an inflammatory disease that occurs due to stagnation of urine or the occurrence of pathological microflora in the organ.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the sphincter.
- Death of a functional unit of renal tissue occurs - this pathology develops as a result of the inflammatory process that occurs in the kidneys; as a result of these abnormalities, the kidneys begin to die.
- Kidney atrophy, which occurs as a result of damage to the structural units of the kidneys.
- Nephroptosis develops, resulting in prolapse of the kidney into the vaginal cavity or urethra.
- Kidney prolapse.
Enlargement of the renal pelvis can lead to serious health consequences in the future. All this may concern the child
Based on all the pathologies that can be caused by an enlargement of the renal pelvis, we can conclude that such a pathology poses a serious danger to the body and the life of the fetus. Therefore, it is very important to diagnose and treat the deviation in a timely manner.
Prevention
Subject to certain recommendations, every woman of reproductive age has the opportunity to protect the body of the unborn child from the occurrence of not only renal cysts, but also other anomalies of intrauterine development. Such recommendations include:
- Complete cessation of bad habits such as smoking, drinking alcohol and using drugs.
- Timely treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary and reproductive systems, as well as prevention of abortions.
- Timely registration with a doctor in case of pregnancy. The recommended period for registration at the antenatal clinic is 12 weeks of gestation. In addition, pregnant women are recommended to consult with a gynecologist, as well as three ultrasound examinations during the entire period of pregnancy.
- Prevention of hypothermia, as well as minimizing contact with household chemicals throughout the entire period of bearing a child.
Timely diagnosis of this pathological condition makes it possible to dynamically monitor the growth of a benign tumor.
Diagnosis methods
As soon as a patient turns to a therapist with such complaints, it is necessary to refer him to a consultation with a urologist or nephrologist: these doctors deal with various kidney ailments. First of all, the doctor will conduct a general survey: the patient needs to describe in as much detail as possible the nature of the pain, its intensity and duration, as well as the time of its first occurrence. Next, you need to provide information about all previous operations, injuries and other ailments.
Based on his experience, the author can say that the most important part of the physical examination is the examination. For this, the patient is asked to undress, exposing the lower back and pubic area. Next, the condition of the skin and mucous membranes is assessed. Patients with kidney cysts have fairly typical external manifestations: pale gray color of the skin, dryness and small cracks in the corners of the mouth, a whitish coating on the tongue with an unpleasant odor. When palpated, the lumbar region is sharply painful; in thin people, you can see the contours of a pathological formation located in the kidney. When measuring blood pressure, an increase of 30–40 millimeters of mercury is observed above the norm typical for this patient.
Laboratory and instrumental examination methods:
- A general urine test allows you to determine the physical characteristics of the biological fluid and its cellular composition. When a cyst develops, cloudiness of the urine and the formation of pathological salt deposits, sand or blood clots are usually observed. Urine has a pale red or dark burgundy tint; it may contain epithelial cells, lymphocytes, red blood cells and casts, as well as atypical elements, which indicates the presence of an inflammatory process.
Blood in the urine may indicate the development of a tumor
The image shows the deformation of the organ
The biopsy is performed under local anesthesia
Forecast
The most unfavorable prognosis concerns multicystic lesions of both kidneys in the fetus. The bilateral form of this disease is incompatible with life, so the woman is recommended to terminate the pregnancy regardless of the gestational age.
If a child was born with a single renal cyst, then as he grows up he may encounter a list of complications such as a rapid increase in the volume of the tumor, mechanical compression of the kidney parenchyma, malignant degeneration of the cyst, as well as rupture of the tumor capsule and hemorrhage into the tumor cavity.
Share:
What are kidneys needed for?
To make it easier to understand the issues of pathology, let’s understand how the urinary system works normally.
The kidneys in humans play a very important role: they take part in maintaining the chemical composition of the body at the proper level through the formation of urine. All human blood passes through the kidneys, it is filtered and cleansed of harmful impurities. In addition, the kidneys regulate the water-salt balance, produce biologically active substances, the role of which is to regulate blood pressure, produce certain hormones and, indirectly, the formation of red blood cells.