Doctors believe that antibiotics for diseases of the genitourinary system are the most effective, universal and widespread group of pharmaceuticals that help in the recovery of patients infected with a urinary tract infection. The patient must immediately seek help from a doctor, since untimely treatment or self-medication affects not only the distal parts of the excretory system, but also other important organs of the human body.
Antibiotics are actively used in the treatment of diseases of the urinary system.
What are the types of diseases of the genitourinary system?
The most common ailments of the genitourinary system among men are:
- urethritis . It is an inflammation of the urethra. As it progresses, the patient experiences redness, sticking and discharge from the urethra, frequent urges and painful urination;
- prostatitis _ Covers mainly men over 30 years of age. The disease is an inflammation of the prostate gland. With it, the patient feels spasms in the groin and perineum, the temperature rises, and chills appear.
The most common diseases in the female half are:
- pyelonephritis . The diagnosis is inflammation of the kidney cavity. With it, the following symptoms are observed: spasms in the sides and lumbar region, pain above the pubis, aggravated by urination, frequent urges, which are accompanied by small discharge, fever;
- cystitis . The disease is very common and causes inflammation of the bladder. During its course, cloudy urine, frequent urge to urinate with small discharge, accompanied by pain are observed;
- urethritis . It occurs in the same way as in men.
Antibiotic drugs for cystitis and kidney inflammation
Cystitis most often inevitably leads to pyelonephritis. And the reason lies in the fact that women, for one reason or another, put off visiting a doctor and try to be treated with folk remedies or homeopathy. As a result, the infection rises through the ureters and chronic pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys and pelvis) develops. This is a very serious condition that after several years (and in some patients even faster) leads to the development of chronic renal failure. And this disease is already fatal and requires either a donor kidney transplant or attending hemodialysis procedures for the rest of your life.
The most effective antibiotics for pyelonephritis and cystitis:
The patient cannot prescribe these antibiotics on his own, since if the type of bacteria that caused pyelonephritis is outside the “action zone” of the drug, then the therapy will be in vain. Only after passing tests and drawing up a complete clinical picture of the disease is it permissible to prescribe treatment.
Causes
The causes of inflammation of the genitourinary system can be:
- viral infections;
- mechanical damage;
- hypothermia;
- activation of opportunistic microflora;
- insufficient or excessive sexual activity;
- decline in immunity;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- entry of bacteria from the perineum into the urethra.
Recommendations for the use of drugs
- Nolocin - during treatment it is necessary to consume a sufficient amount of fluid. This drug should be taken on an empty stomach with water. You need to take 1 tablet 2 times a day, 400 milligrams. Prescribed for 14 days. Analogs are Norfloxacin, Norbactin. The average price for 10 tablets is 170 rubles. Neocytin should be taken orally, before meals. For adults, the course of treatment is 200 milligrams in three doses for 7 days. Children – 50 mg in three doses. Analogues – Neobutin, Trimebutin. Pharmacy price – 400 rubles.
- Monural is to be dissolved in one sachet with a dose of 3 grams in boiled water. Take orally once daily. The course of treatment consists of one dose. Analog – Fosfomycin. Market price – 465 rubles.
- Canephron - the older generation takes 2 tablets three times a day, children - one, regardless of food intake. After symptoms have subsided, prophylactic treatment for a month is recommended. Analogues – Bioprost, Aflazin. Price – 450 rubles.
- Cyston - treatment with this drug will require drinking large amounts of water. You need to take 2 tablets twice a day, 100 milligrams each. The treatment cycle lasts six months. Analogues – Uronefron. Market valuation – 365 rubles.
- ProstaNorm - take 1 tablet of 200 mg twice a day 30 minutes before meals, or an hour after. The duration of treatment is six months. Analogues – Vitaprost, Samprost. Price – 270 rubles.
- Furagin - adults are prescribed two tablets with a dosage of 100 milligrams four times a day, on the first day of treatment. The following are one tablet three times a day. Analogues – Furazidin, Furadonin. The price tag on the market is 250 rubles.
- Ceftriaxone - 1 gram bottles. Dissolve the contents in an anesthetic ampoule or water for injection for intramuscular administration, or in 20 milliliters of saline for intravenous administration. Inject 2 times a day for 7 days. Analogues – Rocephin, Zatseph. The average price per bottle is 25 rubles.
- Meroponem – dilute a 1 gram bottle in 200 milliliters of saline. Administer intravenously twice a day. The course of treatment is 5 days. Analogues – Alvopenem, Diapenem. The price at the pharmacy is 490 rubles.
- Erythromycin - 100 mg tablets, take 1 piece twice a day, before meals. The course of treatment is 7 days. Analogues - Dalatsin, Zerkalin. Price – 200 rubles.
- Amoxiclav - for moderate flow, 625 grams are prescribed every 8 hours. The course of treatment is from 5 to 14 days. Analogues – Ecolinkom, Ecoclave. The average price is 200 rubles.
Video: “Treatment of lower urinary tract infections” - interview with prof. O.B.Laurent
One of the most common reasons for visiting a urologist today is genitourinary infections (UI), which should not be confused with STIs. The latter are transmitted sexually, while MPI is diagnosed at any age and occurs for other reasons.
Bacterial damage to the organs of the excretory system is accompanied by severe discomfort - pain, burning, frequent urge to empty the bladder, and the release of pathological secretions from the urethra. In severe cases of infection, intense febrile and intoxication symptoms may develop.
The optimal treatment option is the use of modern antibiotics, which allow you to get rid of the pathology quickly and without complications.
Symptoms
Signs of different genitourinary diseases are often similar to each other. They may be as follows:
- increased frequency of urination (manifested in prostate adenoma, cystitis, pyelonephritis, prostatitis and glomenuronephritis);
- discharge from the urethra (manifests in men with urethritis, urogenital infection and prostatitis);
- difficulty urinating (manifested with prostate adenoma and prostatitis);
- redness of the genitals in men (manifested with urogenital infections, allergies and urethritis);
- chills;
- intermittent urination (manifested in prostate adenoma, chronic and acute prostatitis);
- difficulty ejaculating;
- spasms in the perineum (manifests in men with prostate disease);
- pain in the upper part of the pubis in women (manifests itself with cystitis and pyelonephritis);
- lack of libido;
- temperature increase.
The use of antibacterial agents for MPI
Normally, the urine of a healthy person is almost sterile. However, the urethral tract has its own flora on the mucous membrane, so the presence of pathogenic organisms in the urinary fluid (asymptomatic bacteriuria) is often recorded.
This condition has no symptoms and treatment is usually not required, except in pregnant women, young children and immunocompromised patients.
If the analysis shows entire colonies of E. coli in the urine, then antibiotic therapy is mandatory. In this case, the disease has characteristic symptoms and occurs in a chronic or acute form. Treatment with antibacterial agents over long courses in small dosages is also indicated to prevent relapses.
The following are antibiotic treatment regimens for genitourinary infections for both sexes, as well as for children.
Pyelonephritis
Patients with mild and moderate stage pathologies are prescribed oral fluoroquinolones (for example, Zoflox 200-400 mg 2 times a day), inhibitor-protected Amoxicillin, or cephalosporins as an alternative.
Cystitis and urethritis
Cystitis and inflammation in the urethral canal usually occur synchronously, so the same antibacterial agents are used.
| Infection without complications in adults | Infection with complications | Pregnant | Children | |
| Duration of treatment | 3-5 days | 7-14 days | Prescribed by a doctor | 7 days |
| Preparations for primary treatment | Fluoroquinols (Ofloxin, Oflocid) | Monural, Amoxicillin | Antibiotics of the cephalosporin group, Amoxicillin in combination with potassium clavulant | |
| Reserve medications | Amoxicillin, Furadonin, Monural | Nitrofurantoin | Monural, Furadonin |
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are divided into several groups, each of which has its own characteristics in terms of its mechanism of action.
Some drugs have a narrow spectrum of antimicrobial action, while others have a broad spectrum.
It is the second group that is used in the treatment of inflammation of the genitourinary system.
Penicillins
These drugs are the very first ABPs discovered by man. For quite a long period of time they were universal means of antibiotic therapy.
But then pathogenic microorganisms mutated, which contributed to the creation of specific defense systems, which required the improvement of medical drugs.
Urogenital infections are treated with the following drugs from this group:
- Amoxicillin . It is an antimicrobial drug. The effectiveness of Amoxicillin is quite similar to the following antibacterial drug. However, its main difference is its increased acid resistance. Thanks to this feature, the drug is not destroyed in the gastric environment. For the treatment of the genitourinary system, it is also recommended to use analogues of the drug Amoxicillin: Flemoxin Solutab and Hiconcil. Combination antibiotics are also prescribed, such as: Clavulanta, Amoxiclav, Augmentin;
- Ampicillin . It is a semi-synthetic drug intended for oral as well as parenteral use. Due to blocking cell wall biosynthesis, its effect is bactericidal. It is characterized by fairly low toxicity, as well as high bioavailability. If it is necessary to increase resistance to beta-lactamases, this medication can be prescribed in combination with Sulbactam.
Cephalosporins
These medications belong to the group of beta-lactams; they differ from penicillins in their increased resistance to the destructive effects of enzymes produced by pathogenic flora. They are prescribed mainly for oral use.
Among the cephalosporins, the following antibiological agents are used to treat the genitourinary system:
- Ceclor, Alphacet, Cefaclor, Taratsev . They belong to the second generation of cephalosporins and are prescribed by a doctor exclusively for oral use;
- Cefuroxime, as well as its analogs Zinacef and Zinnat . They are produced in several dosage forms. They can be prescribed even in childhood (in the first months of a child’s life) due to their low toxicity;
- Ceftriaxone . Available in powder form. Similar substitutes for this medication are Lendacin and Rocephin;
- Cephalexin . It is a drug whose action is aimed at relieving inflammatory processes in all organs of the genitourinary system. It is prescribed for oral administration only and has a minimal list of contraindications;
- Cefoperazone . It is a representative of the third generation of cephalosporins. This medication is available in the form of injections and is intended for intravenous as well as intramuscular use;
- Cefapime. It is a representative of the fourth generation of the antibiological group and is prescribed exclusively for oral administration.
Cephalosporins are often used in urology, but their use is not recommended without a doctor’s prescription. Some of them have a number of contraindications, including for pregnant women and during lactation.
Fluoroquinolones
This type of antibiotics is the most effective today for various infectious diseases of the genitourinary system in men and women.
Norfloxacin tablets
They are powerful synthetic bactericidal agents. However, their scope of use is limited by age categories, because this type of antibiotics is quite toxic. Also not prescribed for pregnant and lactating women.
The most popular drugs in the fluoroquinolone group include:
- Ofloxacin . It is an antibiotic fluoroquinolone, known for its widespread use due to its high efficiency and antimicrobial effect;
- Norfloxacin . Prescribed for oral administration, intravenous or intramuscular administration;
- Ciprofloxacin . This remedy is absorbed quite quickly and copes with various painful symptoms. It is prescribed for parenteral use. The drug has several similar drugs, the most popular of which are Tsiprobay and Tsiprinol;
- Pefloxacin . It is a drug aimed at treating infections of the genitourinary system, used parenterally and orally.
Medicines from the fluoroquinolone group are prohibited for use:
- persons under 18 years of age;
- during pregnancy;
- persons with diagnosed tendonitis;
- during lactation.
When taking fluoroquinolones, you need to pay attention to the fact that they have a negative effect on connective tissue.
Aminoglycosides
This type of antibacterial drugs is prescribed for parenteral administration.
The most well-known representatives of the aminoglycoside group are:
- Gentamicin . It is a drug of the second generation of aminoglycoside antibiotics. It is not adsorbed well enough in the gastrointestinal tract, so it must be administered intravenously or intramuscularly;
- Amikacin is an aminoglycoside whose effectiveness is maximized when used against complicated urinary tract infections.
Contraindications:
- nursing women;
- young children;
- during pregnancy.
Aminoglycosides have a long half-life, which is why they need to be used only once a day.
Additional Information
In case of complicated and severe pathological condition, mandatory hospitalization is necessary. In a hospital setting, a special drug treatment regimen is prescribed using the parenteral route. It should be taken into account that in the stronger sex any form of genitourinary infection is complicated.
If the disease is mild, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis, with the doctor prescribing medications for oral administration. It is permissible to use herbal infusions and decoctions as additional therapy on the recommendation of a doctor.
Urethritis in men
Approximately half of acute nongonococcal urethritis is caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis; in other cases, genitourinary mycoplasma and Ureaplasma urealyticum are responsible for the disease, and less commonly, Mycoplasma genitalium.
Diagnosis of the infectious agent is complicated by the fact that U. urealyticum is a ubiquitous microbe present in the urethral secretions of healthy men.
According to the pathogens, the disease is more related to sexually transmitted diseases than to UTIs.
In treatment, the drug of first choice is Doxycycline or Macrolides.
For some people, the cause of the infection remains unknown. These cases are characterized by repeated recurrence of the disease.
For gonococcal infections, the drugs of choice are Ceftriaxone or Azithromycin, or Ofloxacin is an alternative. Treatment, however, should always be based on laboratory drug susceptibility testing due to the significant increase in resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, in particular to fluoroquinolone chemotherapy drugs.
If treatment of urethritis with the above antibiotics is ineffective, the presence of Trichomonas vaginalis should be considered and, if this etiology is suspected, Metronidazole (2 g) should be administered once.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is characterized by the absence of clinical symptoms, leukocyturia, and sometimes pyuria, and the simultaneous presence of significant bacteriuria of the same strain of bacteria in at least two urine samples collected spontaneously 24 hours apart.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is mainly common among school-age girls and in patients with urinary catheters or urological abnormalities. The onset of the disease is more common in older people.
The disease is considered a benign phenomenon that disappears spontaneously over time.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is not an indication for antibiotic treatment! The exception is the period of pregnancy, when infection occurs in approximately 5% of women, especially in the second trimester of pregnancy. If left untreated, pregnant women may develop acute pyelonephritis; the disease can cause premature birth or the birth of low birth weight babies. Therefore, routine repeat urine culture is recommended during pregnancy, preferably at the first visit and then for 28 weeks.
The need for treatment with drugs such as antibiotics for other groups of patients should be assessed strictly individually, since the toxicity of repeatedly used antibiotics may outweigh their therapeutic effect. Antibiotics for people with urinary catheters for this type of infection do not eliminate the bacteria, but increase resistance and the development of multidrug-resistant bacteria.
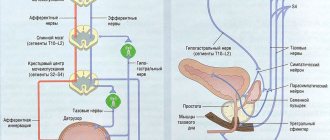
Prostatitis
Diagnosis and treatment of prostatitis belongs exclusively to the hands of a urologist. The penetration of most antibacterial drugs into the prostate is usually limited. The acute form requires parenteral treatment, preferably for at least two weeks. Aminopenicillins in combination with beta-lactamase inhibitors, higher-generation cephalosporins, Cotrimoxazole, Aminoglycosides in combination with beta-lactam antibiotics and Fluoroquinolones are suitable for therapy.
If started late or improperly treated, acute prostatitis can lead to complications - the development of a prostate abscess.
It is believed that in case of acute inflammation, the tissue availability of all the claimed compositions is sufficient.
In the case of chronic infections, drugs with reliable penetration should be preferred, even without the presence of acute inflammation. Only Trimoxazole, Trimethoprim and Fluoroquinolones are reliable in this regard. General treatment for chronic prostatitis is extended to 4-6 weeks or longer.